Business in DR Congo, Kinshasa

Congolese economy, mining (copper, diamonds) Foreign Trade of the Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Introduction to the Democratic Republic of the Congo (Central Africa)
- Economy of the DR Congo
- Amini Kajunju (President of the Africa-America Institute)
- International Trade of the DR Congo
- Business and Investment Opportunities in the DR Congo
- Health and education
- Water and electricity
- Housing
- Industry
- Energy
- Case Study:
- Infrastructures in the DR Congo
- Agriculture, fishing, and breeding
- Mines and hydrocarbons
- Feronia Inc. (oil palm)
- TEXAF
- Access to the Congolese market
- Business Plan for the Democratic Republic of the Congo
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in the Democratic Republic of the Congo” are the following:
- To analyze the Congolese Economy and Global Trade
- To know the trade opportunities in the DR Congo
- To explore the trade relations of the DR Congo with the country of the student
- To know the Congolese Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of Congolese businesspeople and enterprises
- To develop a business plan for the Congolese market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in the Democratic Republic of the Congo” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate in African Business, World Trade.

Master in Business in Africa, Transport in Africa, International Business, Foreign Trade.


EENI Partnerships with Educational Institutions
Languages:  or
or  République démocratique du Congo
République démocratique du Congo  Congo
Congo  Congo.
Congo.
- Credits of the subject “Doing Business in the DR Congo”: 3

- Duration: three weeks

The Democratic Republic of the Congo: The third most populated nation in Sub-Saharan Africa. 99 million Congolese in 2025.
International Trade and Business in the DR Congo

- Nearest ports;
- Port of Luanda (Katanga) and Port of Lobito (Angola)
- Port of Maputo (Lubumbashi - Mozambique: 1,600 kilometers)
- Port of Mombasa (Kenya): Eastern provinces of the DR Congo
- Port of Dar es-Salaam (Tanzania)
- Port of Walvis Bay (Namibia). Via the Trans-Caprivi Corridor - Southern provinces of the DR Congo
- Trans-African Corridors;


Preferential trade agreements of the DR Congo:
- The Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Central African Economic Area
- Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS)
- Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA)
- Southern African Development Community (SADC)
- EU-SADC Agreement
- COMESA-EAC-SADC Agreement
- African Continental Free-Trade Area
- Nile Basin Initiative
- Conference on the Great Lakes
- Economic Community of the Great Lakes Region
- EU-Democratic Republic of the Congo
- The U.S.-Democratic Republic of the Congo
- AGOA-United States
- COMESA-U.S. Agreement
- OHADA

- WTO
- GATS
- Agreement on the Application of Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- Rotterdam Rules (Sea)
- Hamburg Rules (Sea)

African Trade and Economic Organizations. the DR Congo is a member of:
- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Union
- Africa Agriculture Development Programme
- African Union Convention on Preventing and Combating Corruption (not signed)
- AUDA-NEPAD
- African Development Bank
- Africa-South America Summit
- China-Africa Cooperation
- BADEA
- Africa-Asia Partnership
- Africa-Korea Partnership
- Africa-Japan Cooperation (TICAD)

- UN
- WB
- WTO
- IMF
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (formerly known as Zaire) is the third most populated nation in Sub-Saharan Africa (72 million people), and the second regarding the area.
The Democratic Republic of the Congo is gifted with abundant human and natural resources, including a tropical forest; is the second in the World by area, fertile soil, abundant rainfall and significant and varied mineral resources.
- Congolese population: 78 million inhabitants.
- The Democratic Republic of the Congo is the fourth most populous nation in sub-Saharan Africa
- 99 million in 2025
- Median age: 17.4 years old
- Largest cities in the DR Congo: Kinshasa, Lubumbashi, Mbuji-Mayi, Kananga, Kisangani, Bukavu, and Goma
- ,Currency of the DR Congo: Congolese Franc (CDF)
- Languages in the DR Congo: French (official), Lingala, Kingwana, Kikongo, Swahili, and Tshiluba
- Borders of the DR Congo: Angola, Congo, the Central African Republic, South Sudan, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Tanzania, and Zambia
- Lar
- 6% of the World tropical reserves
- 106 million Mw of power energy
- Area of the DR Congo: 2,345,410 km².
- The second-largest African country (four times the size of France)
- Unitary Republic. Constitution (2005)
- Independence of the DR Congo: 1960 (Belgium)
More information: The DR Congo (EENI African Business Portal).

