African Business and Economy, Dangote
Training: African Business. Frontier Markets. Governance (Online, 5 ECTS,  )
)

Nigeria is the largest African Economy, followed by South Africa, Egypt, Algeria, Angola, Morocco, Sudan, Kenya, Ethiopia, Libya.
African manufacturing sector: only 10% of Africa’s GDP
Top African economic sectors: agriculture (25% of GDP) and services.

Six subjects compose the Online training “African Business and Economy” offered by EENI Global Business School:

- African Economy
- Role of African Women
- African Businesswoman
- African Businessman
- Economic Governance in Africa
- Frontier Markets in Africa
- Africa: The Next Emerging Continent
Sample - African Economy:

- Credits: 5

- Duration: 1 month It is recommended to dedicate about twelve hours of study per week following a flexible schedule. It is possible to reduce the duration dedicating more hours a week
- Download the syllabus (PDF)
Languages: 
- Also available in For improving international communication skills, student has free access to the learning materials in these languages (free multilingual training).
 Afrique Economie
Afrique Economie  Africa Economia
Africa Economia  Africa Economia
Africa Economia
Doctorate in African Business.

Master in Business in Africa, Transport and Logistics in Africa.
The goals are to know:
- The State of the African Economy: economic trends by region, most dynamic countries, influence of the commodity prices, fiscal policy, Risks that the African Economy faces, Foreign Direct Investment flows, official development assistance, tax revenue in Africa, socio-economic impact of the Ebola
- The Role of African Women (519 million): one of the pillars of the African Economy
- The profile of twenty-five African Women who are Leading African Transformation, such as the former President of the African Union, Nkosazana Dlamini-Zuma or the Angolan businesswoman Isabel dos Santos (the richest African Women)
- The profile of forty African Businessman who are Leading African transformation as the Nigerian, Alhaji Aliko Dangote (the richest African), Mohammed Ibrahim (Sudan), or Patrice Motsepe (South African)
- The state of governance in Africa, index on how to do business, business climate, state of corruption, the African civil conflicts or the relevant Ibrahim Index of African Governance
- Understand the concept of “Frontier or pre-emergent markets in Africa” related to investment opportunities and business environment in Africa
Course intended for all those wishing to understand the state of the African Economy and the business environment in Africa.
Subject 1- African Economy. Syllabus:
- Introduction to African Economy
- Macroeconomics prospects for
Africa
- Case Study: Saving, investment, and growth in Africa
- Economic trends in the Africans regions
- East and West African Countries: The fastest growing regions
- Central Africa
- Southern Africa
- North Africa
- Influence of commodity prices, inflation, monetary and fiscal policies
- Case Study: Fiscal policy in Africa and business cycles
- Risk affecting the African Economy
- Investment in Africa
- Largest receptors (countries and sectors)
- FDI sources in Africa
- Intra-African investments
- Portfolio investments to Africa
- Remittances to Africa
- Official development assistance (ODA)
- Tax revenues in Africa
- Case Study:
- Socio-economic impacts of the Ebola Virus Disease in Guinea, Liberia, and Sierra Leone
- Historical evolution of the African Economy
Subject 2- Role of African Women - African Businesswoman. Syllabus:
- Nkosazana Dlamini-Zuma
- Isabel dos Santos
- Folorunsho Alakija
- Cheryl Carolus
- Hajia Bola Shagaya
- Divine Ndhlukula
- Mimi Alemayehou
- Tara Fela-Durotoye
- Minoush Abdel-Meguid
- Adenike Ogunlesi
- Bridgette Radebe
- Wendy Appelbaum
- Iman
- Amina Odidi
- Rapelang Rabana
- Monica Katebe Musonda
- Amini Kajunju
- Folake Folarin-Coker
- Irene Charnley
- Sibongile Sambo
- Wangari Maathai
- Ellen Johnson-Sirleaf
- Leymah Gbowee
Subject 3- African Businessman. Syllabus:
- Alhaji Aliko Dangote
- PhD Mike Adenuga
- Tony Elumelu
- Orji Uzor Kalu
- Hussein Ali Al-Amoudi
- Naushad Merali
- Hakeem Belo-Osagie
- Adewale Tinubu
- General Theophilus Danjuma
- Oba Otudeko
- Patrice Motsepe
- Cyril Ramaphosa
- Mohamed Ibrahim
- Osama Abdul Latif
- Onsi Sawiris
- Othman Benjelloun
- Hassan Abdalla
- Mohamed Mansour
- Tarek Talaat Moustafa
- Ahmed Mekky
- Bhimji Depar Shah
- Mohamed Bensalah
- Miloud Chaabi
- Anas Sefrioui
- Aziz Akhannouch
- Ali Wakrim
- Mohamed Ali Harrath
- Sifiso Dabengwa
- Strive Masiyiwa
- Mohammed Dewji
- Said Salim Bakhresa
-
Reginald Mengi
- André Action Diakité Jackson
- Abdulsamad Rabiu
- Olufemi Otedola
- Jim Ovia
-
Alhaji Indimi
- Tunde Folawiyo
- Ali Haddad
- Issad Rebrab

