Course: Islam, Ethics and Business
Five pillars of Islam. Sharia. Zakat. Islamic Economic Areas (Course) Businesspeople

The Professional Course “Islam, Ethics and Business” (15 ECTS) taught by EENI Global Business School consists of five modules:
- Introduction to Islam (2 ECTS)
- Islam and Business (3 ECTS)
- Main Economic Organizations related to the Muslim Countries (5 ECTS)
- Islamic Economic Areas (4 ECTS)
- Arab Development Funds (1 ECTS)
“There is no God but Allah, and Muhammad is his messenger.”
 Enrol / Request for Information
Enrol / Request for Information

Languages: 
- Also available in For improving the international communication skills, the student has free access to the learning materials in these languages (free multilingual training).
 Islam
Islam  Islam
Islam  Islão
Islão
intended for all those that want to specialize in all the aspects related to Islam and businesses.
- Credits: 15

- Duration: 15 weeks It is recommended to dedicate about twelve hours of study per week following a flexible schedule. It is possible to reduce the duration dedicating more hours a week
- Tuition Fees: EUR 360
- Open Online Enrollment

The objectives of the course are the following:
- To understand the pillars of Islam and its influence on business
- To analyze the main branches of Islam: Sunni and Shi'a
- To understand the ethical principles of Islam
- To study the distribution of Islam in the World
- To know the fundamental role of Islam on the Islamic Civilization
- To learn about the importance of the Zakat, Sharia (Islamic law) and Fiqh (Islamic jurisprudence) in the Islamic Markets
- To understand the principles of the Islamic Economics (finance, Islamic banks...)
- To identify the leading Islamic economic organizations (Arab League, Islamic Development Bank, Organization for Islamic Cooperation and the affiliated bodies...)
- To learn to design an intercultural negotiation for the Islamic Countries
- To analyze the figures of the main Muslim Businessman and Businesswomen
- To analyze the Islamic Economic Areas, the economic integration processes and their relationships with the other civilizations
- To understand the role of the Islamic Countries in the global economy
- To analyze the trade agreements between the Islamic markets and the importance of the Trade Preferential System among the Member States of the OIC (TPS-OIC)
- To understand role of the Arab Development Funds in the expansion of the Islamic Civilization
Download the Syllabus of the Course: “Islam, Ethics and Business” (PDF).
- Islamic Institutions (PDF)
- Arab Development Funds (PDF)
- Arab Economic Area (PDF)
- Central Eurasian Economic Area (PDF)
- Maghrebian Economic Area (PDF)

EENI delivers to His Royal Highness Prince Alwaleed bin Talal a Master Honoris Causa.

This course contains exercises that are evaluated, which the student must work out and pass to obtain the Diploma of the Professional Course: “Islam, Ethics and Business” issued by EENI Global Business School.
The course belongs to the following Higher Education Programs taught by EENI:
Master in Business in Africa, International Business, Foreign Trade, Religions and Business.
Doctorate: Ethics, Religions, and International Business, Islamic Business, African Business.

Higher Education programs adapted to the Middle East Students.
“To each of you We prescribed a law and a method. Had Allah willed, He would have made you one nation united in religion, but He intended to test you in what He has given you; so race to all that is good.” Holy Quran (5:48).
Modules of the Course
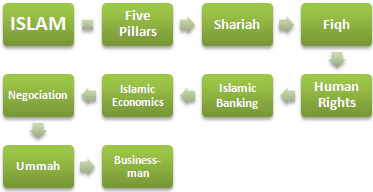
Module 1- Introduction to Islam (2 ECTS)
- Introduction to Islam
- Prophet Muhammad
- Holy Quran
- Expansion of Islam
- The first schism of Islam: Sunnis and Shiites
- Introduction to Sufism
- The Five pillars of Islam: Profession of Faith, Prayer, Charity (Zakat), Fasting, and Pilgrimage to Mecca
- Cairo Declaration on Human Rights in Islam
- Case Study: two prominent Arab Women
- Tawakkol Karman - Nobel Peace Prize (Yemen)
- Haifa Al-Mansour - Film Director (Saudi Arabia)
- Introduction to Arabic language
- The Ummah (Muslim Community) in...
2- Islam and Businesses (3 ECTS)
- Economic Impact of Zakat
- Sharia (Islamic Law)
- Fiqh (Islamic Jurisprudence)
- Islamic Economics
- Islamic Banking
- Islamic Marketing
- Islamic Consumer
- How to negotiate with the Muslim Countries
- Cultural Profiles of the Arab Countries. Patterns by country
- Saudi Arabia: Lubna Olayan (one of the most influential businesswomen in the world), Hayat Sindi
- United Arab Emirates: Lubna Bint Khalid Al Qasimi (the most powerful Arab woman), His Excellency Reem Ebrahim Al-Hashimi, Amina Al Rustamani, Shaikha Al Maskari
- Kuwait: Shaikha Al Bahar, Maha Al-Ghunaim
- Qatar: Hanan Al Kuwari
- Jordan: Randa Ayoubi
- Lebanon: Ayah Bdeir
Arab Businessmen
- Saudi Arabia: His Royal Highness Prince Al Waleed Bin Talal (one of the largest investors in the world), Sulaiman Al-Rajhi (founder of one of the largest banks in the region, renounced to all his riches), Mohamed Al Jaber, Mohammed Al-Amoudi
- Bahrain: Yusuf Bin Ahmed Kanoo
- United Arab Emirates: Abdul Aziz Ghurair, Majid Al Futtaim
- Kuwait: Jawad Ahmed Bukhamseen, Nasser Al Kharafi
- Oman: Mohammed Al-Barwani
African Muslim Businesswoman
- Egypt: Minoush Abdel-Meguid
- Nigeria: Hajia Bola Shagaya (one of the richest women in Africa), Amina Odidi
- Somalia: Iman
African Muslim Businessmen
- Algeria: Ali Haddad
- Egypt: Hassan Abdalla, Tarek Talaat Moustafa, Mohamed Mansour, Ahmed Mekky
- Kenya: Naushad Merali
- Morocco: Othman Benjelloun (the richest man in Morocco), Anas Sefrioui, Mohamed Hassan Bensalah, Aziz Akhannouch, Miloud Chaabi
- Nigeria: Alhaji Aliko Dangote (the richest person in Africa), Alhaji Indimi, Adewale Tinubu, Abdulsamad Rabiu, Olufemi Otedola, Tunde Folawiyo
- Sudan: Mohamed Ibrahim (one of the hundred most influential people in the world), Osama Abdul Latif
- Tanzania: Reginald Mengi (from being born in a mud hut to being one of the biggest entrepreneurs in East Africa), Said Salim Bakhresa, Mohammed Dewji
- Tunisia: Mohamed Ali Harrath
Asian Muslim Businessmen
- Bangladesh: Muhammad Yunus (founder of the microcredit concept, banker and Nobel Peace Prize winner), Muhammad Abdul Mannan, Salman Rahman
- India: Azim Premj (third richest in India), Yusuf Hamied (founder of one of the largest generic laboratories in the world: vaccines for all at affordable prices)
- Indonesia: Sandiaga Salahuddin Uno
- Iran (companies): Bonyads (20% of the Iranian GDP), Islamic Revolutionary Guard
- Malaysia: Tan Sri Mokhtar
- Pakistan: Mian Muhammad Mansha, Dewan Farooqui

3- Main Economic Organizations related to the Muslim Countries (5 ECTS)
- Arab League
- Greater Arab Free-Trade Area (GAFTA)
- OIC
- Islamic Trade Preferential System
- Committee for Economic Cooperation
- Islamic Chamber of Commerce
- Islamic Centre for Development of Trade
- Economic Centre for Islamic Countries
- United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Western Asia (ESCWA)
- Islamic Development Bank
- Cooperation Council of Turkic Speaking States
- Asia-Middle East Dialogue
- Summit of South American-Arab Countries
- Afro-Arab Cooperation
- Africa-Turkey Partnership
- IORA
- Asia Cooperation Dialogue
4- Islamic Economic Areas (4 ECTS)
- Introduction to the Islamic Civilization
- Islamic Economic Areas:
- Arab Economic Area
- Central Eurasian Economic Area
- Maghrebian Economic Area
- Malay Economic Area
- African Economic Area (belonging to the African Civilization)
- Main economic institutions related to the Muslim Countries in Asia, Africa, the Middle East, and Europe
- Islamic Countries and Globalization
- Economic Integration of the Islamic Civilization
- Major Free Trade Agreements related to the Muslim Countries
- Interactions of the Islamic Civilization
5- Arab Development Funds (1 ECTS)
- Arab Monetary Fund
- Arab Fund for Economic and Social Development
- Arab Trade Financing Programme
- OPEC Fund for International Development
- Abu Dhabi Fund for Development
- Saudi Fund for Development
- Arab Gulf Programme for United Nations Development Organizations
- Kuwait Fund for Arab Economic Development
- Arab Bank for Economic Development in Africa (BADEA)
“The principles of Islamic Finance may represent a possible solution to the global financial crisis.” (Osservatore Romano).

In this subject; we will discuss Islam and the main features of the Islamic Countries from the viewpoint of the intercultural negotiation.
It is crucial to note that this subject has been written with a maximum and absolute respect for this religion, which has 1,570 million followers around the world.
After the 11-S, the international businessman wishing to do business with the Muslim Countries needs a closer approach to Islam and its culture as a premise to establish trusting relationships to develop long-term business. This is the main objective of this subject: to introduce the students to Islam and this interesting culture and therefore on their way of doing business.
- Muslim Population: 1.57 billion people (23% of the world's population)
- Only 15% of Muslims are Arabs (Middle East)
- 62% of the World's Muslim population lives in Asia and 20% in the MENA region (Middle East and North Africa)
- 300 million Muslims live in countries where Islam is not the majority religion: China, India, or Russia
We also aim to break the negative topic that many Westerners have against Islam.


African Muslim Historians:
- Ali Al'amin Mazrui
- Hichem Djaït
- Sheikh Anta Diop
- Ahmadou Hampaté Bá
- Boubou Hama
- Pathé Diagne
- Djibril Tamsir Niane
EENI - Middle East and Maghrebian Students:

Why study the course “Islam, Ethics and Business”?.
Islam is currently the second religion in the world (1,570 million Muslims, 23% of humanity), being the religion with the fastest growing population in the world.
This Professional Course is aimed primarily at those companies and managers who wish to do business in the fifty-four countries where Islam is the majority religion. These “Islamic countries” make up the economic area of the Islamic Civilization, composed of the Arab, Eurasian, Malay and Maghreb economic areas.
It also includes the economic areas of West and East Africa (although they belong to the African Civilization) being Islam, Christianity and the Traditional African Religions the main beliefs.
Anyone who does not belong to the Islamic Civilization (Western, Hindu, Buddhist, Sinic...) should know the pillars of Islam and how they influence on the way of doing business of the “Islamic companies”, which can be very different compared to the companies from other economic areas, thus avoiding the intercultural conflicts (more information).

(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page




