Business in Uzbekistan. Petrol, Gas

Uzbek Foreign Trade. Gold. Economic Profile (provinces of Uzbekistan), Tashkent
- Introduction to the Republic of Uzbekistan (Central Asia)
- Uzbek Economy
- Economic Profile of the Provinces of Uzbekistan
- Uzbek Financial system
- Uzbek Tourism sector
- Six advantages of Uzbekistan in the global economy
- Business in Tashkent
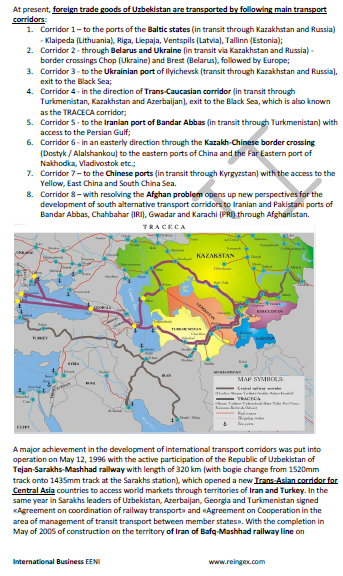
- Case Study: International transport corridors of Uzbekistan
- Foreign Trade of Uzbekistan
- Business Opportunities in Uzbekistan
- Petrol and gas industry
- Automotive
- Chemical industry
- Agricultural
- Machinery manufacturing
- Biotechnology
- Uzbek Pharmaceutical industries
- Information technologies (IT)
- Case Study: SC “Uzavtosanoat” (automotive industry)
- Access to the Uzbek market
- Business Plan for Uzbekistan
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in Uzbekistan” are the following:
- To analyze the Uzbek Economy and Foreign Trade
- To know the trade opportunities in Uzbekistan
- To explore the Uzbek trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the Uzbek Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of Uzbek companies
- To develop a business plan for the Uzbek market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Uzbekistan” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
Doctorate: Islamic Business, World Trade.
Languages:  (or
(or  Uzbekistán
Uzbekistán  Ouzbekistan).
Ouzbekistan).
- Credits of the subject “Doing Business in Uzbekistan”: 1

- Duration: one week

Masters and Doctorate in Global Business adapted to  Uzbek Students.
Uzbek Students.
International Trade and Business in Uzbekistan.
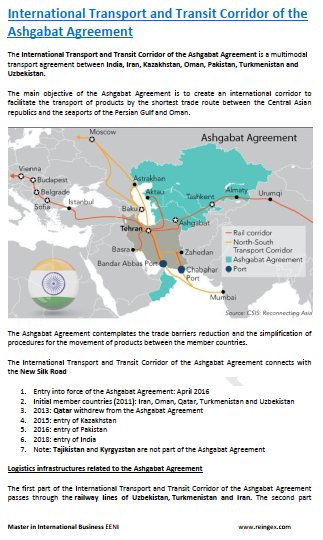
Uzbekistan: The Central Asian Trade Oasis.

- Almaty-Bishkek Corridor
- Corridor of the Ashgabat Agreement
- Silk Road
- Europe-Caucasus-Asia Corridor
- Trans-Caspian Corridor
- China-Central-West Asia Corridor

Uzbek Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Uzbekistan and the Central Eurasian Economic Area
- Commonwealth of Independent States
- Economic Cooperation Organization (ECO)
- Shanghai Cooperation Organization
- Central Asia Cooperation (CAREC)
- Trade Agreement with the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU)
- Ukraine-Uzbekistan Agreement
- Russia-Uzbekistan Agreement
- Kyrgyzstan-Uzbekistan Agreement
- Uzbekistan-Georgia Agreement
- Iran-Pakistan-Turkey Transit Transport Framework Agreement (TTFA) - has not ratified the TTFA
- Islamic Trade Preferential System
- Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) - Observer country

- WTO (in process of accession)
- WCO
- BIC (Containers)
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization
- Customs Convention on Containers
- IRU
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport
- Organization for Cooperation between Railways (OSJD)

- OIC
- Islamic Development Bank
- Tajikistan - Middle East (AMED)
Euro-Asian Organizations:
- ESCAP
- Asian Development Bank
- Asia Cooperation Dialogue
- Boao Forum for Asia
- European Investment Bank
- UNECE
- Africa-Asia Strategic NAASP

- UN
- WB
- WTO
- IMF
- WCO
- Uzbekistan-EU:
- European Investment Bank
- UNECE
- The Republic of Uzbekistan is the largest country in Central Asia
- Strategic location in the region
- Uzbekistan is very rich in natural and human resources
- The Republic of Uzbekistan consists of twelve provinces and the autonomous Republic of Qoraqalpoghiston
- Independence of Uzbekistan from the URSS in 1991
- Uzbekistan is a landlocked country
- Borders of Uzbekistan: Afghanistan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Turkmenistan
- Are of Uzbekistan: 447,400 km²
- Uzbek Population: 29 million people (the largest in Central Asia and third in CIS countries)
- Capital of Uzbekistan: Tashkent
- Official language of Uzbekistan: Uzbek
- Russian is also used as lingua franca in the region
Main religion in Uzbekistan: Islam (90% of the Uzbek population).

Uzbekistan belongs to the Central Eurasian Economic Area (Islamic Civilization).
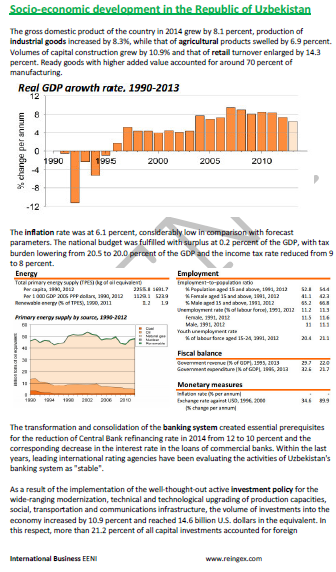
Economy of Uzbekistan.
- Uzbek GDP growth: 8.1%
- Services: 54% of the GDP of Uzbekistan
- Main Uzbek economic sectors: industrial goods, agricultural, construction, and retail
- Uzbek Natural resources: mineral (petrol and gas) and agricultural
- Copper, gold (four largest reserves in the World), uranium, and tungsten reserves
- Uzbek Currency: Uzbek Soum
- Uzbek inflation: 6.1%
- 1 million jobs created
Global Trade and Business in Uzbekistan:

International Trade of Uzbekistan.
- Merchandise exports (% of the GDP): 23%
- Merchandise imports (% of the GDP): 23,6%
- Service exports (% of the GDP): 4.4%
- Services Imports (% of the GDP): 1.4%
- FDI Inflows (% of the GDP): 1.3
- Top export markets of Uzbekistan are China, Kazakhstan, Turkey, and Bangladesh
- Top import suppliers of Uzbekistan are China, Russia, South Korea, Kazakhstan, Germany, and Turkey
- Access to the Eurasian Land Transport Initiative
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page



