Business in the Maldives, Male, Tourism

Maldivian economy and foreign trade. Maldives (Business): fishing and tourism
- Introduction to the Republic of Maldives (Asia)
- Maldivian Economy
- Foreign Trade of the Maldives;
- Investment in the Maldives
- Business Opportunities in the Maldives;
- Tourism sector
- Fishing sector
- Case Study: Villa Shipping and Trading Company. Mr Qasim Ibrahim
- Access to the Maldivian Market
- Business Plan for the Maldives
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in Maldives” are the following:
- To analyze the Maldivian Economy and Global Trade
- To know the trade opportunities in Maldives
- To explore the Maldivian trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the Maldivian Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of Maldivian Companies
- To develop a business plan for the Maldivian Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in the Maldives” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
Doctorate: Islamic Business, World Trade.
Credits of the subject “Doing Business in the Maldives”: 1 
Masters adapted to  Maldivian Students.
Maldivian Students.
International Trade and Business in the Maldives.
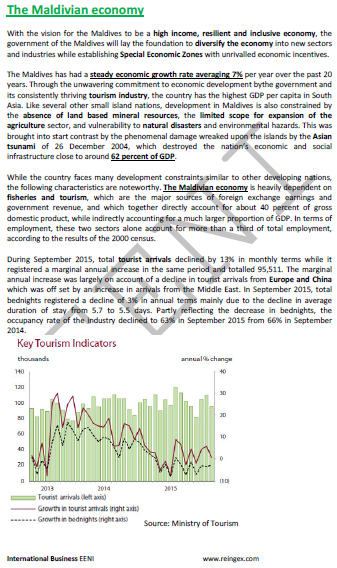
Tourism and fishing sector: 40% of the Maldivian GDP

Maldivian Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:

- WTO
- GATS
- Agreement on Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- International Maritime Organization
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member
- Istanbul Convention - not a member

- Islamic Development Bank
- OIC
- Committee for Economic Cooperation
- Islamic Chamber of Commerce
- Islamic Centre for Development of Trade
- Economic Centre for Islamic Countries
- Asia-Middle East Dialogue

- Boao Forum for Asia
- Colombo Plan
- Africa-Asia Strategic Partnership
- Asia Cooperation Dialogue
- ESCAP
- Asian Development Bank

- UN
- WB
- WTO
- IMF
The Republic of Maldives.
- Maldivian Population: 350,000
- 79% under thirty-five years of age
- Literacy rate: 98%
- Maldivian capital: Male
- Maldivian official language: Dhivehi (Thaana Script), the majority of the Maldivians speaks English
- More than 1,190 Islands
- Tropical climate
- Maldivian Independence: 1968 (UK)
- Sunni Islam is the official religion
- Neighboring countries (by Sea): India, Sri Lanka, Indonesia, and the Seychelles

The Maldives belongs to the Central Eurasian Economic Area (Islamic Civilization).

Maldivian Economy.
- The Maldivian GDP growth of 7% last twenty years
- The main economic sectors are tourism and fishing (40% of the GDP)
- Total imports: 60% of the Maldivian GDP
- Maldivian Petroleum: 31% of the total imports
- Maldivian Currency: Rufiyaa
- Special Economic Zones
- Recent investments (FDI): Hilton, Four Seasons, Club Med, KPMG, and Price Waterhouse
- The largest port in the Maldives: Male. Future Port of Thilafushi
- The Maldives has not mineral resources
- Risk of natural disasters
- Effects of the Asian tsunami (2004): near 62% of the GDP
Global Trade and Business in the Maldives:

International Trade of the Maldives.
- Maldivian merchandise exports (% of the GDP): 23%
- Maldivian Merchandise imports (% of the GDP): 23.6%
- Service exports (% of the GDP): 4.4%
- Service imports (% of the GDP): 1.4%
- Maldivian FDI Inflows (% of the GDP): 1.3%
- Top Maldivian export markets: China, Kazakhstan, Turkey, and Bangladesh
- Top Maldivian import suppliers: China, Russia, South Korea, Kazakhstan, Germany, and Turkey
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page






