Business in Burundi. Burundian Economy
Burundi: cobalt, coffee. Burundian Foreign Trade, Logistics. Bujumbura
Burundi: a cobalt, copper, and coffee exporter. Landlocked country.
One of the ten poorest countries in the World.

- Introduction to the Republic of Burundi (Central Africa)
- Burundian Economy
- International Trade of Burundi
- Business and Investment Opportunities in Burundi
- Infrastructure and logistics
- Agriculture
- Tourism
- Mining sector
- Food and beverages
- Industry and Manufacture
- Energy
- Financial Services
- Health
- Information and communications technology (ICT)
- Real Estate
- Case Study: Inter Cafe Burundi
- Investment in Burundi
- Burundi Investment Promotion Authority (API)
- Access to the Burundian Market
- Business Plan for Burundi

The educational aims of the Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Burundi” are:
- To analyze the Burundian Economy, Logistics and Global Trade
- To conduct research on business opportunities in Burundi
- To explore the Burundian trade relations with the student's country
- To learn about Burundian Trade Agreements
- To develop a business plan for the Burundian Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Burundi” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate in African Business.

Master in Business in Africa, International Business.


Languages:  or
or  Burundi
Burundi  Burundi
Burundi  Burundi.
Burundi.
- Subject Credits “Doing Business in Burundi”: 1

International Trade, Logistics and Business in Burundi.

Transport and Logistics in Burundi
- Trans-African corridors
- Nearest Ports
- Port of Mombasa (Kenya)
- Port of Dar es-Salaam (Tanzania, Rail transport)
Sample: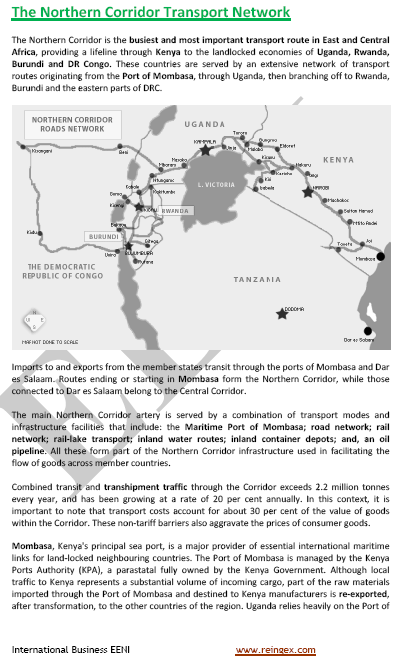


Burundian Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Burundi and the Central African Economic Area / East African Economic Area
- Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA)
- East African Community (EAC)
- Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS)
- African Continental Free Trade Area
- COMESA-EAC-SADC Agreement
- Burundi-U.S.
- Burundi-EU
- Nile Basin Initiative
- Economic Community of the Great Lakes Region
- Conference on the Great Lakes
- Global System of Trade Preferences among Developing Countries (GSTP) - accession process

- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS)
- Agreement on Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Kyoto Convention
- BIC (Containers)
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization (IMO)
- Customs Convention on Containers
- Hamburg Rules (Sea)

- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Union
- AU Convention on Preventing and Combating Corruption
- AUDA-NEPAD
- Africa Agriculture Development Programme
- African Development Bank
- Africa-Asia Partnership
- Africa-India Cooperation
- Africa-BRICS
- Africa-Turkey Partnership
- Afro-Arab Cooperation
- Arab Bank for Africa (BADEA)
- Africa-Korea Partnership
- Africa-Japan Cooperation
- Africa-South America Summit

- United Nations
- World Bank
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- International Monetary Fund
- FAO
- G-77
- International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
- UNESCO
- WHO
- World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO)
The Republic of Burundi is located in Central Africa and is one of the ten poorest countries in the World.
- Area of Burundi: 27,834 km²
- Burundian population: 11 million people
- The official languages of Burundi are Kirundi (97% of Burundian population), French (10%) and English (since 2014)
- Capital of Burundi: Bujumbura (340,000)
- Other largest cities: Gitega, Muyinga, Ngozi
- Burundian Independence: 1962 (Belgium)
- Burundian Government: Presidential representative democratic Republic
- Neighbors countries of the Republic of Burundi: Rwanda, Tanzania, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo
More information about Burundi (EENI African Business Portal).
Religions in Burundi:
- Christianity (Catholicism: 3.9 million)
- African Traditional Religions
Burundi belongs to the Central African Economic Area and the East African Economic Area.

Burundian Economy:
- The Agricultural sector of the Republic of Burundi remains the pillar of the Burundian economy
- Main cash crops of Burundi (tea and coffee) are the main drivers of the economic growth and make up a significant proportion of the Burundian exports
- The Burundian Coffee production achieved 31,000 tones. The increase was due to the favorable response from the farmers after the “Office du café du Burundi” augmented the price it pays to the farmers by 44%
- Agriculture: 27% of GDP. 60% of the Burundian exports
- Burundian Manufacturing: 12%
- Main natural resources of Burundi are cobalt and copper
- Top exports of Burundi are coffee and sugar
- Small industries subsist excluding the agricultural export processing
- Petroleum, nickel, copper, and other natural resources are explored
Body responsible for attracting the FDI: Burundi Investment promotion Authority (API).
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page







 WhatsApp
WhatsApp
