Business in Turkmenistan, Ashgabat

Turkmen Economy and Foreign Trade. Business in Ashgabat, Turkmenbashi (Turkmenistan) Petrol
- Introduction to the Republic of Turkmenistan
- Turkmen Economy
- Economic Profile of the Regions of Turkmenistan
- Business in Ashgabat
- Foreign Trade of Turkmenistan
- Business Opportunities in Turkmenistan
- Construction
- Textiles
- Energy
- Food industry
- Case Study:
- Awaza National Tourism Zone
- Gap Pazarlama (Textile)
- Access to the Turkmen Market
- Business Plan for Turkmenistan
The aims of the subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Turkmenistan” are the following:
- To analyze the Turkmen Economy and Global Trade
- To know the trade opportunities in Turkmenistan
- To explore the Turkmen trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the Turkmen Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of Turkmen Companies
- To develop a business plan for the Turkmen Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Turkmenistan” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
Doctorate: Islamic Business, World Trade.
Languages:  (or
(or  Turkmenistán
Turkmenistán  Turkménistan).
Turkménistan).
- Credits of the subject “Doing Business in Turkmenistan”: 1

- Duration: one week

Masters adapted to  Turkmen Students.
Turkmen Students.
International Trade and Business in Turkmenistan.

- Almaty-Bishkek Corridor
- Silk Road
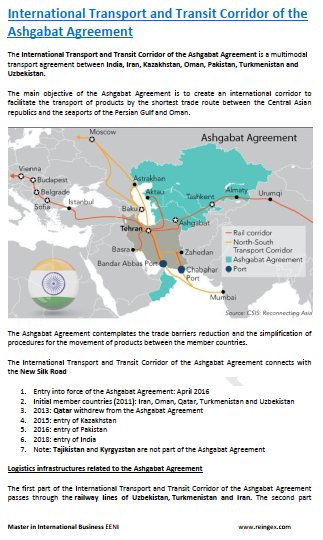
- Corridor of the Ashgabat Agreement
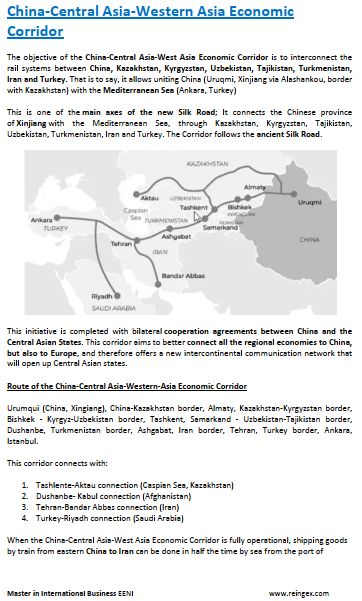
- China-Central-West Asia Corridor
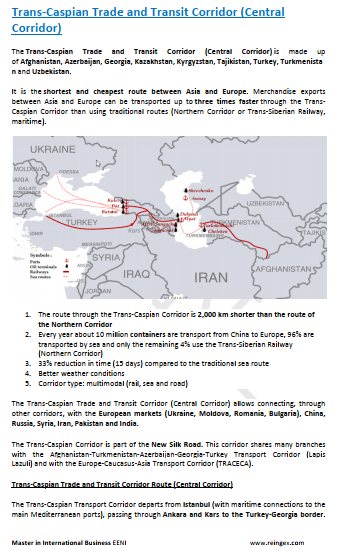
- Trans-Caspian Corridor
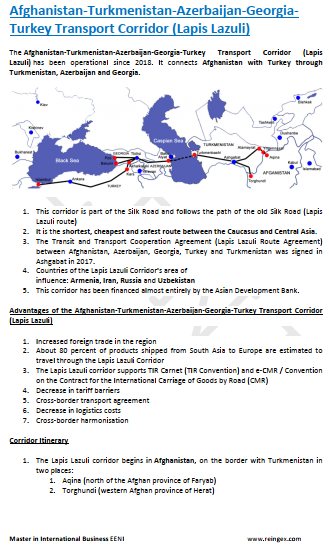
- Afghanistan-Turkey Corridor
- Transit and Transport Cooperation Agreement (Lapis Lazuli Route Agreement)
- Transport Corridor Europe-Caucasus-Asia (TRACECA) - is not a member, but has requested the access

Turkmen Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Turkmenistan and the Central Eurasian Economic Area
- Economic Cooperation Organization (ECO)
- Central Asia Cooperation (CAREC)
- GSP
- Armenia-Turkmenistan Agreement
- Turkmenistan-Georgia Agreement
- Ukraine-Turkmenistan Agreement
- Russia-Turkmenistan Agreement
- Trade Agreement with the Eurasian Economic Union
- Islamic Trade Preferential System
- CIS (associated)
- SCO (Guest Attendance)

- World Trade Organization (WTO) - Government with observer status
- WCO
- Organization for Cooperation between Railways (OSJD)
- BIC (Containers)
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization
- IRU
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport

- OIC
- Islamic Development Bank
- Asia-Middle East (AMED)
Euro-Asian Organizations:
- Boao Forum for Asia
- European Investment Bank
- UNECE
- OSCE
- Africa-Asia Partnership
- ESCAP
- Asian Development Bank
- Asia Cooperation Dialogue

- UN
- WB
- WTO
- IMF
- The Republic of Turkmenistan shares borders with Afghanistan, Kazakhstan, Iran, and Uzbekistan
- Turkmen Population: 5 million people
- 85% of the population are Turkmen
- Area of Turkmenistan: 491,000 km²
- Turkmen Capital: Ashgabat
- Official language of Turkmenistan: Turkmen (Turkic group of languages)
- English and Russian are widely spoken
- The Great Silk Road passes through Turkmenistan
- Territorial organization of Turkmenistan: five velayats (Ahal, Balkan, Dashoguz, Lebap, and Mary)
- Turkmen independence: 1991 (URSS)
- Turkmenistan is a Presidential Republic
Main religion: Islam.

Turkmenistan belongs to the Sunni-Turkic area of the Islamic Civilization
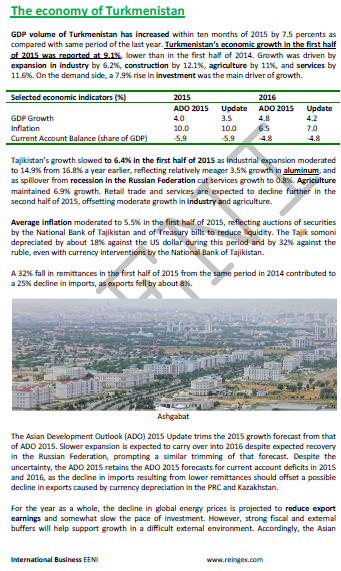
Turkmen Economy.
- Agriculture: 80% of Turkmenistan is farm lands
- Significant water resources (Karakum River)
- Turkmen Mineral resources: hydrocarbon, mining, salt, boron, magnesium, potassium, rubidium, and bentonite
- Drilling and exploration for petrol and gas
- Turkmen industrial sector: petrol and gas, chemical, electric power, engineering, and textile (60 textile complexes)
- The main sectors of the Turkmen economy are petrol and gas, power engineering, agriculture, construction, transport and communications, chemical, textile, and building materials
- The Turkmenbashi complex of petroleum refineries is the largest high-octane gasoline and kerosene producer in Central Asia
- Gas pipelines to China and Iran
- Turkmen currency: Manat
- Turkmenistan is one of the ten most corrupt countries

Global Trade and Business in Turkmenistan:

International Trade of Turkmenistan.
Sample:
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page



