African Economic Areas (Online Bachelor of Science)
African Economic Areas (Bachelor of Science, e-learning)
| Bachelor of Science in Inter-African Business |
| Bachelor of Science in International Trade |

Subject - “African Economic Areas” (7 ECTS) - Bachelors of Science in Inter-African Business and International Trade.
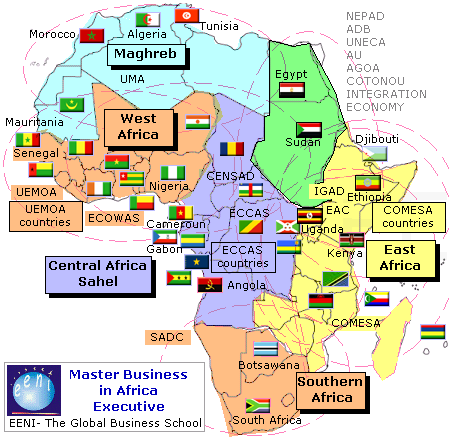

Objectives of the subject “African Economic Area”:
- To define the characteristics of the Economic Area of the African Civilization
- To know the economic profile of the African Countries
- To understand the influence of Islam and Christianity on the African Economic Area
- To understand the African Civilization Economic Integration process
- To analyze the main African Businessmen
- To know economic relations of the African Civilization with the other civilizations (Western, Sinic, Buddhist, Hindu, Orthodox and Islamic)
- To analyze the main economic institutions related to the African Economic Area
- To know the main socio-economic characteristics of the fifty-four African countries

