Customs Procedures (Foreign Trade) Origin of Goods

World Customs Organization and international trade. Customs clearance
- Introduction to the Customs procedures
- Functions of Customs
- Customs clearance
- Examination of goods
- Customs treatment or use of goods
- Summary declaration
- Release for free circulation
- Dispatch for consumption
- Import Procedures
- VAT payable on imported goods
- Single Administrative Document
- Origin of goods. Customs Legislation.
- Customs valuation in the EU
- Classification of goods
- TARIC (Integrated Tariff of the Community)
- Customs agents
- Case Study:
- Market Access database
- China Customs
- European Customs Union
- New EU Customs Code
- EU-Turkey Customs Union
- Istanbul Convention
- Customs Convention on Containers
- World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Customs and the WTO
- Trade Facilitation
The objectives of the subject “Customs Procedures” are to:
- Understand the role and functioning of Customs and the role of a customs agent
- Analyze the different customs procedures, products classification methods and learn to complete the Customs documents
- Become familiar with the import procedures and analyze the existing customs procedures
- Know how to identify and distinguish the non-tariff measures (technical and non-technical) in Foreign Trade
- Understand the role of the WCO and the WTO
- Know the main regional integration processes in the world: MERCOSUR, Andean Community, Central American Integration System, ASEAN, GCC, Arab Maghreb Union, ECOWAS, WAEMU, ECCAS, CEMAC, SADC, EAC, and IGAD
In addition, we are going to studying the importing products process into the EU.
- The student will learn how to dispatch products for free circulation and consumption
- We will also go through all the stages from the moment that the products arrive at the port of entry till they are ready for sale
- We will study the main customs procedures as well

The Subject “Customs Procedures” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Courses: Export Assistant, Foreign Trade Management.


Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade, International Transport.

Doctorate: Global Logistics, World Trade.
Languages:  or
or  Douanes
Douanes  Aduanas
Aduanas  Alfandegas.
Alfandegas.
Credits of the Subject “Customs Procedures”: 4 ECTS.

Customs Procedures.
In this subject; we will study the functioning of the Customs authorities, the customs procedures and the various duties imposed by the Customs.
- To place the products under a certain customs procedure; it is necessary to identify their destination country and the customs classification
- To classify products means to assign them a classification code in agreement with the existing international regulations
- The classification code determines the customs duty, and the customs tariffs applied
- On the basis of the Combined Nomenclature and customs duty, the European Union has established the Integrated Tariff of the Community (TARIC), which offers a further classification under the Combined Nomenclature, which is necessary find out the export products subject to special treatment
- The New Community Customs Code (EU) contains the general customs rules and procedures applicable in foreign trade between the EU members and the third countries
Related subjects to Customs Procedures:
- Non-tariff Measures
- Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures
- Technical Barriers to Trade
- Pre-shipment Inspection
- Anti-dumping Measures and Safeguards
- Import Licensing and Quotas
Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS).
- WIPO
Sample - Customs Procedures:
Inspection Control.
When products arrive at the EU to be imported; they are inspected and checked by the customs authorities until a relevant customs procedure for these products is established. The products may be taken to be stored in a customs warehouse without payment of import duties or being re-exported. The responsible for taking the products through the customs is the carrier.
Summary Declaration
When products arrive at the EU; they must be taken to the customs authorities for inspection. This is done by presenting a declaration, which contains all the necessary information for the product identification. Without the declaration, the products cannot be cleared (unless under an express authorization).
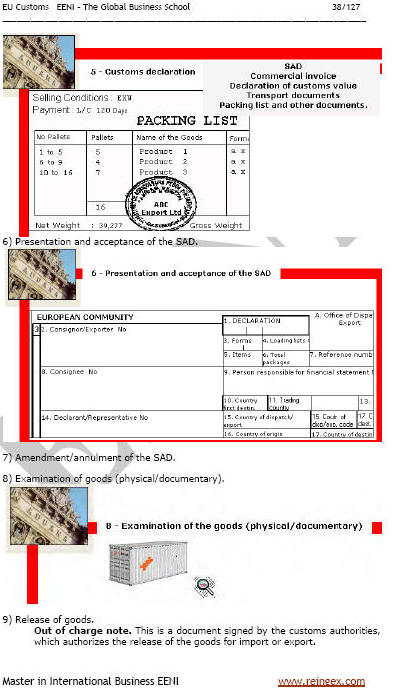
Single Administrative Document.
The Single Administrative Document (SAD) is the declaration form used in the EU for declaring products for any of the Customs Procedures. The declaration must be made by the importer/exporter or the agent. The declaring must sign the Single Administrative Document.
VAT
The Value-added Tax (VAT) is chargeable on imported products in addition to any customs and excise duties to which the products may be liable.

ATA System
ATA is a system enabling free movement of export products across frontiers and their temporary admission into a customs territory with release from duties and taxes. The export products are covered with only one document: ATA carnet.
Dumping is the practice of selling a product in a foreign market at an unfairly low price (a price which is lower than the cost in the home market, or lower than production cost) to gain a competitive advantage over other exporters. Dumping is considered an unfair trade practice under the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade and the WTO agreements.
National governments regulate dumping through the imposition of anti-dumping duties.





(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page


