Business in Angola. Angolan Economy, Trade
Foreign Trade, Angola (African oil exporter) Port of Luanda. Diamonds
Angola is the second-largest African Oil exporter (after Nigeria).
Angola is an African frontier market.
Angola is the largest Central African market.

- Introduction to the Republic of Angola (Central Africa)
- Angolan Economy:
- Mineral Resources
- Diamonds
- Petrol
- Isabel dos Santos (the richest African Women)
- International Trade of Angola
- Transport and Logistics
- Investment in Angola
- Case Study:
- Angola Telecom
- Sonangol
- National Diamond Company of Angola
- Access to the Angolan Market
- Business Plan for Angola
Sample:
The purposes of the subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Angola” are:
- To analyze the Angolan Economy, Logistics and Global Trade
- To conduct research on business opportunities in Angola
- To research the trade relations with the student's country
- To learn about Angolan Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of Angolan companies
- To develop a business plan for the Angolan Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Angola” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Master in Business in Africa, International Business.

Doctorate in African Business.

Languages:  or
or  Angola
Angola  Angola
Angola  Angola.
Angola.
- Subject Credits “Doing Business in Angola”: 3

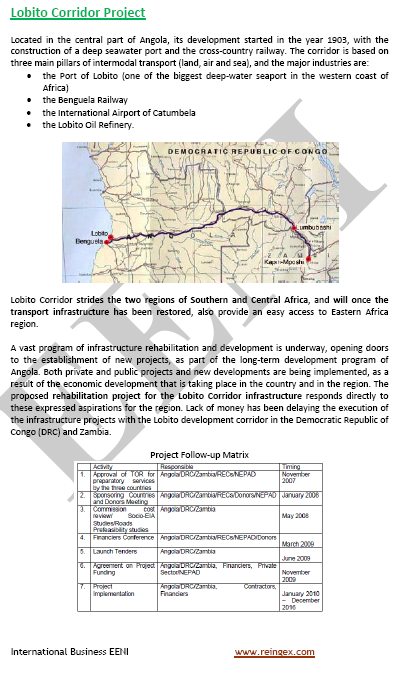
International Trade, Logistics and Business in Angola

- Ports of Luanda and Lobito
- Access to the Port of Walvis Bay (Namibia)
- Trans-African Highway crossing Angola


Angolan Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Angola and the Central African Economic Area
- Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS)
- Southern African Development Community (SADC)
- European Union-SADC Agreement
- COMESA-EAC-SADC Agreement
- African Continental Free Trade Area
- European Union-Angola
- AGOA (U.S.)
- Trade Agreement with India
- Conference on the Great Lakes
- Arab Bank for Africa (BADEA)

- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS)
- Agreement on Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Kyoto Convention (Containers)

- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Union
- AU Convention on Preventing and Combating Corruption (not signed)
- AUDA-NEPAD
- African Development Bank
- Africa-Asia Partnership
- Africa-Korea Partnership
- Africa-Japan Cooperation
- Africa-South America Summit
- China-Africa Cooperation
- Africa-India Cooperation
- Africa-BRICS
- Africa-Turkey Partnership
- Afro-Arab Cooperation
- Arab Bank for Africa (BADEA)

- Community of Portuguese Speaking Countries
- United Nations
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- International Monetary Fund
Angola is the fifth largest country in Sub-Saharan Africa, with an area of 1,246,700 km².
- Atlantic Marine line of Angola: 1,650 kilometers
- Angolan territory is located on the western coast of Southern Africa
- Borders of Angola: The Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo, Namibia, and Zambia
- Angola was a Portuguese colony (500 years)
- Independence of Angola: November 11, 1975 (Portugal)
- Angolan population: 29 million people
- The capital of Angola is Luanda
- The largest Angola cities are Luanda, Huambo, Benguela, Lobito, Kuito, Lubango and Cabinda
- Official language of Angola: Portuguese
Sample:
More information about Angola (EENI African Business Portal).
Religions in Angola:
- Christianity (16 million) - Catholicism
- African Traditional Religions
Angola belongs to the Central African Economic Area.
Angolan Economy:
- The Republic of Angola is the largest Central African market
- The economy of Angola (Africa) depends on the Oil sector (1% of the Angolan workforce)
- Angola is an African frontier market
- Angola is one of the fastest growing economies in the World
- The population is an essential element of the economic growth
- The Angolan economy is predominantly agricultural
- Top Angolan agricultural products are coffee, sugar-cane, sisal, maize (corn), coconut oil and peanut
- Angola is rich in minerals, such as diamonds, petrol, iron
- Huge copper, lead, phosphate, salt, gold, silver, and platinum deposits
- Main Angolan industries are petrol, cereals, meat, cotton, sugar, beer, cement and wood
International Trade and Business in Angola
Angolan Oil sector
- With a 750,000 barrels per day production, Angola is the second-largest producer in Africa (after Nigeria)
- Analysts point to a 1,000,000 barrels per day production in the coming years
Advantages of Angola.
- A strong Government engagement applying economic and political reforms, leading to a free-market economy
- Respect for the private property and legal guarantees for the investors
- Flexible economic regulation
- One-stop-shop business, Foreign Direct Investment aid and support international Office
- Abundant, available labour and skilled young people
- Accessibility to the raw materials and energy resources (natural gas)
- Strategic location (access to the Central African Markets)

Angolan Foreign Trade:
Angola imports (Products and services): 5 million dollars. The largest Angolan imports are:
- Machinery and electrical equipment
- Vehicles and parts
- Medications
- Food
- Textiles
- Sugar-cane
- Coffee
- Sisal
- Maize (corn)
- Cotton
- Cassava root
- Snuff
- Vegetables
- Livestock
- Fish and fishery products
Angola exported 14.5 million dollars (FOB). The largest Angolan exports:
- Petrol and derivates
- Diamonds
- Gas
- Coffee
- Sisal
- Fish and fishery products
- Wood
- Cotton
The largest ports of Angola: Port of Lobito and Port of Luanda.
The nearest foreign port (Southern provinces on Angola) is the Port of Walvis Bay (Namibia), via the Trans-Cunene Corridor
Sectors on which the Government is focusing:
- Agriculture and livestock
- Food products
- Mining
- Fisheries
- Light industry
- Industrial materials for construction and public work
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp
