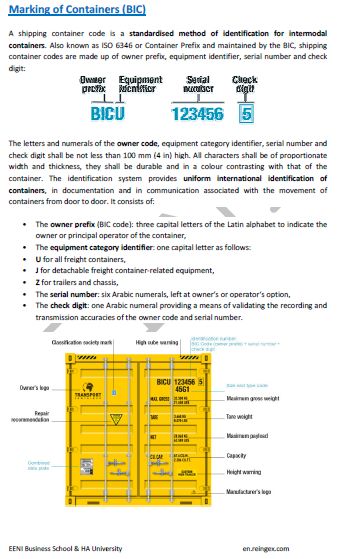
TIR Convention, road transport

Customs Convention on the International Transport of Goods under Cover of the TIR Carnets
- Introduction to the TIR Convention
- The role of the International Road Transport Union (IRU) in the TIR Convention
- Customs Convention on the International Transport of Goods under Cover of the TIR Carnets
- How to fill in a TIR Carnet
- The Convention Harmonization of Frontier Controls of Goods and the TIR Convention

The Subject “Customs Convention on the International Transport of Goods under Cover of the TIR Carnets” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Courses: Road transport, Multimodal transport, Transport in Africa.

Diplomas: Foreign Trade, International Transport.

Masters: International Transport, Transport in Africa, International Business, Foreign Trade.
Doctorate: Global Logistics, World Trade.
Languages: 
 Convenio TIR
Convenio TIR
 Convention TIR
Convention TIR  Convenção TIR.
Convenção TIR.
Area of Knowledge: Foreign Trade - Incoterms.


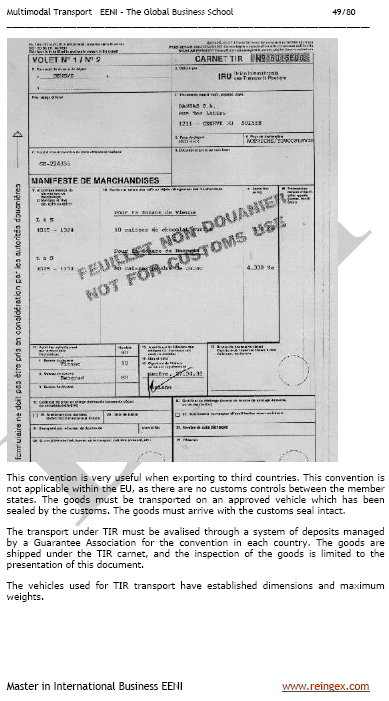
Sample - TIR Convention, International road transport

TIR Convention, International road transport
The TIR Convention (Transports Internationaux Routiers, in French) allows transporting goods through several countries (transit country) through the containers or cargo compartments previously sealed and controlled by customs with a single document (TIR Carnet).
The TIR Convention is practically global.
The main advantages of the TIR Convention are:
- Customs, documentary or inspection procedures reduction, which implies significant savings in time (up to 38%) and costs (up to 80%), both for the carriers, customs and therefore for the end customer
- It is estimated that 34,000 logistics companies use the TIR system
- Number of countries adhering to the TIR Convention: 70
- The TIR is carried out with a single document: the TIR Carnet
- Allows the electronic tracking
- Restricted to the TIR Authorized Consignors and Consignees
- Insurance: maximum protection of € 100,000 for each logistics operation
- TIR Identification: blue square lorry plate
The TIR Convention was created by the International Road Transport Union (IRU) in 1949
- 1975: new TIR Convention (adapted for the intermodal transport)
Member countries of the TIR Convention: Afghanistan, Albania, Algeria, Argentina, Armenia, Austria, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Canada, Chile, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, the EU, Finland, France, Georgia, Germany, Greece, Hungary, India, Indonesia, Iran, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyz Republic, Kuwait, Latvia, Lebanon, Liberia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Macedonia, Malta, Morocco, Moldova, Mongolia, Montenegro, Netherlands, Norway, Oman, Pakistan, Palestine, Poland, Portugal, Qatar, Romania, Russia, Saudi Arabia, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, South Korea, Syria, Sweden, Switzerland, Tajikistan, Tunisia, Turkmenistan, Turkey, Ukraine, UAE, UK, the U.S., Uzbekistan, Uruguay.


- Almaty-Bishkek Corridor
- Bangladesh-Myanmar Corridor
- China-Russia Corridor
- India-Afghanistan Corridor
- China-Pakistan Corridor
- China-Central-West Asia Corridor
- Europe-Caucasus-Asia Corridor
- Nanning-Singapore Corridor
- Corridor of the Ashgabat Agreement
- Trans-Siberian Railway (Russia, North Korea)
- North-South Corridor (India-Russia)
- Afghanistan-Turkey Corridor
- Trans-Caspian Corridor
- East-West Corridor (Myanmar-Vietnam)
- Kyrgyzstan-Iran Corridor
- Islamabad-Istanbul Corridor
- Nanning-Singapore Corridor

(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page



