Business in Bangladesh, Dhaka, Chittagong

Bangladeshi Economy and Foreign Trade, garments, electronics. Muhammad Yunus
- Introduction to the People's Republic of Bangladesh
- Bangladeshi Economy
- International Trade of Bangladesh
- Investment in Bangladesh
- Business in Dhaka and Chittagong
- Business Opportunities in Bangladesh
- Agribusiness
- Electronics
- ICT
- Business Services
- Garments and textiles sector
- Companies in Bangladesh:
- Desh Group (Textile)
- Walton Group (Bangladeshi business conglomerate)
- Access to the Bangladeshi market
- Business Plan for Bangladesh
- Muhammad Yunus (Grameen Bank)
- Mohammad Abdul Mannan
- Salman F Rahman (Beximco Group)
- Jahirul Islam (AFTAB Group)
- Samson H Chowdhury (Square)
Sample - Salman F Rahman

The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in Bangladesh” are the following:
- To analyze the Bangladeshi Economy and Foreign Trade
- To know the trade opportunities in Bangladesh
- To explore the Bangladeshi trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the Bangladeshi Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of Bangladeshi businesspeople and enterprises
- To develop a business plan for the Bangladeshi market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Bangladesh” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
Doctorate: Islamic Business, World Trade.
 Higher Education programs adapted to the Bangladeshi Students.
Higher Education programs adapted to the Bangladeshi Students.
Languages:  or
or  Bangladesh
Bangladesh  Bangladesh.
Bangladesh.
- Credits of the subject “Doing Business in Bangladesh”: 2

- Duration: two weeks
International Trade and Business in Bangladesh.

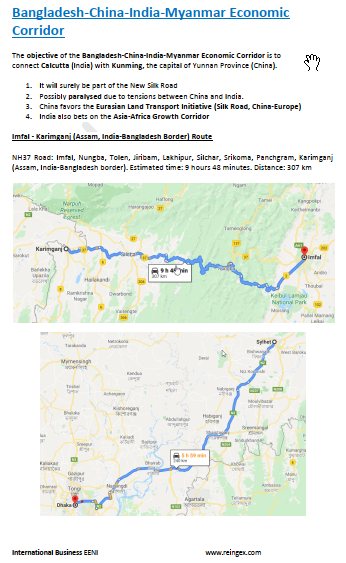
- Bangladesh-Myanmar Corridor
- Access to the Islamabad-Tehran-Istanbul Rail and Road Corridor (ITI-ECO)

Preferential Access and Trade Agreements of Bangladesh
- Bangladesh and the Central Eurasian Economic Area
- Trade Agreements with Pakistan, Sri Lanka, India, Bhutan, Nepal
- Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement
- South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation
- Bay of Bengal Initiative
- Asian Clearing Union
- South Asia Economic Cooperation (SASEC)
- Indian-Ocean Rim Association
- Trade Preferential System (TPS-OIC)
- Islamic Centre for Development of Trade
- Global System of Trade Preferences
- GSP
- Trade Negotiations Among Developing Countries

- WTO
- GATS
- Agreement on the Application of Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- BIC (Containers)
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- IMO

- Islamic Development Bank
- OIC Asia-Middle East Dialogue (AMED)

- Boao Forum for Asia
- Asia Cooperation Dialogue
- ESCAP
- Asian Development Bank
- Colombo Plan
- Africa-Asia Strategic Partnership

- UN
- WB
- WTO
- IMF
- The People's Republic of Bangladesh is one of the most densely populated countries in the World (167 million)
- Borders of Bangladesh: Bharat (India) and Myanmar
- 98% of the population speak Bangla language (official language)
- The capital of Bangladesh is Dhaka (7 million inhabitants)
- Area of Bangladesh: 147,570 km²
- Government type: Bangladesh is a Parliamentary Republic
- Independence of Bangladesh from Pakistan in 1971 (previously it was part of India)
Main religion in Bangladesh: Islam.
- Islam is the largest religion in Bangladesh; the Muslim population is about 149 million people (90% of the total population), the fourth-largest Muslim population in the World (after Indonesia, Pakistan, and India)
- Bangladesh is a country with a Sunni Muslim majority, mainly follow the Hanafi school of jurisprudence
- Hindus (15 million, 9% of the population)
- Christians (1 million)

Bangladesh belongs to the Central Eurasian Economic Area (Islamic Civilization).
Economy of Bangladesh.
Bangladesh (Asia) is advantageously situated near to India, China, and the ASEAN markets.
- The efficiency of the industrial sector in Bangladesh was principally based on the growth in textile and wearing apparel, petroleum products, drugs and pharmaceuticals, fertilizer, footwear, glass products, cement, electronics, and food and beverage industries
- The Services sector is the largest contributor to the real GDP of Bangladesh
- Agriculture in Bangladesh still holds an important position in their economy
- The Annual market size for information technology (computer hardware, peripherals, and software): 25 million dollars
- Currency of Bangladesh: Taka (BDT)
- Bangladeshi GDP (nominal): 118.7 billion dollars;
- Agriculture: 17.3% of the GDP
- Industry: 28.6%
- Services: 54.1%
- Bangladeshi GDP per capita: 2,000 USD
Sample - Muhammad Yunus (Bangladesh)

Desh Garments was the first export-oriented ready-made garment industry in Bangladesh. It was set-up in a joint venture with Daewoo (South Korea). Desh was the single largest and the most modern garment manufacturing unit in the sub-continent.
Walton HIL is the pioneer of Refrigerator, Freezer, Air Conditioner and Motorcycle Manufacturing Technology in Bangladesh.

International Trade of Bangladesh.
- Textiles and clothing industry is the largest export segment of Bangladesh. Their factories design and produce for leading brands and retailers - distributors in the World
- Main exports of Bangladesh are ready-made garments, frozen foods (shrimps), leather, leather products, jute, jute products, tea, ceramic, textile fabrics, home textile, chemical product, light engineering products (bicycle)
- The largest trade partners of Bangladesh are Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka
- Export Processing Zones are export-oriented industrial areas, which supply: infrastructures, facilities, administrative and assistance services
- Established under the Investment Board Act 1989, the Board of Investment is the leading private investment promotion and Trade Facilitation agency of Bangladesh
Bangladeshi Trade Agreements.
As the South Asian Free-Trade Area (SAFTA) comes into force, the foreign investors in Bangladesh will benefit from duty-free access to the Indian market and other SAFTA member countries (Afghanistan, Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka).
Bangladesh started bilaterally negotiations to form Trade Agreements with India, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka and recently, a trade and investment framework agreement with the U.S. is also under active consideration. Bangladesh is a beneficiary of the EU Generalized System of Preferences (GSP).
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page



