Business in Guinea-Conakry, Exports, Bauxite

Guinea-Conakry (Foreign Trade) iron, bauxite, Kankan, Nzérékoré
- Introduction to the Republic of Guinea (West Africa)
- Guinean Economy
- International Trade of Guinea-Conakry
- Customs System of Guinea-Conakry
- Business and Investment Opportunities:
- Health
- Environmental
- Energy
- Information and Communication Technologies
- Mining
- Industrial
- Agriculture
- Legal Framework. Investment Code
- Investment Promotion Agency of Guinea
- Case Study: Guinean mining sector
- Access to the Guinean Market
- Business Plan for Guinea-Conakry
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in Guinea” are the following:
- To analyze the Guinean Economy and Global Trade
- To know the trade opportunities in Guinea
- To explore the Guinean trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the Guinean Trade Agreements
- To develop a business plan for the Guinean Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Guinea Conakry” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Master in Business in Africa, Transport in Africa, International Business, Foreign Trade, International Transport.
Doctorate in African Business, World Trade.


EENI Partnerships with Educational Institutions
Languages:  or
or  Guinée-Conakry
Guinée-Conakry  Guiné-Conacri
Guiné-Conacri  Guinea-Conakry.
Guinea-Conakry.
- Credits of the subject “Doing Business in Guinea-Conakry”: 1

- Duration: one week

International Trade and Business in Guinea-Conakry.
Guinea-Conakry: huge iron and bauxite deposits.

- Port of Conakry
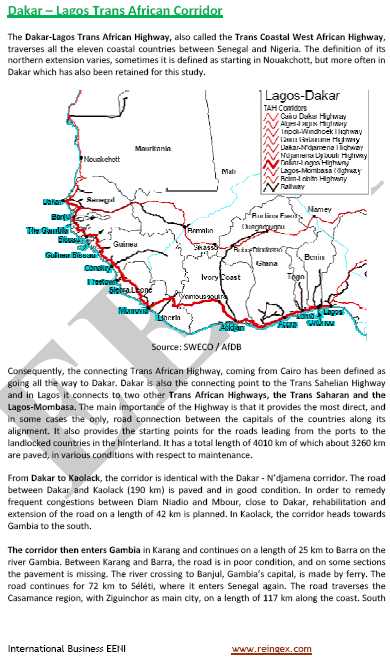
- Access to the Dakar-Lagos Corridor


Trade Agreements and preferential access of Guinea-Conakry
- Guinea-Conakry and the West African Economic Area
- Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)
- West African Monetary Zone (WAMZ)
- African Continental Free-Trade Area
- Mano River Union
- Niger Basin Authority
- Organization for the Development of the Senegal River
- Community of Sahel-Saharan States (CEN-SAD)
- The EU:
- AGOA
- OHADA
- Islamic Trade Preferential System
- Arab Bank for Africa (BADEA)
- Global System of Trade Preferences (GSTP)

- WTO
- GATS
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- Agreement on the Application of Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- WCO
- Rotterdam Rules
- Hamburg Rules (Sea)

- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Union
- Africa Agriculture Development Programme
- African Union Convention on Preventing and Combating Corruption
- AUDA-NEPAD
- African Development Bank
- Africa-Asia Partnership
- Africa-Korea Partnership
- Africa-Japan Cooperation
- Africa-India Cooperation

- Afro-Arab Cooperation
- BADEA
- Islamic Development Bank
- Organization of Islamic Cooperation

- UN
- WB
- WTO
- IMF
The Republic of Guinea-Conakry (Africa).
- Borders of Guinea-Conakry: Guinea-Bissau, Senegal, Mali, Ivory Coast, Liberia, and Sierra Leone
- Independence of Guinea-Conakry: 1958 (France)
- Guinean population: 10 million people
- Only 41% of adults were literate in 2010
- Area of Guinea-Conakry: 245,857 km²
- Guinean Capital: Conakry (2.7 million).
- Port of Guinea
- Guinean largest cities: Conakry, Kankan, Nzérékoré and Guéckédou
- Official language of Guinea-Conakry: French
- President of Guinea-Conakry: Alpha Conde
- Ebola virus crisis in 2014
More information about Guinea (EENI African Business Portal).
Main Religions in Guinea-Conakry:
- Islam (85% of the Guinean population)
- African Traditional Religions

Guinea-Conakry belongs to the West African Economic Area.

Guinean Economy
- 66% of the bauxite deposits in the World
- Largest iron ore deposits
- Simandou: The largest undeveloped iron ore
- Currency of Guinea-Conakry: Guinean Franc (GNF)
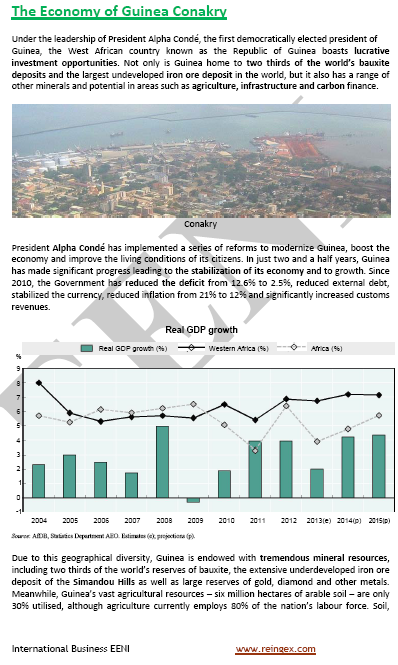
- Guinean GDP growth: 2%
- Agriculture (13%)
- Industry (48%)
- Services (39%)
- Inflation in Guinea-Conakry: 9.9%
- Most Guinean dynamic sectors: agriculture and construction
- Stabilization of the Guinean Economy
- Deficit and external debt reduction
- Declining in mining sector (gold, diamonds, and alumina)
- Poor business environment
- Top exports of Guinea-Conakry: bauxite, alumina, gold, diamonds, coffee, and fish
- Top Guinean trade partners: Ivory Coast, France, South Korea, Spain, Ireland, and the U.S.
Sample - Foreign Trade and Business in Guinea-Conakry
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page



