Business in Myanmar, Yangon. Burmese Economy

Burmese International Trade. Business in the Union of Myanmar. Port of Yangon
- Introduction to the Union of Myanmar (Burma) - Southeast Asia ASEAN.
- Burmese economy
- Business in Yangon
- Burmese International Trade
- Port of Yangon
- Investment in Myanmar
- Case Study:
- Myanmar Brewery
- Waaneiza
- Mobilemate Telecommunications
- Access to the Burmese market
- Business Plan for Myanmar
The purposes of the subject “Foreign Trade and Business in the Union of Myanmar” are the following:
- To analyze the Burmese Economy and Global Trade
- To know the trade opportunities in the Union of Myanmar
- To explore the Burmese trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the Burmese Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of Burmese companies
- To develop a business plan for the Burmese market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Myanmar” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
Languages:  or
or  Myanmar
Myanmar  Myanmar.
Myanmar.
- Credits of the subject “Doing Business in Myanmar”: 1

- Duration: one week

Masters
adapted to  Burmese students.
Burmese students.
International Trade and Business in Myanmar (Burma).

- Port of Yangon
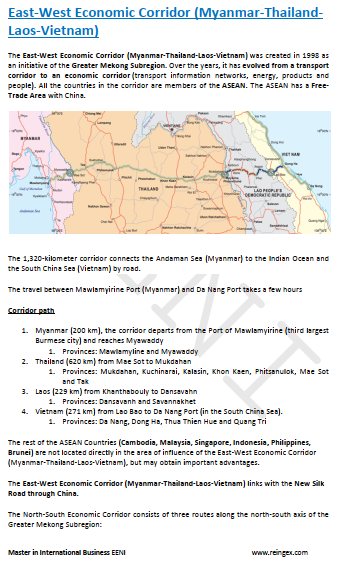
- East-West Corridor (Myanmar-Vietnam)
- Bangladesh-Myanmar Corridor
- Asia-Africa Corridor
- Access to the Nanning-Singapore Economic Corridor

Burmese Trade Agreements and preferential market access:
- Myanmar and the Buddhist Economic Area
- ASEAN
- ASEAN Economic Community
- ASEAN Free-Trade Area
- Trade Agreements (as a member of the ASEAN): Australia-New Zealand, India, Canada, China, the EU, Japan, South Korea, the U.S., Australia- New Zealand and Pakistan
- Mekong Economic Cooperation
- Mekong River Commission (dialogue partner)
- Greater Mekong Subregion
- Bay of Bengal Initiative
- Asian Clearing Union
- Regional Comprehensive Economic Association
- GSP
- Trade Agreements with Bangladesh, Israel, and Sri Lanka
- Global System of Trade Preferences
- South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (Observer)

- WTO
- GATS
- Agreement on Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- BIC (Containers)
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization
- Istanbul Convention - not a member
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member

- Boao Forum for Asia
- Asia Cooperation Dialogue
- ESCAP
- Asian Development Bank
- Colombo Plan
- East Asia-Latin America Cooperation
- Africa-Asia Strategic Partnership
- Asia-Middle East Dialogue

- UN
- WB
- WTO
- IMF
- Borders of the Republic of the Union of Myanmar: China, Laos, Thailand, Bangladesh, and India
- Capital of Burma is Naypyidaw
- The largest city of Myanmar: Yangon (Rangoon)
- Burmese is the official language (32 million speakers)
- 68% of the population of Myanmar are Burmese
- Burmese population: 51.4 million people
- Area of Myanmar: 676,578 km²
- Type of Government of Myanmar: Unitary Parliamentary Republic
- Burmese Independence: 1948 (UK)
Main religion in Burma: Theravada Buddhism (89% of the Burmese population - 60 million people).
- Christianity is the second religion (7%)
- 1 million of Baptists

Burma belongs to the Buddhist Civilization

Burmese Economy:
- The Government controlled the activity in the strategic sector of the Burmese economy: energy, heavy industry, and international trade of rice (control local rice prices)
- The Military commercial entities dominate the economy of Myanmar
- The Republic of the Union of Myanmar is rich in resources (hardwood timber, natural gas, fishery reserves, gems, and jade)
- The agricultural sector (agriculture, livestock, fisheries, and forestry) represent 50% of the Burmese GDP
- In the recent years, the Union of Myanmar has liberalized local and international trade, promoting the private sector and opening the country to the FDI
- Burmese Currency: Kyat (K) (MMK)
Global Trade and Business in Myanmar:

International Trade of Burma.
- Rice exports of Burma hit a record
- The main Burmese export products of Myanmar are natural gas (38%), agricultural export products (18%), precious stones, timber and forest products, and marine products
- The largest export markets of Myanmar are Thailand (40%), Singapore (13%), Hong Kong and India (11%), China (8%), and Malaysia
- The main imports products of Myanmar are petroleum, textiles, machinery parts, steel, iron, and bars
- The largest Burmese import markets of Myanmar are Singapore (30%), China (18%), the Bahamas (13%), Thailand, and Japan
- The Port of Yangon is the largest port in the Union of Myanmar (90% of the foreign trade -exports and imports-)

(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page



