Business in Morocco

Foreign Trade and Business in Morocco. Rabat, Casablanca, Tangier. Moroccan Businesspeople
- Introduction to the Kingdom of Morocco (Maghreb)
- Moroccan Economy
- Key Sectors of the Moroccan Economy:
- Industry
- Energy
- Agriculture and Fisheries
- Transport
- Mines
- Domestic trade
- Moroccan International Trade
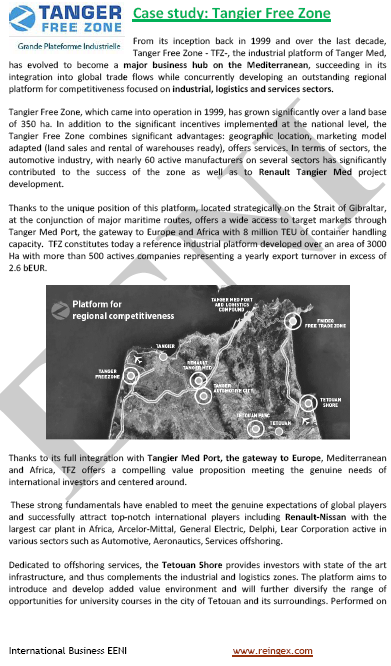
- Tangier Free Zone
- Business Opportunities in:
- Industry
- Solar and wind energy
- Tourism
- Moroccan Agriculture and Fishing
- Logistics
- Retail
- ICT
- Real Estate
- Invest in Morocco
- Moroccan Investment and Development Agency (MIDA)
- Case Study:
- Business Opportunities in Casablanca
- Business Opportunities in Rabat
- Access to the Moroccan Market
- Business Plan for Morocco
Moroccan Businesspeople
- Othman Benjelloun (the richest men in Morocco)
- Aziz Akhannouch
- Anas Sefrioui
- Miloud Chaabi
- Mohamed Hassan Bensalah
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in the Kingdom of Morocco” are the following:
- To analyze the Moroccan Economy and Global Trade
- To know the business opportunities in the Kingdom of Morocco
- To explore the Moroccan trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the Moroccan Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of the Moroccan Businesspeople
- To develop a business plan for the Moroccan Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Morocco” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate: Islamic Business, African Business, World Trade.
Course: Business in the Maghreb.

Master: International Business.
Languages:  or
or  Maroc
Maroc  Morrocos
Morrocos  Marruecos.
Marruecos.
- Credits of the subject “Doing Business in Morocco”: 2

- Duration: two weeks

International Trade and Business in Morocco.
The Kingdom of Morocco: an African Frontier Market. The Emergence of the Moroccan Businessman in Africa.

- Port of Casablanca
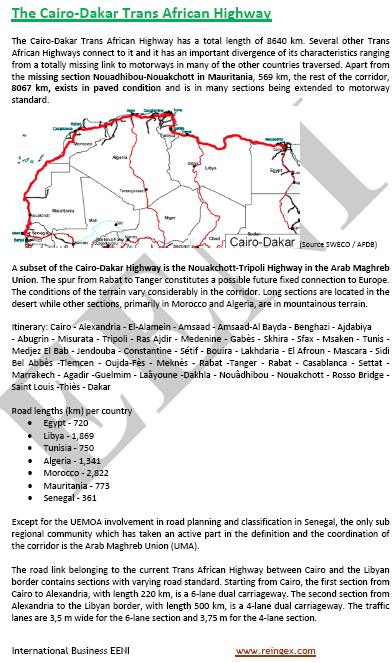
- Cairo-Dakar Corridor
- Access to the Atlantic Transport Corridor (Portugal-Germany)


Moroccan Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Morocco and the Maghrebian Economic Area
- Arab Maghreb Union
- Community of Sahel-Saharan States (CEN-SAD)
- Greater Arab Free-Trade Area (GAFTA)
- Arab Mediterranean Agreement (Agadir)
- Egypt-Jordan-Morocco-Tunisia Free Trade Agreement (FTA) / Agadir Agreement
- Trade Preferential System (TPS-OIC)
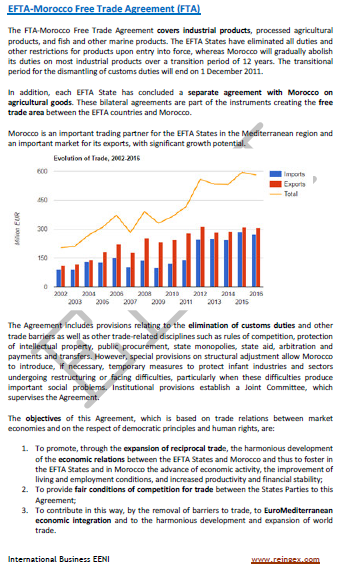
- EFTA-Morocco Agreement
- US-Morocco Free Agreement
- Turkey-Morocco Agreement
- Morocco-United Arab Emirates Agreement
- EU-Morocco:
- UK-Morocco Agreement
- In 2017, Morocco applied to the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)
- Global System of Trade Preferences
- Association of Caribbean States (Observer)
- Andean Community (Observer)
- SICA (observer)
Sample of the Subject: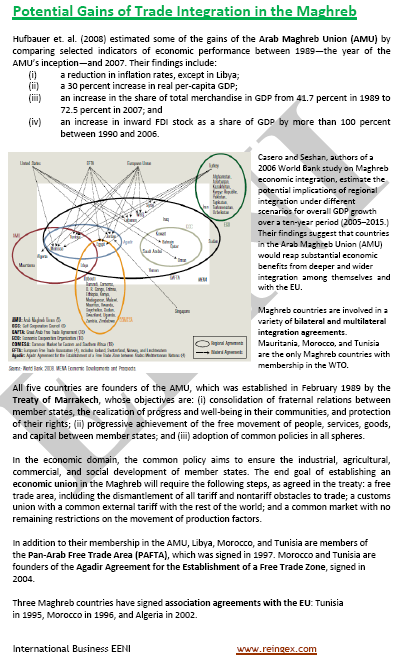

