Islamic Economic Area. Muslim Civilization

Economic Integration, Islamic Civilization (Arab, Maghreb, Eurasia, Africa)

The subject: “Islamic Economic Area” consists of six parts:
- Islam as the unifying factor of the Islamic Civilization
- Introduction to Islam
- Islamic Community in the World (Ummah)
- Islam and Business
- Muslim Personalities
- Islamic Economic Area
- Muslim Businesspeople
- Major Economic Institutions of the Islamic Civilization
- Arab Economic Area (PDF)
- Central Eurasian Economic Area (PDF)
- Malay Economic Area
- Maghrebian Economic Area (PDF)
- African Economic Area (*)
- Economic Integration of the Islamic Civilization (Economic Organizations, Trade Agreements)
- Trade Preferential System of the OIC
- Integration in the Arab Area
- Integration in the Central Eurasian Area
- Integration in the Malay Area
- Integration in the Maghrebian Area
- Trade Agreements and institutions covering all the Islamic Economic Areas
- Interactions of the Islamic Civilization
- African Civilization
- Hindu Civilization
- Western Civilization
- Sinic Civilization
- Buddhist Civilization
- Orthodox Civilization
- Businesspeople of the Islamic Economic Area
- Arabs
- Asiatic
- Maghrebians
- Economic institutions related to the Islamic Civilization
- The Case of Guyana and Suriname
Important note: Sub-Saharan Africa countries with Muslim majorities (with their agreements, institutions, Businesspeople) are analyzed in the module “African Civilization” because of its growing economic integration with the rest of the African economies.

The Subject “Islamic Economic Area” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate: Ethics, Religions & Business, Islamic Business, African Business, World Trade.
Masters: International Business, Religions & Business.
Why study “Islam and Business”?.
Languages:  or
or  Civilization Islamique
Civilization Islamique  Civilização Islâmica
Civilização Islâmica  Civilización Islámica.
Civilización Islámica.
- Credits of the Subject “Economic Area of the Islamic Civilization”: 4 ECTS
- Duration: four weeks
The purposes of the subject “Islamic Economic Area” are the following:
- To define the characteristics of the Economic Area of the Islamic Civilization
- To understand the influence of Islam on the Islamic Economic Area
- To know the economic profile of the Muslim Countries
- To understand the economic integration process of the Islamic Civilization
- To analyze the main Muslim Businesspeople
- To explore the economic relationships of the Islamic Civilization with the other civilizations (Western, Sinic, Buddhist, Hindu, Orthodox, African)
- To analyze the main Economic Organizations related to the Islamic Economic Area
Observation
This module presents a summary on Islam, Muslim Businesspeople, regional agreements and institutions related to the Islamic Economic Area. The detailed analysis of each of them is carried out in its corresponding subject.
Islam as the unifying factor of the Islamic Civilization.
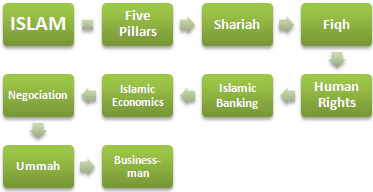
- Introduction to Islam
- Sunnis and Shies
- The Five pillars of Islam
- Human Rights in Islam
- Sharia
- Islamic Jurisprudence (Fiqh)
- Principles of Islamic Economics
- Islamic Banking
- Muslim Countries
- Islamic Community in the World (Ummah): Africa, Asia, India, ASEAN
- Muslim Personalities: Tawakkol Karman (Nobel Peace Prize), Haifa Al-Mansour, Lubna Bint Khalid Al Qasimi, Reem Ebrahim Al-Hashimi, Hayat Sindi, Hanan Al Kuwari, Hichem Djaït, and Muhammad Yunus

Major Economic Institutions of the Islamic Civilization.
- Organization of Islamic Cooperation (Formed by fifty-seven Muslim Countries around the world)
- Islamic Development Bank (OIC member countries)
- Arab League (formed by twenty countries in the Middle East and North Africa)
Islamic Economic Area. Economic profile of the countries of the Islamic Civilization
From the economic integration of the Islamic Civilization; we can identify the following economic areas grouping thirty-two Muslim Countries:

Arab Economic Area.
- The Arab Economic Area consists of twelve countries:
- The Central State is Saudi Arabia
- Arabic is the common language

Central Eurasian Economic Area.
- The Economic Area of Central Eurasia consists of twelve countries: Azerbaijan, Albania, Iran, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Pakistan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Turkey, and Uzbekistan
- Because of its economic integration with these countries, its included Bangladesh and the Maldives
- It is not clear which country is the Central State; Turkey, Iran or Pakistan could be
- NOTE: 170 million of the Indians are Muslims; Islam is the second religion in Bharat (India). However, from this analysis, India belongs logically to the Hindu Civilization
Malay Economic Area.
- The Malay Economic Area consists of the three ASEAN Muslim Countries (Indonesia, Malaysia, and Brunei)

Maghrebian Economic Area
- The Maghrebian Economic Area consists of the five countries of the Arab Maghreb Union (AMU): Morocco, Mauritania, Algeria, Tunisia, and Libya; and Western Sahara
- Culturally we could consider to North Africa as a part of the Islamic Civilization (Sunnite), but from the economic integration also to the African Civilization
- Arabic and French are the main languages in the Maghreb
African Economic Area.


- The African Economic Area consists of the Muslim-majority African Countries: Somalia, Djibouti, Niger, Senegal, Mali, Guinea, the Gambia, Egypt, Sudan, Chad, Sierra Leone, Burkina Faso, Nigeria, Eritrea, and Guinea-Bissau
- These countries are framed within the African Civilization due to its full integration with the rest of the African Countries
Businesspeople in the Islamic Economic Area.
Arab Businesspeople.
- HRH Prince Alwaleed Bin Talal
- Sulaiman Al-Rajhi
- Mohammed Hussein Ali Al-Amoudi
- Yusuf Bin Ahmed Kanoo
- Nasser Al Kharafi
- Mohammed Al-Barwani
- Mohamed Bin Issa Al Jaber
- Abdul Aziz Ghurair
- Majid Al Futtaim
- Jawad Ahmed Bukhamseen

EENI delivers to HRH Prince Alwaleed bin Talal a Master Honoris Causa.
Arab Businesswomen.
- Lubna Olayan
- Shaikha Al Bahar
- Haifa Al-Mansour
- Amina Al Rustamani
- Shaikha Al Maskari
- Randa Ayoubi
- Maha Al-Ghunaim
- Ayah Bdeir
Asian Muslim Businesspeople
- Mian Muhammad Mansha
- Sandiaga Salahuddin Uno
- Dewan Yousuf Farooqui
- Muhammad Abdul Mannan
- Tan Sri Mokhtar
- Salman F Rahman
- Islamic Revolutionary Guard and the Bonyads in Iran
Maghrebians Muslim Businesspeople.
The Islamic Civilization had existed since the 7th century BC when Muhammad proclaimed Islam.
Islam and the Islamic Community (the Ummah) are the unifying factors. We also observe the trends towards the economic integration of their economies, such as the Gulf Cooperation Council as well as the growth of the Islamic Economy and Finance .
Islam is the second religion in the World by the number of followers:
- 1.57 billion people are Muslim
- 23% of the World's population practices Islam
- Only 15% of Muslims are Arabs
- 20% lives in the MENA region (Middle East and North Africa)
- 62% of the World's Muslim population lives in Asia
- Furthermore, 300 million Muslims live in countries where Islam is not the majority religion: China, India, and Russia
Islam, on the other hand, shares borders with all World's faiths:
- With Christianity in the east and south of Europe and the entire strip of Southern African Sahel
- With Hinduism in India itself, along with Zoroastrianism, Jainism, and Sikhism
- With Buddhism, Confucianism, and Taoism in eastern and northern China and much of Southeast Asia
- With Jews in Palestine
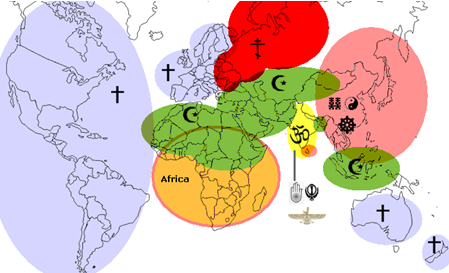
This central position with these religions generates strong political tensions, but it is also an opportunity for the Islamic Civilization and the rest of the World. No other civilization shares more borders with other religions, which may allow that the Islamic Civilization can play a unique role in the inter-religious relations.
From a socio-cultural and historical view; we should consider two distinct spaces.
- Sunni area. With Saudi Arabia as the central state. From the economic integration within Sunnite Area we can identify four sub-areas:
- Arab area, covering the Middle East countries
- Malay area (Southeast Asia), formed by three countries: Indonesia, Malaysia, and Brunei, all ASEAN members
- Turkic area (Turkey), formed by the countries of influence of Turkic culture (Turkey, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan)
- Maghrebian area: Morocco, Mauritania, Algeria, Tunisia, and Libya
- African area
- Shiite area (Iran). Iran is the Central State of the Shiite space. The following countries have Shiite majorities: Iran (90% of the population), Iraq (65%), Azerbaijan (70%), and Bahrain (70%)
- Other countries with significant Shiite communities are the Lebanon (30% of the population), Yemen (40%), Kuwait (30%), India, Turkey (20%), Pakistan (20%), Afghanistan (15%), and Saudi Arabia (15%)


(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page



