China Customs. Import/Export Procedures

Chinese Customs: supervises all arrivals and departures from China
- Introduction to China Customs
- Import/Export customs procedures in China
- Shanghai Customs
- Guangzhou Customs

The Subject “China Customs” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
Course: Taoism, Confucianism & Business.

Languages:  or
or  Aduanas Chinas
Aduanas Chinas  China
China  China.
China.


- WTO
- GATS
- Agreement on Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- BIC
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- IMO
- Convention for Safe Containers
- Istanbul Convention
- Customs Convention on Containers
- ICS
- Organization for Cooperation between Railways (OSJD)
- IRU
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport
Sample - China Customs

The main objective of China Customs (the Chinese public agency) is to supervise and manage the international trade from the Customs territory of the Mainland China.
China Customs practices a centralized management structure. The principal tasks of China Customs are:
- Customs control
- Revenue collection
- Fighting contraband
- External trade statistics
- Supervision and management of bond operations for processing International Trade
- Audit-based monitoring and risk management
- Port management
The revenue collected by the Customs of China includes:
- Customs duties
- Import VAT
- Consumption tax
- Vessel tonnage tax
China Customs have played a significant position in the conception and implementation of the import and export tariff schedule and preferential tax policies, CEPA (Closer Economic Partnership Arrangements with Hong Kong SAR and Macau SAR), negotiations on Free Trade Agreements, implementation of rules of origin, zero import tariff treatment for fruits originating from Taiwan Province, and other relevant policies and measures.

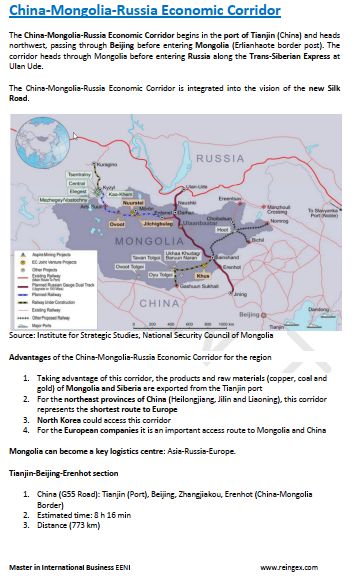
- China-Russia Corridor
- Trans-Siberian Railway (Russia, North Korea)
- Almaty-Bishkek Corridor
- Bangladesh-Myanmar Corridor
- China-Central-West Asia Corridor
- Nanning-Singapore Corridor
- China-Pakistan Corridor
- Access to the:
- East-West Economic Corridor (Myanmar-Thailand-Laos-Vietnam)
- Kyrgyzstan-Iran Corridor
- Transport Corridor Europe-Caucasus-Asia (TRACECA)
- India-Chabahar (Iran)-Afghanistan Economic Corridor
- Trans-Caspian Trade and Transit Corridor (Central Corridor)
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page



