Asia-Africa Growth Corridor, Kenya, India

Afro-Indo-Asian Economic Area: Asia-Africa Growth Corridor
- Introduction to the Asia-Africa Growth Corridor
- The Asia-Africa Growth Corridor as an alternative of India and Japan to the New Silk Road led by China
- The Asia-Africa Growth Corridor: a key project of the Indian-Ocean Rim Association (IORA)
- Main characteristics of the Asia-Africa Growth Corridor
- Asian member countries: Bangladesh, India, Iran, Japan, Maldives, Mongolia, Myanmar, Singapore, Sri Lanka, and Thailand
- African member countries: Kenya, Madagascar, Mauritius, Seychelles, Tanzania, Zambia, Zimbabwe
Sample - African Asia-Africa Growth Corridor

The Subject “Asia-Africa Growth Corridor” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:

Logistics Courses: Transport in Africa, Road transport, Multimodal transport, Rail transport.

Diploma: International Transport.

Courses Business in: East Africa, Southern Africa.

Masters: Transport in Africa, International Transport, Business in Africa, Foreign Trade.
Doctorate: Global Logistics, African Business, World Trade.

Languages:  or
or  Corridor de croissance Asie-Afrique
Corridor de croissance Asie-Afrique  Corredor Asia-África
Corredor Asia-África  Corredor Ásia-África.
Corredor Ásia-África.
Asia-Africa Growth Corridor.
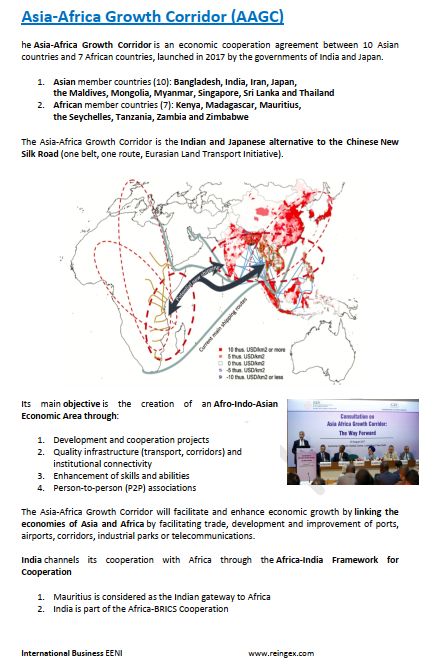
The Asia-Africa Growth Corridor is an economic cooperation agreement between 10 Asian countries and 7 African countries, launched in 2017 by the governments of India and Japan.
- Asian member countries (10): Bangladesh, India, Iran, Japan, the Maldives, Mongolia, Myanmar, Singapore, Sri Lanka and Thailand
- African member countries (7): Kenya, Madagascar, Mauritius, the Seychelles, Tanzania, Zambia and Zimbabwe
The Asia-Africa Growth Corridor is the Indian and Japanese alternative to the Chinese New Silk Road (one belt, one route, Eurasian Land Transport Initiative).

Its main objective is the creation of an Afro-Indo-Asian Economic Area through:
- Development and cooperation projects
- Quality infrastructure (transport, corridors) and institutional connectivity
- Enhancement of skills and abilities
- Person-to-person (P2P) associations
The Asia-Africa Growth Corridor will facilitate and enhance economic growth by linking the economies of Asia and Africa by facilitating trade, development and improvement of ports, airports, corridors, industrial parks or telecommunications.
India channels its cooperation with Africa through the Africa-India Cooperation.
- Mauritius is considered as the Indian gateway to Africa
- India is part of the Africa-BRICS Cooperation
- Bangladesh-Myanmar Corridor
Japan channels its cooperation with Africa through the Tokyo International Conference on African Development.
The Africa-Asia Strategic Partnership NAASP is the framework for economic collaboration between the two regions.
The Indian-Ocean Rim Association plays a key role in the Asia-Africa Growth Corridor strategy.
The IORA is made up of 20 countries from (not all of them are part of the Asia-Africa Growth Corridor):
- Asia: Australia, Bangladesh, India, Indonesia, Iran, Malaysia, Singapore, Sri Lanka and Thailand
- Africa: the Comoros, Kenya, Madagascar, Mauritius, Mozambique, the Seychelles, South Africa, and Tanzania
- Middle East: Oman, the Emirates, and Yemen
Main related African ports:

