Business in Libya. Tripoli. Libyan Economy

Libya (Foreign Trade): largest proven African petroleum reserves. Gas
- Introduction to the State of Libya (Maghreb)
- Libyan Economy
- International Trade of Libya
- Business and Investment Opportunities in Libya
- General Board of Privatization and Investment
- Case Study:
- Libyan Oil sector
- Libyan Free Trade Zones
- Access to the Libyan Market
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in the State of Libya” are the following:
- To analyze the Libyan Economy and Global Trade
- To know the trade opportunities in the State of Libya
- To explore the Libyan trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the Libyan Trade Agreements

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Libya” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate: Islamic Business, African Business, World Trade.
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
Course: Business in the Maghreb.

Languages:  or
or  Libye
Libye  Libia
Libia  Libia.
Libia.
Credits of the subject “Doing Business in Libya”: 1 
Masters adapted to Libyan Students.

International Trade and Business in Libya.
Libya: The largest proven Africa's petroleum reserve.



Libyan Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Libya and the Maghrebian Economic Area
- Arab Maghreb Union
- Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA)
- COMESA-EAC-SADC Agreement
- Community of Sahel-Saharan States (CEN-SAD)
- African Continental Free-Trade Area
- Libya-EU
- Agadir Agreement
- Greater Arab Free-Trade Area (GAFTA)
- Trade Agreement with Jordan
- Islamic Trade Preferential System
- Islamic Centre for Development of Trade
- Global System of Trade Preferences
Sample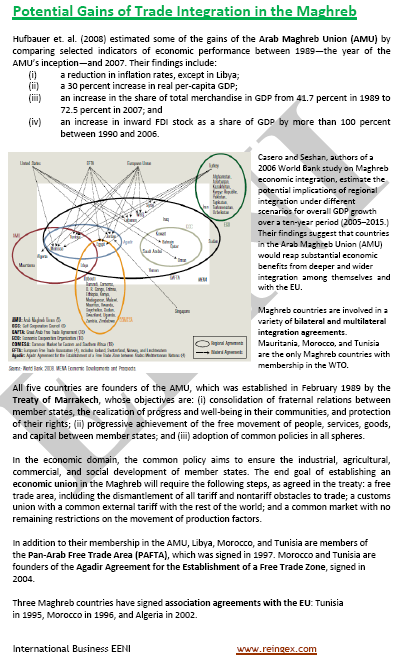

- WTO (in process of accession)
- WCO
- BIC (Containers)
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization
- Istanbul Convention - not a member
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member

- Economic Commission for Western Asia (ESCWA)
- Arab League
- OIC
- Committee for Economic Cooperation
- Islamic Chamber of Commerce
- Economic Centre for Islamic Countries
- Asia - Middle East Dialogue
- Summit of South America-Arab Countries
- Afro-Arab Cooperation
- Arab Bank for Africa (BADEA)
- Arab Development Funds

- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Union
- African Development Bank
- Africa-Turkey Partnership
- Africa-Asia Partnership
- China-Africa Cooperation
- Africa-India Cooperation
- Africa-BRICS
- Africa-South America Summit

- OPEC
- WCO
- UN
- WB
- WTO
- IMF
The State of Libya.
Due to the complexity of the political situation in Syria; it is discouraged to travel to Syria. Business opportunities are small outside the energy sector.
- Capital of Libya: Tripoli (1.1 million people)
- Second city: Benghazi (Cyrenaica region)
- Largest Libyan cities: Tripoli, Benghazi, Misrata, El-Beida, Al Khums, Zawiya
- Neighbor countries: Algeria, Chad, Egypt, Niger, Sudan, and Tunisia
- Area of Libya: 1.8 million km² (the fourth-largest African Country)
- Libyan Population: 6.2 million people
- Libyan Mediterranean coast: 2,000 kilometers
- Political: towards a Democratic transition
- Recent Libyan Civil War
- Volatile political environment
- Libyan official language: Arabic and Tamazight
More information about Libya (EENI African Business Portal).
religion in Libya:
- Islam (97%)
- The main branch: Sunni
- School of Fiqh: Fiqh-al-Maliki

Libya belongs to the Maghrebian Economic Area (Islamic Civilization and African Civilization).

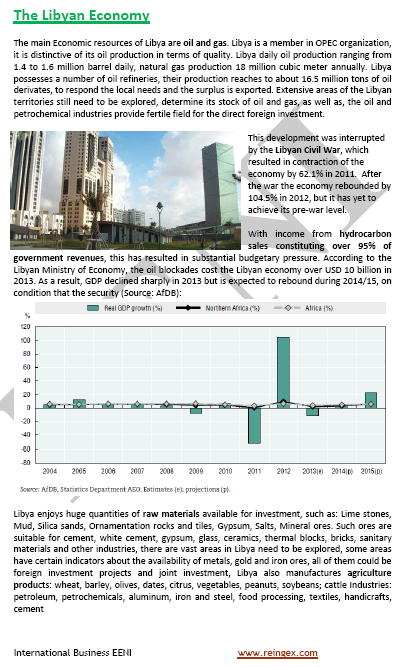
Economy of the State of Libya:
- Economic recovery in 2012
- Real Libyan GDP growth: 4.3
- The main economic resources are petrol and gas (95% of the Libyan Government revenues/50% of the GDP)
- Libyan inflation: 7.5%
- Currency of Libya: Libyan Dinar
- Great Manmade River Project
- Zwara and Mesratha Free Trade Zones
- Tripoli International Fair
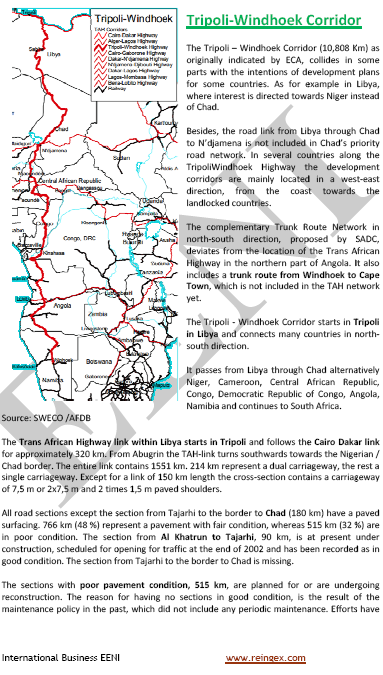
Global Trade and Business in Libya:
Nearest foreign ports:
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page