Religions in the DR Congo.
- African Traditional Religions
- Christianity
- Catholicism (36 million)
- Protestants (12 million, 20% of the population; Baptists: 1.9 million)

The Democratic Republic of the Congo belongs to the Central African Economic Area.

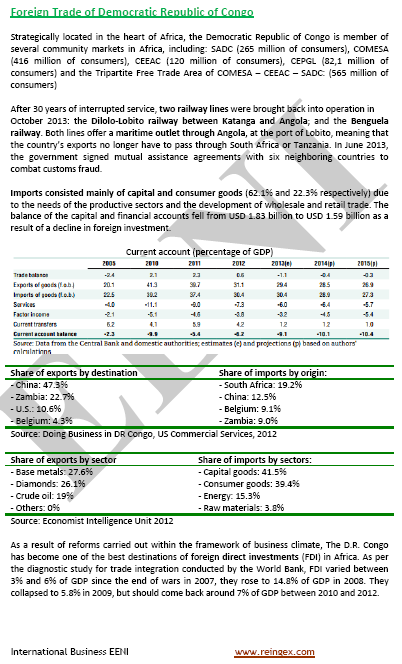
Mining and petrol represent 75% of the total exports.
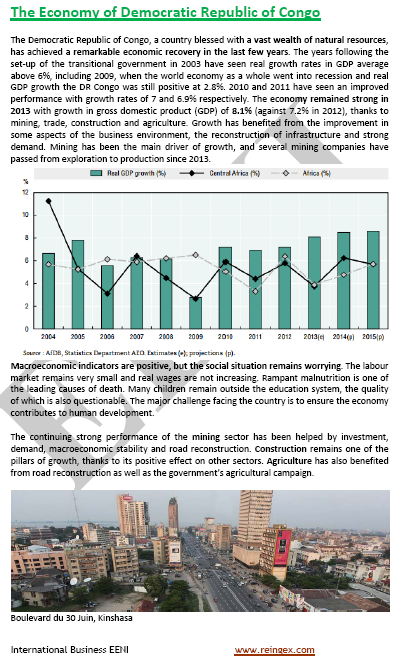
- The economy of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (Africa) began to recuperate
- The main contributors to the total growth were mining (12%), construction (10%) and wholesale and retail trade (6%)
- The World Bank projects the economy of the DR Congo is set to increase to 7% annually for the next biennium. (Source: African Development Bank)
- Mining (copper, cobalt, diamonds, gold, zinc and other metals) and petrol represent 75% of total export revenues of the DR Congo and 25% of its GDP
- Mineral resources of the DR Congo: cobalt, gold, diamond, iron ore, bauxite, coltan, limestone, nickel-chromium
- The International position of the DR Congo advanced thanks to the good oil price levels, improved productivity from some reserves, and recuperation of the timber exports
Global Trade and Business in the DR Congo:
Sample: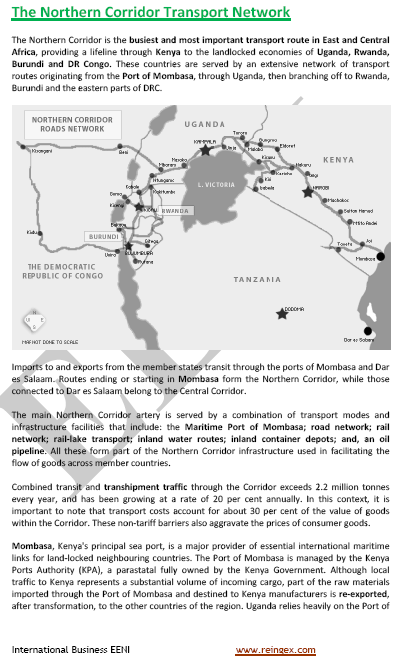
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page