- Northern Corridor
- Cairo-Gaborone Corridor
- Lagos-Mombasa Corridor
- North-South Corridor
- Central Corridor
Sample: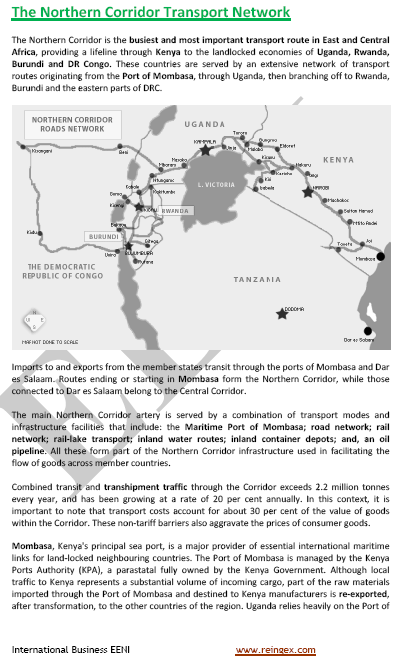
Other African corridors related to the Asia-Africa Growth Corridor:
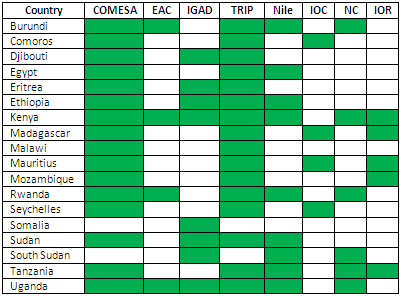
African Regional Economic Communities related to the Asia-Africa Growth Corridor
- East African Community (EAC): Kenya, Uganda, Tanzania, Rwanda, Burundi and South Sudan
- Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD): Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Kenya, Somalia, Sudan and Uganda
- Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA): Burundi, Comoros, the DR Congo, Egypt, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Kenya, Libya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mauritius, Rwanda, Seychelles, Sudan, Eswatini, Tanzania, Uganda, Djibouti, Zambia and Zimbabwe
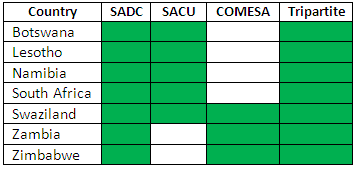
- Southern African Development Community (SADC): Angola, Botswana, the Comoros, the DR Congo, Lesotho, Malawi, Madagascar, Mauritius, Mozambique, Namibia, the Seychelles, South Africa, Eswatini, Tanzania, Zambia and Zimbabwe
- COMESA-EAC-SADC Tripartite: all the African countries of the Asia-Africa Growth Corridor are members of the tripartite agreement
- Nile Basin Initiative: Burundi, the DR Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, Kenya, Rwanda, South Sudan, Sudan, Tanzania and Uganda
- Conference on the Great Lakes: Angola, Burundi, the Central African Republic, the Republic of the Congo, the DR Congo, Kenya, Rwanda, South Sudan, Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda and Zambia
- Indian Ocean Commission: the Comoros, the Reunion Island, Madagascar, Mauritius and the Seychelles
Trade relations of the African countries of the corridor with the U.S.:
- COMESA-United States Trade and Investment Framework Agreement
- East African Community-U.S. Agreement
- AGOA
Relations of the African countries of the corridor with the EU
- Africa-European Union Strategic Partnership
- GSP
Trade Agreements:
- Almost all the African countries in the corridor have trade agreements with India
- Mauritius: India, Turkey, EFTA and Pakistan
- India has a trade agreement with the SACU (South Africa, Lesotho, Eswatini, Botswana, and Namibia). Although none of these countries is a member of the corridor)
Main African Institutions:
Asian countries of the corridor
Asian regional economic communities related to the Asia-Africa Growth Corridor
- South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation: Bangladesh, India, Maldives and Sri Lanka
- Bay of Bengal Initiative: Myanmar, Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka and Thailand
- Asian Clearing Union: Bangladesh, India, Iran, Myanmar, Maldives and Sri Lanka
- South Asia Economic Cooperation (SASEC): Bangladesh, India, Maldives and Sri Lanka
- Economic Cooperation Organization (ECO): Iran
- Organization for Cooperation between Railways (OSJD): Iran and Mongolia
- APEC: Japan, Singapore and Thailand
- ASEAN: Myanmar,
Singapore and Thailand
- ASEAN Economic Community
- ASEAN Free-Trade Area
- IMT-GT: Thailand
- Mekong Economic Cooperation: Myanmar y Thailand
- Greater Mekong Subregion: Myanmar and Thailand

Asian Trade Agreements related to the countries of the Asia-Africa Growth Corridor (AAGC)
- Trade Agreements of India: Sri Lanka, Thailand, Singapore, Mauritius, Maldives, ASEAN
- Trade Agreements of Bangladesh: India, Sri Lanka
- Economic Association Agreements of Japan: Singapore, ASEAN
- Trade Agreements of Myanmar: Sri Lanka, Bangladesh
- Trade Agreements of Singapore: India, Japan
- Trade Agreements of Sri Lanka: India, Bangladesh
- Trans-Pacific Partnership: Singapore and Japan
- Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement: Bangladesh, India, Mongolia and Sri Lanka
- Islamic Trade Preferential System (TPS-OIC)
Main Asian institutions related to the Corridor
- Asian Development Bank
- ESCAP
- Boao Forum for Asia
- Colombo Plan
- Asia Cooperation Dialogue
Main Islamic institutions
- OIC
- Islamic Development Bank
The main Religions of the region of the Asia-Africa Growth Corridor are:
The Asia-Africa Growth Corridor belongs to:

(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page