- WTO
- GATS
- Agreement on the Application of Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- Convention Harmonization of Frontier Controls of Goods
- Hamburg Rules (Sea)
- COTIF Convention (Rail)
- BIC
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- IMO
- Customs Convention on Containers
- CIM & CIT Rules (Rail)
- IRU
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport


Islamic Organizations:
- Arab League
- Arab Development Funds in Africa
- OIC
- Islamic Development Bank
- ESCWA
- Asia-Middle East (Morocco) Dialogue
- Summit of South American-Arab Countries
- Afro-Arab Cooperation
- BADEA
African Organizations:
- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Union
- AUDA-NEPAD
- African Development Bank
- Africa-Asia Partnership
- Africa-Korea Partnership
- Africa-BRICS
- Africa-Turkey Partnership

- UN
- WB
- WTO
- IMF
Kingdom of Morocco
- Moroccan Capital: Rabat
- Economic Capital: Casablanca
- The largest cities in Morocco:
- Official languages in Morocco: Arabic and Amazighe
- French is widely used, and Spanish in the North of Morocco
- Moroccan Government: Unitary Parliamentary Constitutional Monarchy. His Majesty the King: King Mohammed VI
- Area of Morocco: 446,550 km²
- Moroccan Population: 33 million people
- Morocco share frontiers with Algeria, Western Sahara (Mauritania), and Spain
- Abolition of Slavery in Morocco: 1922
- Independence of Morocco from France: 1956
More information about Morocco (EENI African Business Portal).
Religion in Morocco:
- 99% of the Moroccan population is Muslim Sunni (Islam)
- Fiqh (Islamic Jurisprudence): Maliki school
- The King of Morocco is considered as a direct descendant of the Prophet Mohammed

Morocco belongs to the Maghrebian Economic Area (Islamic Civilization / African Civilization).

Moroccan Economy
- The economic development of the Kingdom of Morocco (30 million people) in the last years, allowed to set up the basic infrastructures and improve the socio-educational needs of the Moroccan population
- Moroccan GDP growth: 4.7%
- Agriculture sector: 15% of the GDP
- Manufacturing: 15% of the GDP
- Fiscal deficit: 5.5% of the GDP
- Moroccan Inflation: 1.9%
- High youth unemployment (ages 15-24): 19%
- Moroccan strategic sectors: aeronautics, off-shoring, agribusiness, textiles, electronics, and cars
- Moroccan Aeronautical industry: 100 enterprises
- Top Moroccan economic sectors: tourism, industry, fishing, water, housing, and international trade
- Excellent political stability
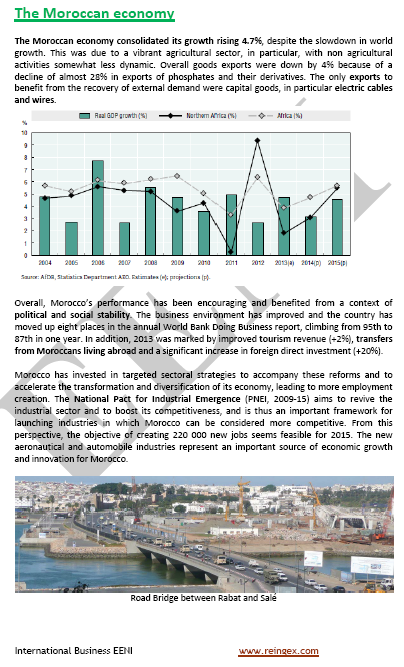
- Morocco is a frontier market
- Stable banking sector
- Weakness of Morocco: environmental fragility.
- The Green Plan of Morocco
- Moroccan Currency: Dirham
- Top Moroccan trade partners are France, Spain, India, Brazil, China, the U.S., and Saudi Arabia
- Existence of investment, industrial zones and free zones (Tangier, Dakhla, Nador, Kenitra, Kebdan, and Laayoune)
- The headquarters of the Islamic Centre for Development of Trade are in Morocco
- The Arab Monetary Fund was founded in 139 6A.H. in Morocco
- The Businessman Sefrioui Anas (1957) is the third-richest person in Morocco. He is the owner (62%) of the Addoha Group
- The Moroccan Businessman and politician, Miloud Chaabi (1930) is the founder of the Ynna Holding and owner of the chain of hotels “Riad Mogador” and supermarket group “Aswak Assalam” in Morocco
- The largest port of Morocco: Port of Casablanca