Generalized System of Preferences GSP EU

New Generalized System of Preferences GSP. Everything But Arms (EU)
- Introduction to the EU's Generalized System of Preferences (GSP)
- The New GSP preferences (2014-2024)
- Revised EU trade scheme to help the developing countries
- Beneficiary countries under the current GSP
- Products enjoying preferences in the reformed Generalized System of Preferences
- Practical guide to the new GSP trade regimes for the developing countries
- The New EU Customs Code and the GSP
- The three EU import regimes
- European Union's Foreign Trade with the GSP countries
- GSP+ scheme
- Background of the GSP+
- Everything But Arms arrangement (EBA)
- Duty-free and quota-free treatment for all the least-developed countries
- GSP rules of origin
- Tolerance or De Minimis
- Types of accumulation (Bilateral, Regional, Extended)
The objectives of the subject “Generalized System of Preferences (GSP)” are the following:
- To understand the characteristics of the new EU's Generalized System of Preferences (GSP)
- To analyze the SPG + scheme and the Everything but Arms arrangement
- To know which countries and under what conditions are beneficiaries of the GSP
- To know how to use the rules of origin under the Generalized System of Preferences

The Subject “Generalized System of Preferences (GSP)” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate: European Business, African Business, World Trade.
Masters: Africa, International Business, Foreign Trade.
Courses: International Relations of Africa, Export to the EU.

Languages:  or
or  Sistema Preferencias Generalizadas (SPG)
Sistema Preferencias Generalizadas (SPG)  Système préférences généralisées SGP
Système préférences généralisées SGP  Sistema de preferências generalizadas SPG.
Sistema de preferências generalizadas SPG.
Masters adapted for  EU Students.
EU Students.


Sample - EU Generalized System of Preferences
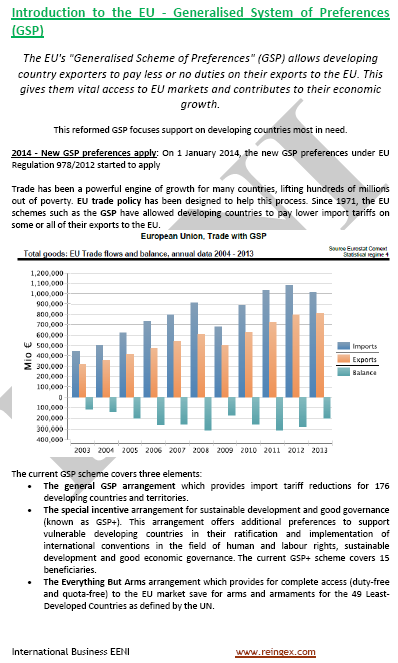
Since 1971, the EU schemes like the Generalized System of Preferences (GSP) have allowed to the developing countries to pay lower import tariffs.
Under the revised scheme of the GSP (Generalized System of Preferences), imports that will receive the Generalized System of Preferences are estimated at EUR 37.7 billion.
The actual Generalized System of Preferences scheme covers three factors:
- The General Generalized System of Preferences Arrangement (import tariff reductions)
- The Special incentive arrangement for sustainable development and good governance (GSP+). GSP+ offers additional preferences to support the vulnerable developing countries in their ratification and implementation of international conventions in the field of human and labour rights, sustainable development and good economic governance
- The Everything But Arms Arrangement, which provides for the complete access (duty-free and Quota-free) to the EU's market except for arms and armaments for the Least-Developed Countries (as defined by the UN)
In 2001, the Council adopted the “Everything But Arms Regulation,” granting duty-free access to imports of all the products from the Least-Developed Countries, except arms and ammunitions.
Total GSP (Generalized System of Preferences) beneficiary countries: 88 (177 in the previous scheme).
The Least-Developed Countries benefiting from “Everything But Arms” arrangement (40 countries):
- Africa (34 countries): Angola, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Benin, Chad, the DR Congo, the Central African Republic, Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, the Gambia, Guinea, Equatorial Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, the Comoros, Liberia, Lesotho, Madagascar, Mali, Mauritania, Malawi, Mozambique, Niger, Rwanda, São Tomé, Sudan, South Sudan, Sierra Leone, Senegal, Somalia, Togo, Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia, Kenya, and Cape Verde
- Asia-Pacific (9): Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar, Nepal, East Timor, Yemen, Kiribati, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Tuvalu, and Vanuatu
- The Caribbean: Haiti
GSP+ beneficiaries (13): Armenia, Bolivia, Cape Verde, Costa Rica, Ecuador, El Salvador, Georgia, Guatemala, Mongolia, Pakistan, Panama, Paraguay, and Peru.
GSP Beneficiaries until 31 December 2015: Colombia, Costa Rica, Guatemala, Ecuador, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, Panama, Peru, China, Ecuador, Maldives, Turkmenistan, and Thailand.
Countries that are no longer on the GSP beneficiary list (current scheme).
- All the EU members, the U.S., Australia, and New Zealand are not beneficiaries
- Mediterranean Partnership (EUROMED): Algeria, Egypt, Jordan, Lebanon, Morocco, and Tunisia
- CARIFORUM members
- Latin America: Argentina, Brazil, Cuba, Mexico, Uruguay, and Venezuela
- Russia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, and Kazakhstan
- Africa: Gabon, Libya, Mauritius, the Seychelles, South Africa, and Zimbabwe
- The Middle East: Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), and Oman
- Asia: Brunei, Iran, Macau, Maldives, Malaysia, and Papua New Guinea
The Generalized System of Preferences belongs to the European Economic Area of the Western Civilization.
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page



