Business in China
International Trade and Business in China. Chinese Economy

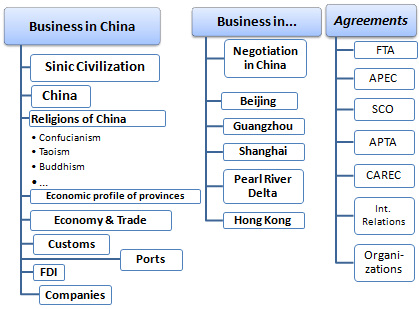
The main objective is to offer a global vision of the Chinese Market and the business opportunities in China (Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou - Shenzhen, the Greater Pearl River Delta) and Hong Kong:
- To know the business opportunities in China
- To analyze foreign trade and foreign direct investment flows
- To know the Chinese free trade agreements
- To carry out an International Marketing Plan or a Project to Set Up a Company in China

Global Trade and Business in China

 Masters adapted to Chinese Students.
Masters adapted to Chinese Students.

Introduction to China. Economic Profile of the Chinese provinces.
Chinese Economy and Foreign Trade.
Foreign direct investment in China.
Business in Guangzhou - Shenzhen.
Marine transport and ports in China.

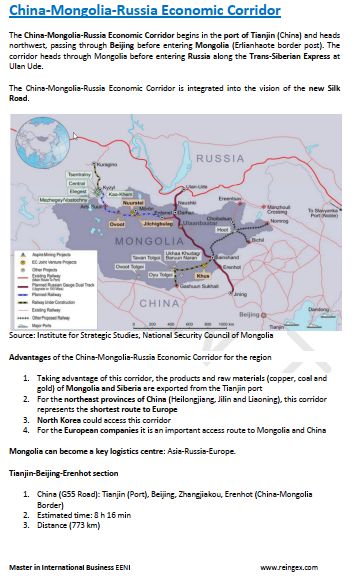
- China-Russia Corridor
- Trans-Siberian Railway (Russia, North Korea)
- Almaty-Bishkek Corridor
- Bangladesh-Myanmar Corridor
- China-Pakistan Corridor
- China-Central-West Asia Corridor
- Nanning-Singapore Corridor
- Access to the:

Chinese Free Trade Agreements: ASEAN, Singapore, Pakistan, New Zealand, Peru, Costa Rica, Chile, EU, ASEAN+3, Andean Community, Macao, Hong Kong, Georgia, Switzerland, Iceland, South Korea, Australia...
Chinese Regional Trade Agreements:
- APEC
- Shanghai Cooperation Organization
- Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement
- Regional Comprehensive Economic Association
- Central Asia Cooperation (CAREC)
- Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) - Candidate Country
- IORA (dialogue partner)
- Mekong River Commission (dialogue partner)
- ALADI (observer)
- South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (Observer)
Chinese International Economic Relations.
- Africa-BRICS Cooperation (China is a BRICS Country)
- China-Africa Cooperation
- Greater Mekong Subregion
Access to the Chinese market.
The Professional Certificate “Trade and Business in China” includes the Market Access Tool:

- WTO
- GATS
- Agreement on Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- BIC (Containers)
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- IMO
- Convention for Safe Containers
- Istanbul Convention
- Customs Convention on Containers
- International Chamber of Shipping
- Organization for Cooperation between Railways (OSJD)
- IRU
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport

- ESCAP
- Asian Development Bank
- Boao Forum for Asia
- Asia-Middle East Dialogue
- Colombo Plan
- Asia-Europe Meeting
- Asia Cooperation Dialogue (ACD)

- UN
- UNCTAD
- ITC
- UNCITRAL
- WIPO
- WB
- WTO
- African Development Bank
- IMF
-
OECD (Key
Partner)
- OECD anti-corruption measures
China is the world's largest market with more than 1,369 million potential consumers (25% live in cities). Regarding the GDP, is the second largest Economy (ahead of countries like Japan, Canada, and Brazil). According to the WB is expected that by 2020, China will be the first economic power in the World, representing nearly 40% of the world production.
China produces more than half of the world's cameras, 30% of air conditioners and televisions, 25% of washing machines, 20% of refrigerators and 70% of toys. “Galanz” produces 40% of microwave ovens sold in Europe. The Brand “Haeir” is recognized worldwide.

We will study the largest economic regions of China:
- Beijing, as China's political, cultural, and international exchange centre; it is a dynamic city with a broad range of industries. High tech and modern manufacturing sector have become the leading forces of the industrial growth of Beijing
- Since 1992, Shanghai has sustained a double-digit GDP growth rate. The city has seen fast growth in its modern service industries. The pillar industries in Shanghai refer to electronic and information technology products manufacturing, auto making, petrochemical and fine chemical processing, fine steel products manufacturing, complete equipment production, and biomedicine. Shanghai is the largest port on Chinese mainland and one of the largest entrepots in the World
- The Greater Pearl River Delta region comprises Hong Kong, nine municipalities of the Guangdong Province in the Mainland China and Macau. Many multi-national companies already enjoy the benefits of this multi-jurisdiction, cost-efficient business model and have established there. Companies can source or manufacture competitively in China and use Hong Kong as logistical, financial, legal, design and marketing services to export their products to the world
- Hong Kong has a prime location at the geographical and Economic centre of Asia. Business Executives in Hong Kong have fast and easy access to all the largest markets in the Asia-Pacific region. This central position is one of the key reasons for the city's popularity as a location for regional operations
Area of Knowledge: Asia.