Cairo-Gaborone Trans-African Corridor

Trans-African Highway (Cairo-Gaborone): Egypt, Ethiopia, Kenya, Tanzania
- Introduction to the Cairo-Gaborone Corridor
- Main features of the Cairo-Gaborone Trans-African Highway
- Access to nine Southern, Eastern and Northern African Markets: Botswana, Egypt, Ethiopia, Kenya, South Africa, Sudan, Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe

The Subject “Cairo-Gaborone Trans-African Highway” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Courses: Transport in Africa, Road transport, Multimodal transport.

Diploma: International Transport.

Masters: Transport in Africa, Business in Africa, International Transport, Foreign Trade.

Doctorate: Global Logistics, African Business.

EENI Partnerships with Educational Institutions
Languages:  or
or  Corridor Cairo-Gaborone
Corridor Cairo-Gaborone
 Corredor Cairo-Gaborone
Corredor Cairo-Gaborone  Corredor Cairo-Gaborone.
Corredor Cairo-Gaborone.


Sample - Cairo-Gaborone Trans-African Highway
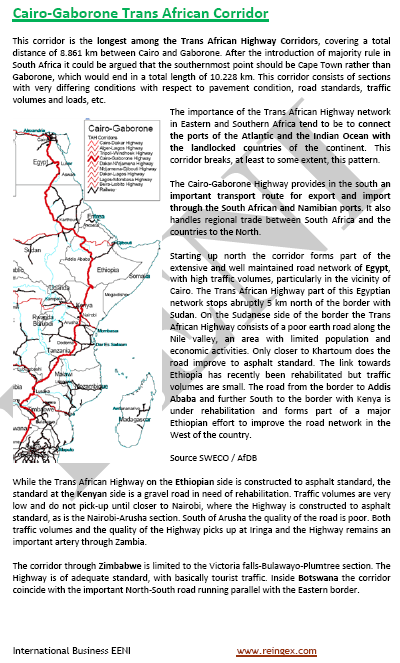
The Cairo-Gaborone Trans-African Highway, 8,861 kilometers, links:
- North Africa: Egypt (1,140 kilometers)
- East Africa: Sudan (1,321 kilometers), Ethiopia (1,692 kilometers), Kenya (938 kilometers), and Tanzania (1,216 kilometers)
- Southern Africa: Zambia (1,496 kilometers), Zimbabwe (538 kilometers), Botswana (520 kilometers), and South Africa
Key features of the Cairo-Gaborone Trans-African Corridor:
- Countries of the Cairo-Gaborone Corridor: Egypt, Sudan, Ethiopia, Kenya, Tanzania, Zambia, Zimbabwe, Botswana, and South Africa
- Main languages: Arabic and English
- Main linked cities by the Cairo-Gaborone Trans-African Corridor: Cairo, Aswan, Arkeen, Wadi Halfa (Sudan), Omdurman, Khartoum, Doka, Gedaref, Galabat (Ethiopia), Azezo, Merawu, Dejen, Addis Ababa, Mojo, Dila, Mega, Moyale, Marsabit (Kenya), Nanyuki, Marua, Nairobi, Athi River, Namanga, Arusha (Tanzania), Dodoma, Iringa, Mbeya, Nakonde (Zambia), Serenje, Lusaka, Zimba, Victoria Falls, Bulawayo (Zimbabwe), Plumtree, Francistown (Botswana), Mahalapye, and Gaborone

- Extension to South Africa: Gaborone - Lobatse - Ramatlabama
- The Cairo-Gaborone Trans-African Highway is the longest Trans-African Corridor
- In Cairo begin the Cairo-Dakar Corridor
- Lagos-Mombasa Corridor
- In Senar (Sudan), links with N’Djamena-Djibouti Corridor
- In Zambia (Kapiri Mposhi), links with the Beira-Lobito Corridor (Beira, access to the Port of Lobito)
- In Tanzania: Central Corridor
- Final part of the Corridor arrives to Cape Town (South Africa), if we include this final part, the total length of this corridor is 10,228 kilometers
The main religion in the Cairo-Gaborone Trans-African Highway region are Islam and Christianity.
The Cairo-Gaborone Trans-African Highway belongs to the African Civilization.
Largest ports:
- Egyptian ports - Suez Canal
- Port of Lobito (Angola)
- Port of Mombasa (Kenya)
- Port of Dar es-Salaam (Tanzania)
- Port Sudan
- Port of Durban (South Africa)
Access to the Asia-Africa Growth Corridor.

African Regional Economic Communities involved:

(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page



