Business in Jordan, Amman, Port of Aqaba

Jordanian Economy and Foreign Trade. Randa Ayoubi. Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan
- Introduction to the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan (Middle East)
- Jordanian Economy
- Jordanian Advantages
- Jordanian Foreign Trade
- Business in Amman
- Port of Aqaba
- Business Opportunities in Jordan
- Minerals (cement, phosphate, and potash)
- Electricity
- Communications
- Transport
- Tourism
- Industrial sector
- Investment in Jordan
- Privatization Process in Jordan
- Jordan Investment Commission
- Qualified Industrial Zones in Jordan
- The largest Jordanian companies;
- Azadea Group
- Abu Khader Group
- MS Group
- Randa Ayoubi
- Access to the Jordanian market: distribution, customs, and regulations
- Business Plan for Jordan
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan” are the following:
- To analyze the Jordanian Economy and Global Trade
- To know the trade opportunities in the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan
- To explore the Jordanian trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the Jordanian Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of Jordanian businesspeople and enterprises
- To develop a business plan for the Jordanian Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Jordan” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate: Islamic Business, World Trade.
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
- Credits of the subject “Doing Business in Jordan”: 1

- Duration: one week

 Master in International Business for
the
Jordanian Students.
Master in International Business for
the
Jordanian Students.
Global Trade and Business in Jordan:

Jordan: a logistics hub in the Middle East.

Jordanian Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Jordan and the Arab Economic Area
- Greater Arab Free-Trade Area (GAFTA)
- Jordan-Singapore Agreement
- Canada-Jordan Agreement
- U.S.-Jordan Agreement
- Islamic Trade Preferential System
- EU-Jordan Agreement
- Euro-Mediterranean Agreement
- Trade Agreements with Malaysia, Egypt, the EFTA, Tunisia, Algeria, Libya, Lebanon, Turkey, and Syria
- Agadir Agreement
- Egypt-Jordan-Morocco-Tunisia Free Trade Agreement


- WTO
- GATS
- Agreement on Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- Convention on the Harmonization of Frontier Controls of Goods
- COTIF Convention (Rail)
- BIC
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- IMO
- Convention for Safe Containers
- Istanbul Convention
- Hamburg Rules (Sea)
- CIM & CIT Rules (Rail)
- IRU
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member

Islamic Organizations.
- Arab League
- Summit of South American-Arab Countries
- Asia-Middle East Dialogue
- Islamic Development Bank
- Economic Commission for Western Asia (ESCWA)
- OIC
- Committee for Economic Cooperation
- Islamic Chamber of Commerce
- Islamic Centre for Development of Trade
- Economic Centre for Islamic Countries
- Afro-Arab Cooperation
- Arab Development Funds
- Arab Trade Financing Programme
- Arab Bank for Africa (BADEA)

- UN
- WB
- WTO
- IMF
The Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan
- Jordan shares borders with Syria, Iraq, Saudi Arabia, Israel, and Palestine
- Arabic name: المملكة الأردنية الهاشمية
- Jordan people are Arabs (98%)
- The official language of Jordan is Arab.
- English is widely spoken
- Capital of Jordan: Amman (4 million people)
- Jordanian population: 5.9 million people
- 87% of the Jordanian population is literate
- Jordanian Area: 92,300 km²
- Jordan is a Constitutional Monarchy
- Head of State of Jordan: King Abdullah
- Jordanian Independence: 1946
Religion in Jordan.
- Islam (Sunni Muslim) is the main religion of Jordan: 92% of the Jordanian population
- 6% of the population are Christians (Orthodox)
- Legal System of Jordan: Based on the Islamic Law and French codes

Jordan belongs to the Arab Economic Area.

- Jordanian Economy is experiencing a very high growth rates
- Jordan is the second Arab economy that has grown over the past fifty years
- Jordanian GDP growth: 3%
- Services sector: 68% of the total GDP
- Manufacturing: 25% of the Jordanian GDP
- Tourism sector: 14% of the GDP
- Inflation rate: 5.6%
- Free Market-Oriented Economy
- Deep privatization of the largest state-owned enterprises
- The largest Jordanian port is the Port of Aqaba
- The Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan has significant natural resources, but its business sector is not well established, their economy is very open
- According to the Heritage Foundation, the Index of Economic Freedom of Jordan was 52
- There are substantial trade and investment opportunities in construction, public sector, and commercial sector
- According to the Central Bank of Jordan the services sector, including construction, accounts for 71.9% of the GDP
- Jordanian tourism has become increasingly important in the recent years (between 8 and 10% of the Jordanian GDP)
- In the recent years the most dynamic sector of the Jordanian economy has been the construction sector
- Jordanian industry comprises a broad range of products: meat products, fruits, vegetables, dairy, animal food, confectionery, soft drinks, snuff, olive oil, alcohol, and others
- Jordan exports only 15% of his production
- Currency: Jordanian dinar (JOD)
- Deregulated telecommunication Market


Jordanian Foreign Trade.
- The main suppliers of Jordan were Saudi Arabia (21%), China (10%), Germany (6%), the U.S. (4%), Egypt (4%), South Korea (3%) Italy (3%), India (3%), Japan (2.9%), and Turkey (2%)
- The EU accounts for 24% of the Jordanian imports
- The largest export markets of Jordan were India (20%), the U.S. (16%), Iraq (13%), Saudi Arabia (7%), the UAE (3%), and Syria (3%)
- Jordanian main exports are apparel and clothing, fertilizers, vegetables, and pharmaceutical products
- Jordanian main imports are Mineral fuels, nuclear reactors, electrical machinery, and vehicles
- Qualifying Industrial Zones: free access to the U.S. market
- Free Zones (Aqaba and Zarqa)
Jordan has more Trade Agreements than any other Arab country: the U.S., Canada, Singapore, Malaysia, Egypt, the EFTA, Tunisia, Algeria, Libya, Lebanon, Turkey, and Syria.
More Trade Agreements are provided with Iraq, Palestine, the GCC countries, Lebanon, and Pakistan.
Sample: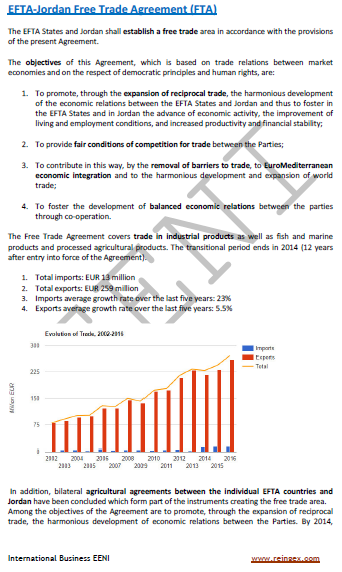


Sample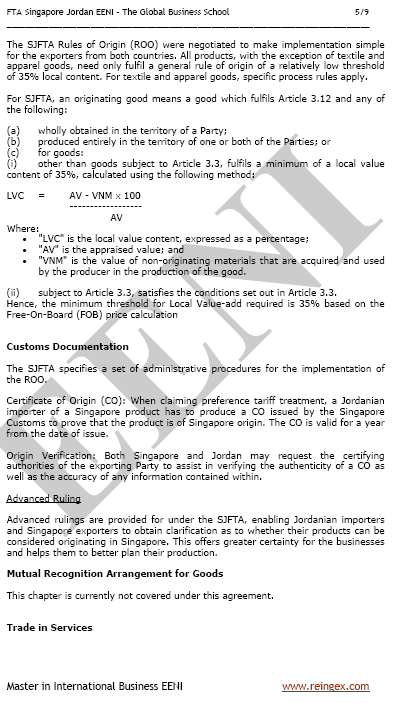
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page




 or
or 
