Business in Guinea-Bissau, Cashew, Nuts

Economy and Foreign Trade of Guinea-Bissau, Bafatá, Gabú
- Introduction to the Republic of Guinea-Bissau (West Africa)
- Bissau-Guinean Economy
- International Trade of Guinea-Bissau
- Business and Investment Opportunities in Guinea-Bissau
- Agro-processing industries
- Fisheries
- Mining
- Tourism
- Energy
- Guinea-Bissau Expansion Corporation
- Access to the Bissau-Guinean Market
- Business Plan for Guinea-Bissau
The purposes of the subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Guinea-Bissau” are the following:
- To analyze the Bissau-Guinean Economy and Global Trade
- To know the trade opportunities in Guinea-Bissau
- To explore the Bissau-Guinean trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the Bissau-Guinean Trade Agreements
- To develop a business plan for the Bissau-Guinean Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Guinea-Bissau” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate in African Business, World Trade.

Master in Business in Africa, Transport in Africa, International Business, Foreign Trade.


EENI Partnerships with Educational Institutions
Languages:  or
or  Guinée Bissau
Guinée Bissau  Guinée-Bissau
Guinée-Bissau  Guinea-Bissau.
Guinea-Bissau.
Credits of the subject “Doing Business in Guinea-Bissau”: 1


International Trade and Business in Guinea-Bissau
The Republic of Guinea-Bissau is one of the ten poorest countries in the World.



Bissau-Guinean Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Guinea-Bissau and the West African Economic Area
- Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)
- West African Economic and Monetary Union (WAEMU)
- Community of Sahel-Saharan States (CEN-SAD)
- African Continental Free-Trade Area
- Guinea-Bissau - United States
- Guinea-Bissau - EU:
- OHADA
- Arab Bank for Africa (BADEA)

- WTO
- GATS
- Agreement on Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- Rotterdam Rules
- Is not a member of the WCO

- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Union
- Africa Agriculture Development Programme
- AU Convention on Combating Corruption
- AUDA-NEPAD
- African Development Bank
- Africa-Asia Partnership
- Africa-Korea Partnership

- Afro-Arab Cooperation
- BADEA
- OIC
- Islamic Development Bank

- Community of Portuguese Speaking Countries
- UN
- WB
- WTO
- IMF
The Republic of Guinea-Bissau
- Bissau-Guinean Population: 1.5 million people
- The official language of Guinea-Bissau is Portuguese (only 14% speak Portuguese) and Creole
- Capital of Guinea-Bissau: Bissau (400,000)
- Bissau-Guinean largest cities: Bissau, Bafatá, Gabú, Bissorã, Bolama
- Borders of Guinea-Bissau: Senegal and Guinea
- Total area of Guinea-Bissau: 36,120 km²
- Independence of Guinea-Bissau from Portugal: 1973
More information about Guinea-Bissau (EENI African Business Portal).
Main religions in Guinea-Bissau:
- African Traditional Religions
- Christianity
- Islam (50% of the Bissau-Guinean population, 0.7 million)


Guinea-Bissau belongs to the West African Economic Area.

Economy of Guinea-Bissau:
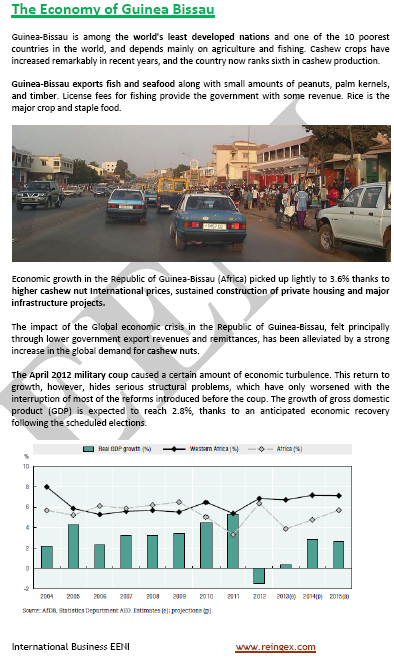
Economic growth in Guinea-Bissau (Africa) picked up slightly to 3.6% thanks to higher international prices of cashew nut, sustained private housing construction, and major infrastructure projects.
- The impact of the global economic crisis in Guinea-Bissau felt principally through the lower Government export revenues and remittances, has been alleviated by a strong increase in the global demand for cashew nuts
- Guinea-Bissau is one of the ten world's poorest countries
- Bissau-Guinean agriculture: 12% of the total area of the Republic of Guinea-Bissau (38.4% is pasture, Forests 38.1%)
- The Republic of Guinea-Bissau makes most of its turnover with cashew nuts exports
- Main harvests in Guinea-Bissau: bananas, little mango flavor
- Guinea-Bissau has many natural resources, whose reserves are scarcely exploited (phosphates, bauxite, and petroleum)
- High traffic of arms and drugs
- Military coup in 2012
- Bissau-Guinean GDP growth: 2.8%
Global Trade and Business in Guinea-Bissau:
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page


