Business in Djibouti, Port, Marine Transport
Djiboutian Foreign Trade and Economy: based on services (Logistics)
Djibouti: an economy based on services (marine transport and telecommunications).
Access to the Ethiopian Market.
- The Republic of Djibouti wishes to leverage its strategic position to be a regional hub for International Trade, financial services, and telecommunications
- This small country (890,000 inhabitants) is also characterized by a unique climate of security in this region
- Around the Port of Djibouti and the Djibouti-Ethiopia Railway; it has been developed other key sectors: banking, insurance, and Distribution

- Introduction to the Republic of Djibouti (East Africa)
- Djiboutian Economy
- International Trade of Djibouti
- Transport and Logistics
- Telecommunications and New Technologies in Djibouti
- Investment in Djibouti
- Access to the Djiboutian Market
- Business Plan for Djibouti
Sample: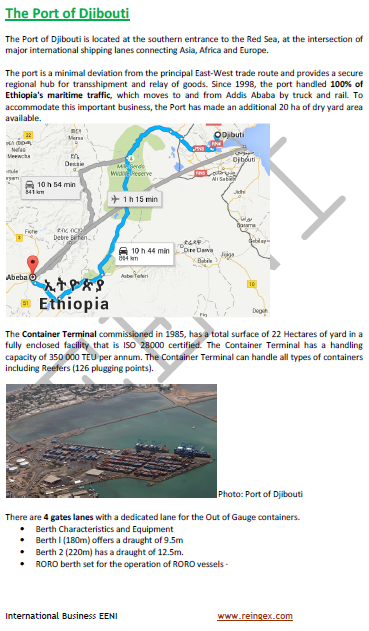

The educational aims of the Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Djibouti” are:
- To analyze the Djiboutian Economy, Logistics and Global Trade
- To conduct research on business opportunities in Djibouti
- To explore the Djiboutian trade relations with the student's country
- To learn about Djiboutian Trade Agreements
- To analyze the importance of the Port of Djibouti
- To develop a business plan for the Djiboutian Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Djibouti” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate in African Business.

Master in Business in Africa International Business.
Languages:  or
or  Djibouti
Djibouti  Djibouti
Djibouti  Djibuti.
Djibuti.
- Subject Credits “Doing Business in Djibouti”: 2

International Trade, Logistics and Business in Djibouti

- Port of Djibouti
- Access to the Ethiopian Market
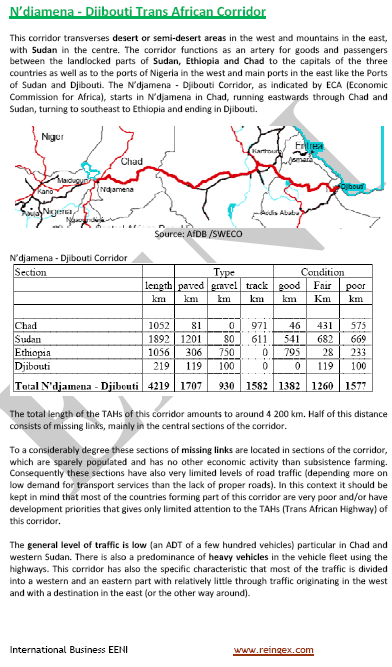
- N’Djamena-Djibouti Logistics Corridor


Preferential Access and Trade Agreements of Djibouti
- Djibouti and the East African Economic Area
- Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA)
- Community of Sahel-Saharan States (CEN-SAD)
- Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD)
- COMESA-EAC-SADC Agreement
- African Continental Free Trade Area
- European Union-Djibouti
- The United States-Djibouti
- AGOA (U.S.)
- COMESA-US Agreement
- Islamic Trade Preferential System
- Islamic Centre for Development of Trade
- Greater Arab Free Trade Area (GAFTA) - not a member

- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS)
- Agreement on the Application of Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- Is not a member of WCO
- Kyoto Convention
Islamic Organizations. Djibouti is a member of:
- Arab League
- Afro-Arab Cooperation Arab Bank for Africa (BADEA)
- Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC)
- Committee for Economic Cooperation (OIC)
- Islamic Chamber of Commerce
- Statistical, Economic and Social Research and Training Centre for Islamic Countries
- Islamic Development Bank
- Asia-Middle East Dialogue (Djibouti)
- Summit of South American-Arab Countries (Djibouti)

- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Union
- AU Convention on Preventing and Combating Corruption (not signed)
- AUDA-NEPAD
- African Development Bank
- Africa-Asia Partnership
- Africa-Korea Partnership
- Africa-Japan Cooperation
- Africa-South America Summit
- Africa-BRICS

- United Nations
- World Bank
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- International Monetary Fund
Djibouti has a strategic location in the Horn of Africa.
The Republic of Djibouti has an advantaged strategic location in the Horn of Africa and serves as a link for the interconnection with other member countries of COMESA.
- Djiboutian Area: 23,200 km²
- Djibouti shares borders with Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Somalia
- Djiboutian Capital: Djibouti (21,200 people)
- The official languages of Djibouti are Arabic, French and Somali
- Djiboutian population: 890,000 people
- Type of Government: Semi-Presidential Republic
- Independence of Djibouti from France: 1977
More information about Djibouti (EENI African Business Portal).
Religion in Djibouti: Islam (94% of Djiboutian population).
- Fiqh: Shafi'i
- After the independence, the Republic of Djibouti built a legal system based partly on the Islamic Law
- The Constitution of Djibouti states Islam as the only religion of the State, while it provides the equality of citizens of all faiths (Article 1) and freedom of Religious practice (Article 11)
Djibouti belongs to East African Economic Area.

Djiboutian Economy:
- Djibouti has created an enabling a good environment for Foreign Direct Investment
- Djibouti, as other city-states like Singapore and Mauritius, wishes to take profit of its strategic position to become a regional centre in financial, logistics, and telecommunications sectors
- Main trading partner of Djibouti is France; but like the rest of Africa, China is every day more important in Djibouti
- The Republic of Djibouti offers access to many regional markets for enterprises seeking to expand their business
- Djibouti has preferential access to the countries of COMESA, Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD), Arab world, the markets of EU, and the United States (AGOA)
- The Djiboutian economy depends on the services sector (87% of GDP)
- The Economic Growth of the port of Djibouti also has been allowed by substantial foreign investment from the United Arab Emirates; in 2000, Dubai Ports (the third world port operator), has obtained the control of the port
- Headquarters of the Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD)
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp