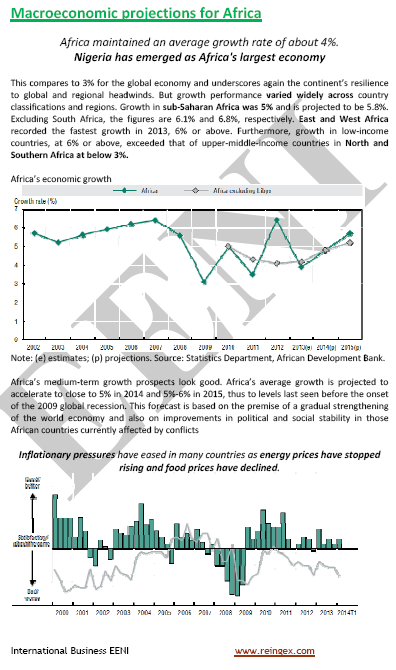
African Economic growth: 5-6%
- East Africa: 6.2%
- West Africa: 7% (the fastest African growth)
- Central Africa: 5.7%
- Southern Africa: 4.4%
- North Africa and: 5.5%
Factors:
- Energy cost
- Food and commodities prices
- Tax revenues
- Inflationary pressures
- External financial flows
- Official development assistance
- Improved Intra-African trade performance
- Top African exports: mainly commodities
- Regional Integration
- Infrastructures
- Private consumption
The proportion of Africans living on less than 1.25 dollars a day fell from 58% in 1996 to 50%.
The creation of several institutions related to economic integration in Africa was expected to increase intra-African trade in products.
Sample: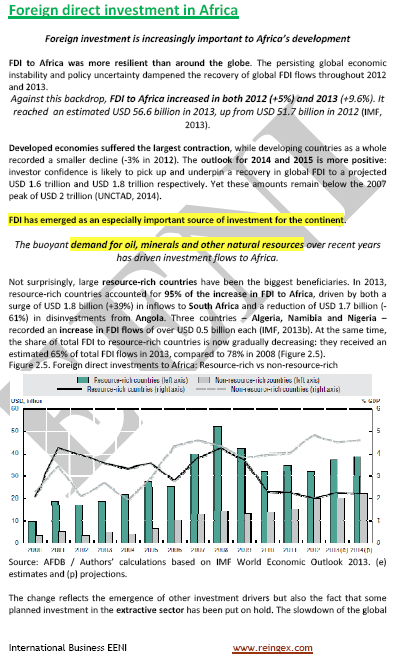
Such International Trade augmented from 2% in the early 1980 to 9% of total African exports, but these statistics underestimate the actual flows as they do not include the unrecorded external trade, which is thought to be crucial.
Even with this caution, intra-African trade flows are low in comparison to those in other regions and relative to African Foreign Trade potential.
The analysis of Foreign Trade destinations show that notwithstanding the low aggregate level of intra-African trade, such regional trade is vital for many African Countries.
At least 25% of exports from twenty African Countries are absorbed by the regional market. The magnitude of trade blocs is highlighted by the fact that 75% of intra-African trade takes place within these regional groups.
Africa has a long tradition of cross-border investment but the lack of reliable data has constrained a detailed analysis. The limited data available show that intra-African Foreign investment represents 13% of the total inward Foreign Direct Investment. This level is less than 50% the figure for the Association of Southeast Asian Nations region, where intraregional investment represents 30% of the total Foreign Direct Investment.
Developing Trade in Services is a key component for successful regional integration in Africa. The services stand for, or have the potential to become, an important export earnings sources for numerous African Countries.
African Countries by GDP (nominal - billion dollars).
1- Nigeria (594.257)
2- South Africa (341.216)
3- Egypt (284.860)
4- Algeria (227.802)
5- Angola (131.407)
6- Morocco (112.552)
7- Sudan (70.030)
8- Kenya (62.722)
9- Ethiopia (49.857)
10- Libya (49.341)
11- Tunisia (49.122)
12- Tanzania (36.620)
13- Ghana (35.475)
14 -Ivory Coast (33.963)
15- The Democratic Republic of the Congo (32.665)
16- Cameroon (32.163)
17- Uganda (26.086)
18- Zambia (25.611)
19- Gabon (20.675)
20- Mozambique (16.590)
21- Botswana (16.304)
22- Senegal (15.881)
23- Chad (15.841)
24- Equatorial Guinea (15.396)
25 Republic of the Congo (14.114)
26- Zimbabwe (13.739)
27- Burkina Faso (13.382)
28- Mauritius (12.720)
29- Mali (12.043)
30- Namibia (11.982)
31- South Sudan (11.893)
32- Madagascar (11.188)
33- Benin (9.237)
34- Niger (8.290)
35- Rwanda (8.002)
36- Guinea (6.770)
37- Sierra Leone (5.411)
38- Togo (4.838)
39- Malawi (4.408)
40- Mauritania (4.286)
41- Eritrea (3.870)
42- Eswatini (3.842)
43- Burundi (3.037)
44- Lesotho (2.458)
45- Liberia (2.073)
46- Cape Verde (1.975)
47- The Central African Republic (1.731)
48- Djibouti (1.582)
49- Seychelles (1.473)
50- Guinea-Bissau (1.040)
51- The Gambia (0.918)
52- The Comoros (0.722)
53- São Tomé and Príncipe (0.362)
54- Somalia
55- Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
Sample:
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp