Business in Egypt. Egyptian Economy, Suez Canal
Foreign Trade of Egypt, Logistics, Transport, Cairo. Egyptian Businessman
Egypt: Strategic location (Africa - the Middle East). Control of the Suez Canal.
- The Arab Republic of Egypt is the economic and cultural centre of a region of 800 million people and a hub for maritime traffic with commercial ports on the Mediterranean and Red Sea
- Main Egyptian economic sectors are tourism, textiles, cement, food industry, chemicals, metals, pharmaceuticals, hydrocarbons, construction, and light manufacturing
- Egypt is considered the gateway to some of the largest markets in the world (Egypt maintains preferential trade agreements with several countries)
Egypt, the “cultural lighthouse” of the Arab Countries.

- Introduction to Egypt
- Egyptian economy
- Growing Sectors of the economy
- International Trade of Egypt
- Transport and Logistics
- Investment in Egypt
- Open a business in Egypt
- Cost of doing business in Egypt
- Business Plan for Egypt
- Access to the Egyptian Market

Egyptian Businessman:
- Ahmed Mekky
- Tarek Talaat Moustafa
- Hassan Abdalla
- Mohamed Mansour
- Onsi Sawiris - Orascom Telecomm
- Minoush Abdel-Meguid

The objectives of the subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in the Arab Republic of Egypt” are:
- To analyze Egyptian Economy, Logistics and Global Trade
- To understand the strategic importance of the Suez Canal
- To conduct research on business opportunities in Egypt
- To explore Egyptian trade relations with the student's country
- To know Egyptian Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of Egyptian Businesspeople
- To develop a business plan for Egyptian Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Egypt” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate in African Business.

Master in Business in Africa International Business.
 Masters adapted to Egyptian Students.
Masters adapted to Egyptian Students.
Languages:  or
or  Égypte
Égypte  Egito
Egito  Egipto.
Egipto.
- Subject Credits “Doing Business in Egypt”: 3

International Trade, Logistics and Business in Egypt

- Egyptian ports
- Suez Canal
- Trans-African corridors


Egyptian Market Access and Trade Agreements.
- Egypt and the East African Economic Area
-
Arab Mediterranean Free Trade Agreement (العربية المتوسطية اتفاقية للتجارة الحرة -
اتفاقية أغادير)
- Egypt-Jordan-Morocco-Tunisia Free Trade Agreement (FTA) / Agadir Agreement
- Community of Sahel-Saharan States (CEN-SAD)
- Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA)
- COMESA-EAC-SADC Tripartite Agreement
- African Continental Free Trade Area
- Trade Agreement with Cameroon
- MERCOSUR-Egypt Agreement
- Turkey-Egypt Agreement
- EFTA-Egypt Agreement
- Islamic Trade Preferential System
- Greater Arab Free Trade Area (GAFTA)
- Arab Bank for Africa (BADEA)
- Arab Trade Financing Programme
- Global System of Trade Preferences
- Trade Negotiations Among Developing Countries
- Nile Basin Initiative
- European Union:
- European Union-Egypt Agreement
- European Neighborhood Policy
- Euro-Mediterranean Partnership
- UK-Egypt Agreement
- Organization of the Black Sea Economic Cooperation (Observer)
- SICA (observer)
- International Conference on the Great Lakes Region (ICGLR) - Guest Member
- IORA (dialogue partner)

- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS)
- Agreement on the Application of Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Kyoto Convention
- Single African Air Transport Market (SAATM / IATA)
- BIC
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization (IMO)
- Istanbul Convention
- Hamburg Rules
- International Road Transport Union (IRU)
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member


Islamic Organizations. Egypt is a member of:
- Economic Commission for Western Asia (ESCWA)
- Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC)
- Committee for Economic Cooperation
- Islamic Centre for Development of Trade
- Economic Centre for Islamic Countries
- Arab League
- Islamic Development Bank
- Afro-Arab Cooperation
- Asia-Middle East (Egypt) Dialogue
- Summit of South American-Arab Countries
- Arab Development Funds
African Organizations:
- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Union
- AU Convention on Preventing and Combating Corruption (not signed)
- AUDA-NEPAD
- African Development Bank
- Africa-Asia Partnership
- Africa-Korea Partnership
- Africa-Japan Cooperation
- Africa-South America Summit
- China-Africa Cooperation
- Africa-India Cooperation
- Africa-BRICS
- Africa-Turkey Partnership

- United Nations
- Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD)
- International Trade Centre
- World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO)
- World Bank
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- International Monetary Fund
The Arab Republic of Egypt stands at a fortunate strategic location linking Asia (Middle East), Africa, and Europe
- Capital of Egypt: Cairo
- Largest cities: Cairo, Alexandria, Shubra El Kheima, Giza, Port Said, Suez
- Egyptian language: Arabic
- Egypt is Semi-Presidential Republic
- Egypt became independent from the United Kingdom in 1922
- Area of Egypt: 1,001,459 km²
- Egyptian population: 97 million people
- 20% of Egyptian population is under the poverty line
- Currency of Egypt: Egyptian Pound
- Uncertainty after the Arab Spring, so great caution when doing business is advised
- Almost six out of ten Egyptians are under twenty-five years
- Egyptians are enthusiastic, educated, forward-thinking and open to new opportunities
- The educational system has improved significantly
- Egypt offers comparatively well-qualified
- The Arab Republic of Egypt has developed a multi-cultural community, mixing traditions of Africa and the Middle East
- Egyptian borders: Israel, Jordan, Libya, Palestine, Saudi Arabia and Sudan

More information: Egypt (EENI African Business Portal).
Religion in Egypt.
Islam is the state religion since 1980.
- Egypt is predominantly Sunni Muslim, with 80 million Muslims (94.7% of the population in 2010)
- Sharia is the primary source of legislation
- Fiqh (Islamic Jurisprudence): Maliki
- There are an estimated 12 million Coptic Orthodox

Egypt belongs to East African Economic Area of African Civilization, but culturally also it belongs to Islamic Civilization.
Egyptian Economy.
- Egypt is a gateway to the largest markets by the way of preferential and regional trade agreements
- Egypt's 90 million population, growing at a rate of 2% annually, represents a significant local market for any investor
- Customs duties reduction has opened Egyptian market to International Trade
- Business procedures have been reduced
- Corporate and personal taxes have been cut
- The cost of Doing Business in Egypt is greatly favorable, particularly labour and land costs
- Movement of products is being speeded up with an improved transport system
- Egyptian ports are being modernized
- Airports are being remodeled to meet the growing flow of passengers and cargo; a modern road network is linking Egypt to the Middle East, Africa and, through the neighboring countries, to Europe
Ahmed Mekky is the co-founder and Managing Director (CEO) of Gulf Bridge International.
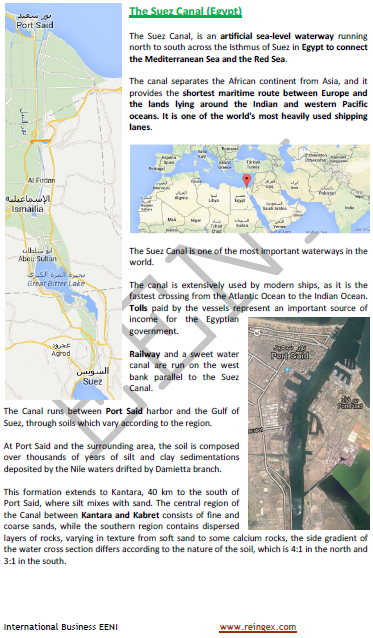

Egyptian Foreign Trade.
- Main Egyptian export markets are Italy, the United States, Spain, India, Syria, Saudi Arabia, and Japan
- Major suppliers of Egypt are the United States, China, Italy, Germany, and Saudi Arabia
Investment Environment in Egypt.
The Ministry of Investment implements definitive policies to promote and develop Foreign Direct Investment by:
- Creating the appropriate organizational and legislative environment for investment
- Foreign Direct Investment promotion
- Efficiency progress measurement
Sample:
Sample:


Sample:

International Trade and Business in Egypt:

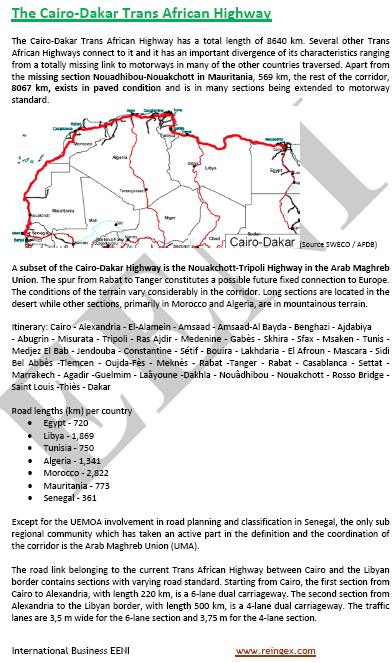
Sample: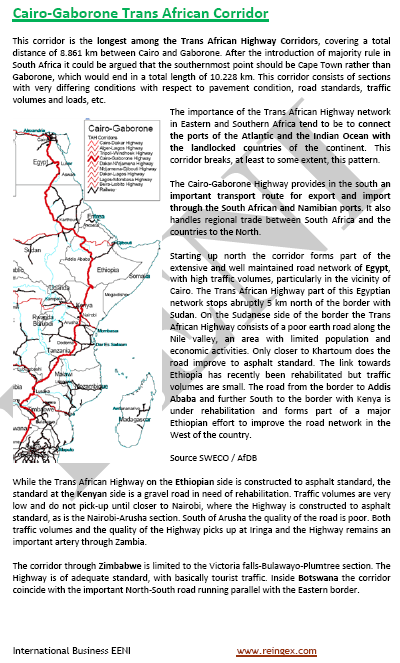
EENI delivers to HRH Prince Alwaleed bin Talal a Master Honoris Causa.
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp
