Business in Zimbabwe, Harare, Gold, Copper

Zimbabwe: landlocked country, mining, Bulawayo. Zimbabwean Foreign Trade
- Introduction to the Republic of Zimbabwe (Southern Africa)
- Business in Harare and Bulawayo
- Zimbabwean Economy
- Foreign Trade of Zimbabwe
- Customs: Zimbabwe Revenue Authority
- Business and Investment Opportunities in Zimbabwe
- Agriculture
- Manufacturing
- Mining
- Tourism
- Energy
- Water and Sanitation
- Information and Communication Technology
- Finance and insurance
- Services
- Case Study: Makomo Resources
- Access to the Zimbabwean Market
- Business Plan for Zimbabwe
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in Zimbabwe” are the following:
- To analyze the Zimbabwean Economy and Global Trade
- To know the trade opportunities in Zimbabwe
- To explore the Zimbabwean trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the Zimbabwean Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of Zimbabwean Businesspeople
- To develop a business plan for Zimbabwean Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Zimbabwe” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate in African Business, World Trade.
Course: Business in Southern Africa.

Master in Business in Africa, International Business, Foreign Trade.

Languages:  or
or  Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe  Zimbabue
Zimbabue  Zimbabue.
Zimbabue.
- Credits of the subject “Doing Business in Zimbabwe”: 1

- Duration: one week

Masters adapted to  Zimbabwean students.
Zimbabwean students.
International Trade and Business in Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe: a landlocked country with huge mineral resources (copper, nickel, gold).

- Nearest Ports to Zimbabwe
- Port of Durban (South Africa). Distance (Port of Durban-Harare): 1.674 kilometers
- Port of Maputo (Mozambique)
- Access to the Port of Lobito (Angola)
- Port of Walvis Bay (Namibia). Via Trans-Caprivi Corridor Livingstone
- Trans-African Corridors:
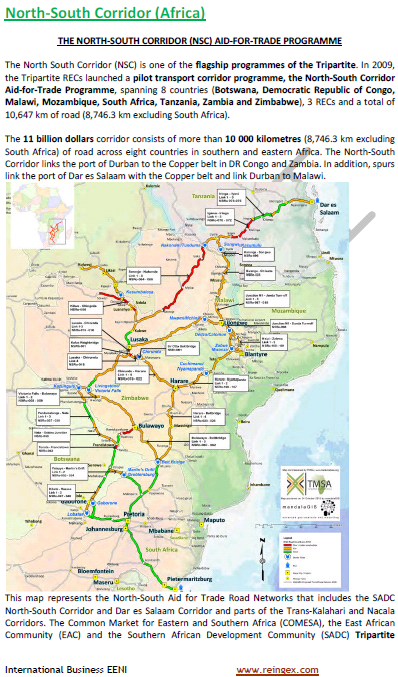


Trade Agreements and preferential access of Zimbabwe
- Zimbabwe and the Southern African Economic Area
- Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA)
- Southern African Development Community (SADC)
- EU-SADC Agreement
- COMESA-EAC-SADC Agreement
- African Continental Free-Trade Area
- Zimbabwe is not eligible for the AGOA
- Africa-EU Partnership
- Namibia-Zimbabwe Agreement
- Free Trade Agreement EU-Eastern and Southern African States (Madagascar, Mauritius, Seychelles, Zimbabwe)
- Bilateral Trade Agreements with China, India, Canada, Malawi, and Japan
- UK-Mauritius-Seychelles-Zimbabwe Agreement
- Global System of Trade Preferences
- International Conference on the Great Lakes Region (ICGLR) - Guest Member

- WTO
- Agreement on Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures
- GATS
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- BIC (Containers)
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- IMO
- Convention for Safe Containers
- Istanbul Convention
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member
- Single African Air Transport Market (SAATM / IATA)

- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Union
- African Development Bank
- Africa-Asia Partnership
- Africa-Turkey Partnership
- Africa-South America Summit
- China-Africa Cooperation
- Africa-India Cooperation
- Africa-BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa)

- WB
- WTO
- IMF
- UN
- Borders of The Republic of Zimbabwe: Zambia, Mozambique, South Africa, and Botswana
- Zimbabwean Population: 16.1 million people
- Zimbabwean Area: 390,580 km²
- Official language of Zimbabwe: English
- Local Languages of Zimbabwe: Shona and Ndebele
- Capital of Zimbabwe: Harare
- Main cities of Zimbabwe: Bulawayo, Mutare-Masvingo, and Gweru
- Independence of Zimbabwe from the UK: 1965

More information about Zimbabwe (EENI African Business Portal).
Religions in Zimbabwe:
- African Traditional Religions
- Christianity (75% of Zimbabweans)

Zimbabwe belongs to the Southern African Economic Area.
Global Trade and Business in Zimbabwe:

Economic Profile of Zimbabwe:
- Zimbabwean GDP growth: 5.6%
- Inflation: 3.9%
- Zimbabwean Currency: Dollar and ZAR (Rand)
- Top Zimbabwean export products: platinum, cotton, tobacco, gold, ferroalloys, and clothing
- Top Zimbabwean imports products: machinery, transport equipment, manufactured goods, chemicals, fuels, and food products
- Largest export markets of Zimbabwe: The DR Congo, South Africa, Botswana, and China
- Main import countries of Zimbabwe: South Africa and China
- Zimbabwean Natural resources: Coal, chromium, asbestos, gold, nickel, platinum, and diamonds
- Main Zimbabwean economic sector: mining industry (copper, nickel, gold)



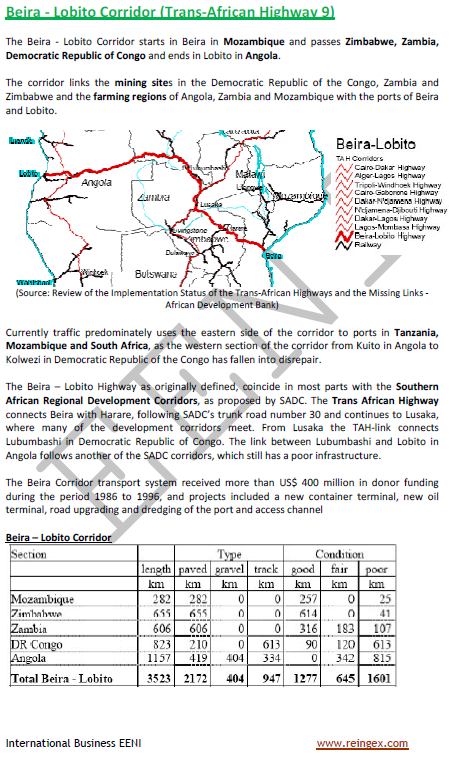
Sample: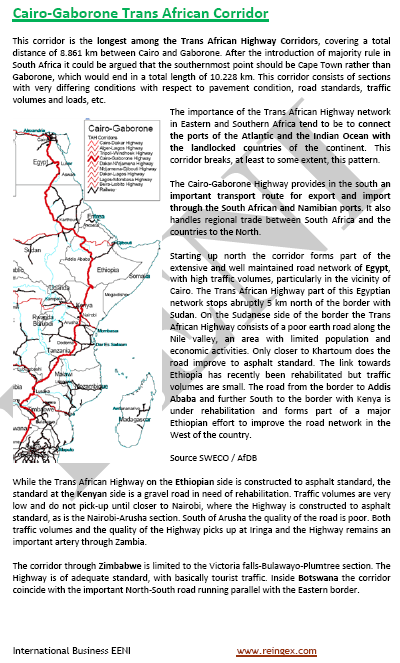
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page


