Customs. Rules of origin. Tariffs (WTO)

Import licensing procedures. Customs Valuation. Preshipment inspection
- The Role of the WTO in the Customs Procedures
- The Multilateral Trading System
- World Trade Organization Agreements;
- Tariffs
- Agriculture
- Standards and safety
- Textiles
- Anti-dumping, subsidies, and safeguards
- Non-tariff barriers
- Agreement on Import Licensing Procedures
- Agreement on Customs Valuation
- Customs Valuation Rules
- Customs Valuation Methods:
- Transaction value
- Identical or similar goods
- Deductive or computed method
- Fall-back
- Pre-shipment Inspection Agreement
- Rules of Origin Agreement
- Trade Facilitation
- Customs and Regional Trade Agreements
- Customs Procedures and the Doha agenda
The objectives of the subject “Customs and the WTO” are to understand the:
- Role of the WTO in the Customs Procedures
- WTO Agreements
- Fundamental concepts related to customs: non-tariff barriers, customs valuation, transaction value, pre-shipment inspection, rules of origin, and import licences
- Customs Valuation Methods

The Subject “Customs and the WTO” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:

Courses: Export Assistant, Foreign Trade Management.

Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade, International Transport.

Doctorate: Global Logistics, World Trade.
Languages:  or
or  Douanes
Douanes  Aduanas
Aduanas  Alfandegas.
Alfandegas.
Customs and the WTO

Import licensing
In Foreign Trade, import licensing are the administrative procedures that need the compliance of documentation to the administrative organization as a previous condition for the importation of products.
The Agreement on Import Licensing Procedures of the WTO refers to “import licensing should be simple, transparent and predictable.”
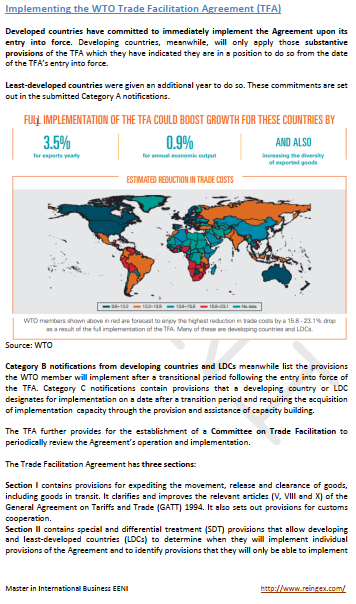
Customs valuation.
Customs valuation is a procedure applied by the Customs to find out the “Customs value of the imported products.”
In the case that the rate of duty is “ad valorem,” the customs value is necessary to find out the duty to be paid on an imported product.
For importers, the process of estimating the value of a product at customs can present some troubles.
The WTO Agreement on Customs Valuation aims for a fair, uniform and neutral system for the Customs Valuation.
The World Trade Organization Agreement on Customs Valuation defines that customs valuation should (excluding in specified circumstances) be based on the actual price of the products (usually marked on the invoice).
The following six methods are considered in the WTO Agreement on Customs:
- Transaction value
- Transaction value of identical products
- Transaction value of similar products
- Deductive method
- Computed method
- Fall-back method
Transaction value is the price paid by the importer to the benefit of the exporter for the imported products.
Pre-shipment inspection
When the exporter or the importer outsource to specialized private companies to control the shipment details (price, quantity, and quality) of the products.
The Pre-shipment Inspection Agreement recognizes that the GATT principles and obligations apply to these pre-shipment activities.
Sample - Customs and the WTO

Rules of Origin
The “Rules of origin” define where a product was produced. The concept of rules and certificate of origin is a fundamental pillar of the international trade rules (quotas, preferential tariffs, anti-dumping, or counter export subsidies).

Related Subjects:
- Non-tariff Measures
- Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures
- Technical Barriers to Trade
- Anti-dumping Measures and Safeguards
- Import Licensing and Quotas
- Pre-shipment Inspection
- Istanbul Convention

(Source: World Trade Organization).
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page


