China India Bangladesh Myanmar Corridor

Economic Corridor: Bangladesh-China-India-Myanmar, Calcutta Kunming
- Introduction to the Bangladesh-China-India-Myanmar Economic Corridor
- Main characteristics of the Bangladesh-China-India-Myanmar Economic Corridor
- The Bangladesh-China-India-Myanmar Economic Corridor as part of the New Silk Road
- Tensions between India and China in relation to the Bangladesh-China-India-Myanmar Economic Corridor
Bangladesh-China-India-Myanmar Economic Corridor

The Subject “Bangladesh-China-India-Myanmar Economic Corridor” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Logistics Courses: Road transport, Multimodal transport, Rail transport.

Diploma: International Transport.

Masters: International Transport, International Business.
Doctorate: Global Logistics, World Trade.
Languages:  .
Summary in
.
Summary in  Corridor Bangladesh-Chine-Inde-Myanmar.
Corridor Bangladesh-Chine-Inde-Myanmar.  Corredor Bangladesh-China-India-Myanmar
Corredor Bangladesh-China-India-Myanmar  Corredor Bangladeche-China-Índia-Mianmar.
Corredor Bangladeche-China-Índia-Mianmar.
The objective of the Bangladesh-China-India-Myanmar Economic Corridor is to connect Calcutta (India) with Kunming, the capital of Yunnan Province (China).
- Status: under study
- It will surely be part of the New Silk Road
Possibly paralyzed due to tensions between China and India.
- China favors the
Silk Road
- Almaty-Bishkek Corridor
- Bangladesh-Myanmar Corridor
- China-Russia Corridor
- China-Pakistan Corridor
- China-Central-West Asia Corridor
- Nanning-Singapore Corridor
- Europe-Caucasus-Asia Corridor
- East-West Corridor (Myanmar-Vietnam)
- India-Afghanistan Corridor
- North-South Corridor (India-Russia)
- Corridor of the Ashgabat Agreement
- Afghanistan-Turkey Corridor
- Trans-Siberian Railway (Russia, North Korea)
- Kyrgyzstan-Iran Corridor
- Islamabad-Istanbul Corridor
- India also bets on the Asia-Africa Corridor
- Atlantic Corridor
- Baltic-Adriatic Corridor
- North Sea-Baltic Corridor
- North Sea-Mediterranean Corridor
- Pan-European Corridor II
- Pan-European Corridor IX
This corridor will promote cross-border transportation, energy networks and telecommunications.
The route passes through several nodal points, such as: Mandalay and Lashio (Myanmar). It heads towards Kolkata after passing through Manipur and Silchar, before crossing Bangladesh through Sylhet and Dhaka, with branches extending to the ports of Cox Bazar and Chittagong.
Section of the Corridor: China - Myanmar border
Route G56: Kunming Autonomous Prefecture, Chuxiong Yi, Dali, Baoshan, Longlign County, Dehong Dai and Jingpo Autonomous Prefecture, Muse (Myanmar border).
Section of the Corridor in Myanmar
Highway 3 (Myanmar): Muse (China-Myanmar Border), Lashio, Hsipaw, Pyin U Lwin, Mandalay.
- Estimated time: 9 hours 3 minutes
- Distance: 453 km
Section of the Corridor: Mandalay (Myanmar) - Imfal (Manipur, India)
Monywa-Kalaywa Highway (AH1): Myanmar (Burma), Monywa, Kalaywa, Khampa, Moreh, India-Myanmar Border, Imphal, India.
- Estimated time: 15 hours 11 minutes
- Distance: 586 km
First Section of the Corridor in India
NH102 Road: Moreh (India-Myanmar border), Sun Rise Lodge, Infal (Manipur, India).
- Estimated time: 3 hours 22 minutes
- Distance: 108 km
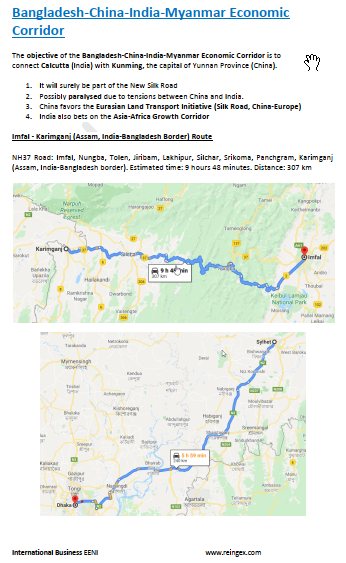
