Non-tariff Measures (Course)
Online Course: Sanitary Measures, Import License, Technical Barriers to
Trade (6 ECTS,  )
)

The Course “Non-tariff Measures to Trade” taught by EENI Global Business School consists of two modules:
- Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures in International Trade
- Technical Barriers to Trade
- Pre-shipment Inspection
- Contingent trade-protective measures (Anti-dumping Measures, Safeguards)
- Non-automatic Import licensing, quotas and prohibitions
- Other Non-tariff measures: Price-control (including additional taxes and charges), Finance Measures, affecting the competition, Trade-related investment measures
- Restrictions, distribution, post-sales services, Government procurement
- Subsidies (excluding export subsidies)
- Rules of origin
- Export-related measures
- Other formalities

The objectives of the module 1 are the following:
- To know how to identify and distinguish the non-tariff measures (technical and non-technical) in Foreign Trade
- To evaluate the possible impact they may have on exports / imports
- To familiarise the student with the use of the “UNCTAD International Classification Manual of Non-Tariff Measures”
- To know how to act before a non-tariff measure implemented by a country
- Introduction to the Trade-Related Aspects of
Intellectual Property
Rights
- Industrial property
- Copyright and rights related to the copyright
- Infringement of the intellectual property rights
- The role of the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO)
- The Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS)
of the WTO
- The Pillars of the TRIPS Agreement
- Berne Convention for the Protection of Literary and Artistic Works (copyright)
- Paris Convention for the Protection of Industrial Property (patents, industrial designs, etc.)
- Case study: Intellectual property rights in the USMCA/NAFTA 2.0
The objectives of the module 2 are the following:
- To understand the key concepts related to the Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights
- To learn the importance and the pillars of the Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of the intellectual property rights (TRIPS) of the WTO
- To know the role of the World Intellectual Property Organization and the different international intellectual property registration systems (Lisbon, Madrid, The Hague...)
 Enrol / Request for Information
Enrol / Request for Information

- Credits: 6

- Duration: six weeks It is recommended to dedicate about twelve hours of study per week following a flexible schedule. It is possible to reduce the duration dedicating more hours a week
- Open Online Enrollment
- Download the syllabus of the Course (PDF)
Languages: 
- Also available in For improving the international communication skills, the student has free access to the learning materials in these languages (free multilingual training).
 Medidas no arancelarias
Medidas no arancelarias
 Mesures non tarifaires
Mesures non tarifaires  Medidas não-tarifárias
Medidas não-tarifárias
The course includes the Market Access Tool:
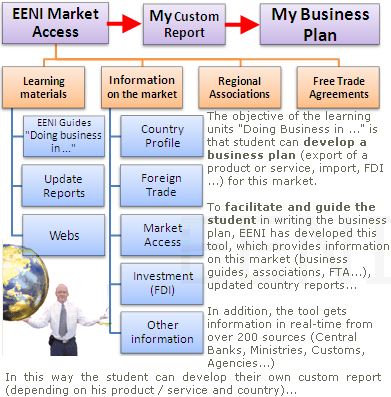
Sample - Non-tariff Measures to Trade:


This course contains exercises that are evaluated, which the student must work out and pass to obtain the Diploma of the Course “Non-tariff Measures to Trade” issued by EENI Global Business School.
The course belongs to the following Higher Education Programs taught by EENI:
Course: Foreign Trade Management.

Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade, International Transport.

According to the definition of the UNCTAD, the Non-tariff measures are:
“... Those political measures, different from the Customs tariffs, that can economically affect on foreign trade in good, modifying Export prices, transactions, or both.”
The Non-tariff measures can distort Foreign Trade, and even harm exporters, importers, companies, and even the final consumer.
Any agent of the value chains of the foreign trade (exporter, importer, distributor, customs or logistics agent, consultant...) must know how to identify these measures and know the possible impact they may have.
The UNCTAD proposes a classification of the different types of measures (16 chapters).
Technical measures:
- Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures (SPS)
- Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT)
- Pre-shipment Inspection and other formalities
Non-technical measures:
- Contingent trade-protective measures
- Non-automatic licensing, quotas, prohibitions and quantity-control measures other than Sanitary and phytosanitary measures and Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT)
- Price-control measures, including additional taxes and charges
- Finance measures
- Measures affecting the competition
- Foreign Trade-related investment measures
- Distribution restrictions in a market
- Restrictions on post-sales services
- Subsidies (excluding export subsidies)
- Government procurement restrictions in a certain market
- Measures related to Intellectual Property
- Rules of origin
Finance Measures
They are all those non-tariff measures whose objective is to regulate access to foreign currency for imports. They increase the import cost.
- Advance payment requirements. They can be: advanced import deposit, cash requirement, advance payment of the customs duties, refundable deposit
- Multiple exchange rates
- Official currency allocation. Bank authorization (Central Bank of the country of the importer). licenses linked to unofficial currencies
- Regulations concerning terms of payment for imports (import credit and financing)
Measures affecting the competition (special preferences or privileges).
- State-trading enterprises
- Compulsory use of national services (transport, insurance)
Trade-related investment measures:
- Measures of local content (minimum quantity of product manufactured in the country of the importer)
- Trade balancing measures (import restriction)
Distribution restrictions (obtaining licenses or certification, distribution services regulations).
- Geographical restrictions
- Restrictions for certain resellers
Restrictions related to post-sales services
Subsidies
Government procurement restrictions (preference to national suppliers).
Intellectual Property (patents, trademarks, copyright...).
Rules of origin
Export-related measures:
- Export-license, quota and prohibition restrictions (include investments)
- Export prohibitions
- Export quotas (quotas)
- License requirements (permission, authorization) to export
- Export registration requirements
- Exports of state companies
- Export price-control measures
- Measures on re-exports (cross-border trade)
- Export taxes and charges
- Export technical measures (technical specifications, conformity assessment)
- Inspection requirement (Quality control)
- Certification required by the exporting country
- Export subsidies
- Export Credits

Source: “International Classification of Non-tariff Measures” (UNCTAD).
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page


