Business in Sierra Leone, Freetown

Foreign Trade and Business in Sierra Leone (fastest growth economy in West Africa). Freetown, Oil, Mining
- Introduction to the Republic of Sierra Leone (West Africa)
- Business in Freetown
- Sierra Leonean Economy
- Foreign Trade of Sierra Leone
- Export Procedures in Sierra Leone
- Business and Investment Opportunities in Sierra Leone
- Sierra Leonean Agriculture
- Tourism
- Marine Resources
- Infrastructure
- Sierra Leonean Mining
- Petrol and gas
- Investment in Sierra Leone
- Access to the Sierra Leonean Market
- Business Plan for Sierra Leone
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in Sierra Leone” are the following:
- To analyze the Sierra Leonean Economy and Global Trade
- To know the trade opportunities in Sierra Leone
- To explore the Sierra Leonean trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the Sierra Leonean Trade Agreements
- To develop a business plan for the Sierra Leonean Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Sierra Leone” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Business in Africa.
Doctorate in African Business, World Trade.

Languages:  or
or  Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone  Sierra Leona
Sierra Leona  Sierra Leona.
Sierra Leona.
- Credits of the subject “Doing Business in Sierra Leone”: 1

- Duration: one week
Area of Knowledge: Africa.
Masters adapted to  Sierra Leonean Students.
Sierra Leonean Students.

International Trade and Business in Sierra Leone.
The Republic of Sierra Leone is the fastest growing economy in West Africa.

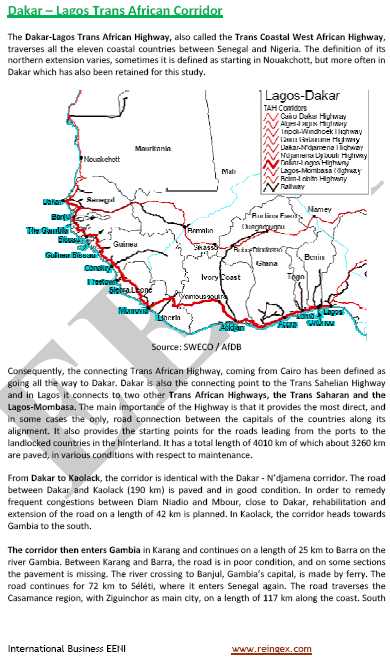
- Dakar-Lagos Corridor
- Access to the West African Ports


Sierra Leonean Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Sierra Leone and the West African Economic Area
- Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)
- West African Monetary Zone (WAMZ)
- Community of Sahel-Saharan States (CEN-SAD)
- African Continental Free-Trade Area
- Mano River Union
- EU-Sierra
Leone:
- GSP
- Africa-EU Partnership/Everything But Arms (EBA)
- African Growth and Opportunity Act (U.S.) - AGOA
- Islamic Trade Preferential System

- WTO
- Agreement on Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures
- GATS
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- Hamburg Rules (Sea)
- BIC
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization
- Istanbul Convention - not a member
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member

- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Union
- AU Convention on Preventing and Combating Corruption
- AUDA-NEPAD
- Africa Agriculture Development Programme
- African Development Bank
- Africa-Japan Cooperation
- Africa-South America Summit
- China-Africa Cooperation
- Africa-Asia Partnership


- WB
- WTO
- UN
- IMF

- Borders of the Republic of Sierra Leone: Guinea-Conakry and Liberia
- Sierra Leonean Area: 72,000 km² (one of the smallest African nations)
- Sierra Leonean population: 7 million people
- Capital of Sierra Leone: Freetown (1.2 million)
- Other cities of Sierra Leone: Bo, Kenema, Koidu Town, and Makeni
- Official language of Sierra Leone: English
- Local languages: Temne, Mende, and Krio
- Government of Sierra Leone: Constitutional Democracy
- Sierra Leonean Legal System: English common law
- Sierra Leone was created in 1787
- Independence of Sierra Leone: 1961 (UK)
More information about Sierra Leone (EENI African Business Portal).
The main religions in Sierra Leone are:
- Islam (78%)
- Christianity (27%)
- African Traditional Religions


Sierra Leone belongs to the West African Economic Area.

Economy of Sierra Leone:
- Sierra Leonean GDP: 1.99 billion dollars
- GDP growth rate: 13.8%
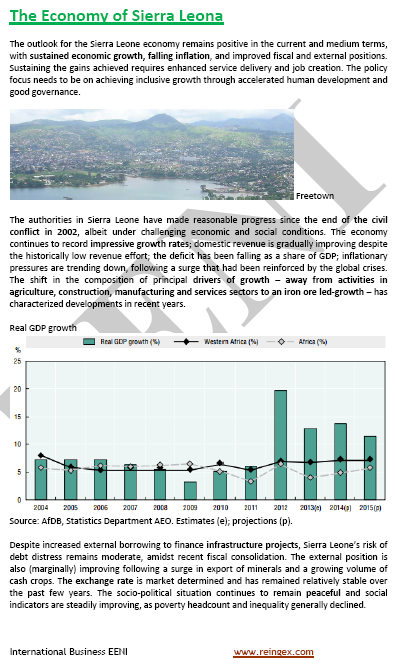
- Sierra Leonean dynamic sectors: agriculture, construction, manufacturing, services, and iron-ore mining
- Sierra Leonean Agriculture sector: 51% of the GDP/17% of exports/61% of workforce
- Top agricultural products of Sierra Leone: coffee, cocoa, and oil palm
- Main resources of Sierra Leone: mineral, tourism, agriculture, marine, petrol and gas, energy, and fishery
- Top Sierra Leonean export products: diamonds, rutile, and bauxite iron ore
- The main economic activities in Sierra Leone are gold and diamond mining
- Sierra Leone has the largest natural African port
- The largest Sierra Leonean trading partners are China, India, the UK, the U.S., South Africa, and Belgium
- Common External Tariff (CET) of the ECOWAS
- FDI stock in Sierra Leone: 740 million dollars
Business in Sierra Leone:

(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page