Imfal - Karimganj (Assam, India-Bangladesh Border) Route
NH37 Road: Imfal, Nungba, Tolen, Jiribam, Lakhipur, Silchar, Srikoma, Panchgram, Karimganj (Assam, India-Bangladesh border).
- Estimated time: 9 hours 48 minutes
- Distance: 307 km
Section of the Corridor in Bangladesh
N2 highway: Sylhet, Bishwanath, Niz Koronshi, Nabiganj, Bhairab, Narsingdi, Dhaka.
- Estimated time: 5 hours 59 minutes
- Distance: 240 km
Dhaka - Jesore Route
N7 Road: Hemayetpur, Aricha, Paturia, Daulatdia (Ferry), Faridpur, Jashore,
Bangladesh-India border
- Estimated time: 6 hours 33 minutes
- Distance: 211 km
- This route includes a ferry
Section Jashore (Bangladesh) - Calcutta (West Bengal, India)
Jashore Road (Bangladesh), Bangaon, Gaighat, Habra, Bamangachi, Calcutta (West Bengal, India).
- Estimated time: 4 hours 32 minutes
- Distance: 123 km
Asian regional economic communities related to the Bangladesh-China-India-Myanmar Economic Corridor
- South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka
- Bay of Bengal Initiative: Myanmar, Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Bhutan and Nepal
- Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement: Bangladesh, China, India, South Korea, Laos, Mongolia and Sri Lanka
- Indian-Ocean Rim Association
- Africa: Comoros, Kenya, Madagascar, Mauritius, Mozambique, the Seychelles, South Africa, and Tanzania
- Asia: Australia, Bangladesh, India, Indonesia, Iran, Malaysia, Sri Lanka, Singapore, and Thailand
- Middle East: Oman, the Emirates, and Yemen
- Asian Clearing Union: Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Iran, Myanmar, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka
- South Asia Economic Cooperation (SASEC): Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal and Sri Lanka
- Greater Mekong Subregion: Cambodia, China, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand and Vietnam
- China is also a member of:
- Myanmar is also a member of
- Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
- Mekong Economic Cooperation Strategy (ACMECS)
Related Trade Agreements
- Bangladesh has Trade Agreements with
Nepal, India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka
- GSP
- Trade Preferential System (TPS-OIC)
- China
- Trade Agreements with the ASEAN, Singapore, Pakistan, New Zealand, Peru, Costa Rica, the EU, the Andean Community
- India
- Trade Agreements with Sri Lanka, Thailand, Indonesia, Singapore, ASEAN, South Korea, the EU, New Zealand, Africa-India, Mauritius, Canada, Australia, GCC, SACU, EFTA, MERCOSUR, Andean Community..
- Myanmar
- Trade Agreements as ASEAN member: China, India, Canada, Australia-New Zealand, the EU, South Korea, Russia, the U.S., Pakistan, Japan..
Main Asian institutions related to the Bangladesh-China-India-Myanmar Economic Corridor
- Asian Development Bank
- ESCAP
- Boao Forum for Asia
- Colombo Plan
- Asia Cooperation Dialogue
Main Islamic institutions related to the Bangladesh-China-India-Myanmar Economic Corridor
- OIC
- Islamic Development Bank
The main Religions of the region of the Bangladesh-China-India-Myanmar Economic Corridor are:
The Bangladesh-China-India-Myanmar Economic Corridor belongs to the:
- Hindu Economic Area
- Economic Area of the Sinic Civilization
- Buddhist Economic Area
- Islamic Economic Area
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page