Syllabus of the Program: West African Economic Area.
- Introduction to the Economic Area of West Africa of the African Civilization
- Islam and Christianity in the West African Economic Area
- Economic profile of the West African Countries: Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, Ivory Coast, the Gambia, Ghana, Guinea-Conakry, Guinea-Bissau, Liberia, Mali, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, and Togo
- Businessmen of the West African Economic Area
- Interactions of the Economic Area of West Africa with the other African Economic Areas (Central Africa, Southern Africa, East Africa and Maghrebian)
- Interactions of the Economic Area of West Africa with the other economic areas
- Logistics in West Africa
- Economic institutions related to the West African Economic Area
West African Countries.
West African countries with access to the sea:
- Benin: predominance of the informal sector in Benin
- Ivory Coast: headquarters of the African Development Bank, an African frontier market
- Gambia: a country oriented towards agricultural exports
- Ghana: An African frontier market and the second African gold producer
- Guinea-Conakry: vast bauxite and iron reserves
- Guinea-Bissau: one of the ten poorest countries in the world
- Liberia: an African country with a Nobel Peace Prize laureate (Ellen Johnson Sirleaf)
- Nigeria: African largest economy. The Nigerian population in 2100: 1 billion people
- Senegal: one of the least corrupt African countries
- Sierra Leone: the fastest economic growth in West Africa
- Togo: phosphates and agriculture. The port of Lomé
Landlocked West African Countries:
- Burkina Faso: one of the West African Countries that have implemented more reforms
- Mali: the third African gold producer, instability in the North
- Niger: the world's largest uranium reserves
Insular countries of West Africa.
- Cape Verde: African leader in stability
Objectives of the Program “West African Economic Area”:
- To define the economic characteristics of the Economic Area of West Africa
- To know the economic profile of the West African Countries
- To understand the influence of Islam and Christianity on the West African Economic Area
- To understand the Economic Integration process in the Economic Area of West Africa
- To analyze the top West African Businessmen
- To know economic relations with the other Economic Areas of different civilizations
- To analyze the main economic institutions related to the West African Economic Area
Syllabus of the Program: Central African Economic Area.
- Introduction to the Central African Economic Area of the African Civilization
- Christianity in the Central African Economic Area
- Economic profile of the countries of Central Africa: Angola, Burundi, Cameroon, the Central African Republic, Chad, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, the Republic of the Congo, the DR Congo, Rwanda and São Tomé and Príncipe
- Businessmen of the Central African Economic Area
- Interactions of the Central African Economic Area with the other African Economic Areas (West Africa, Southern Africa, East Africa and Maghrebian)
- Interactions of the Central African Economic Area with the other economic areas
- Logistics in the Central Africa
- Economic institutions related to the Central African Economic Area
Central African countries
Countries of Central Africa with access to the sea:
- Angola: an African frontier market
- Cameroon: 40% of the GDP of the ECCAS
- Gabon: a strategic position in Central Africa
- Equatorial Guinea: the richest African country by habitant
- Republic of the Congo: a heavily indebted poor country
- Democratic Republic of the Congo: 99 million Congolese in 2025
Landlocked markets of Central Africa:
- Burundi
- Central African Republic: Political crisis
- Chad: a new Petroleum exporter country
- Rwanda
Insular countries of Central Africa:
- São Tomé and Prince: a touristic country
Objectives of the Program “Central African Economic Area”:
- To understand the influence of Christianity on the Central African Economic Area
- To define the economic characteristics of the Economic Area of Central Africa
- To know the economic profile of the countries of Central Africa
- To understand the Economic Integration process in the Economic Area of Central Africa
- To analyze the top Businessmen
- To know economic relations with the other Economic Areas of different civilizations
- To analyze the main economic institutions related to the Central African Economic Area
Syllabus of the Program: Southern African Economic Area.
- Introduction to the Southern African Economic Area
- Christianity in the Southern African Economic Area
- Economic profile of Southern Africa Countries: South Africa, Botswana, Lesotho, Namibia, Eswatini, Zambia, and Zimbabwe
- Businessmen of the Southern African Economic Area
- Interactions of the Southern African Economic Area with the other African Economic Areas (West Africa, Central Africa, East Africa and Maghrebian)
- Interactions of the Southern African Economic Area with the other economic areas
- Logistics in Southern Africa
- Economic institutions related to the Southern African Economic Area
Southern Africa Countries.
Countries of Southern Africa with access to the sea:
- South Africa: the second largest African Economy. The largest African car maker
- Namibia: an economy based on mining and cattle raising
Landlocked markets of Southern Africa:
- Botswana: diamonds (33% of the GDP)
- Lesotho: an African monarchy
- Eswatini: a small African Kingdom
- Zambia: an African frontier market
- Zimbabwe: huge mineral resources
Objectives of the Program “Southern African Economic Area”:
- To define the economic characteristics of the Southern African Economic Area
- To know the economic profile of the Southern African Countries
- To understand the Economic Integration process in the Southern African Economic Area
- To analyze the Southern African Businessmen
- To understand the influence of Christianity on the Southern African Economic Area
- To know economic relations with the other Economic Areas of different civilizations
- To analyze the largest Economic Organizations related to the Southern African Economic Area
Syllabus of the Program: East African Economic Area.
- Introduction to East African Economic Area
- Christianity and Islam in the East African Economic Area
- Economic profile of the East African Countries
- Businessmen of the East African Economic Area
- Interactions of the East African Economic Area with the other African Economic Areas
- Interactions of the East African Economic Area with the other economic areas
- Logistics in East Africa
- Economic institutions related to East African Economic Area
East African Countries.
East African Countries with access to the sea:
- Djibouti: an economy based on Maritime transport and telecommunications
- Egypt: the control of the Suez Canal
- State of Eritrea
- Kenya: the largest East African economy
- Mozambique: one of the poorest countries in the World
- Tanzania: an African pioneer market
- Somalia
- Sudan: the largest African country
Landlocked countries in East Africa:
- Burundi: one of the ten poorest countries in the World
- Ethiopia: Headquarters of the Economic Commission for Africa and the African Union
- Malawi: an agricultural country
- Rwanda: the more densely populated African country
- South Sudan: the youngest country in the world
- Uganda: open to investment (FDI)
Insular countries of East Africa:
- Comoros: 50 percent of the population lives below the international poverty line ($ 1.25 per day)
- Madagascar: one of the poorest Africa countries
- Mauritius: one of the largest African financial centre
- Seychelles: the first African country by the Human Development
Objectives of the Program “East African Economic Area”:
- To define the economic characteristics of the East African Economic Area
- To know the economic profile of the East African Countries
- To understand the Economic Integration process in East African Economic Area
- To understand the influence of Islam and Christianity on the East African Economic Area
- To analyze the top Businessmen
- To know economic relations with the other Economic Areas of different civilizations
- To analyze the main economic institutions related to East African Economic Area
Syllabus of the Program: Maghrebian Economic Area.
- Introduction to Maghrebian Economic Area as a part of the Islamic Civilization and the African Civilization
- Islam in the Maghrebian Economic Area
- Economic profile of the Maghrebian countries: Algeria, Libya, Morocco, Mauritania, and Tunisia
- Businessmen of the Maghrebian Economic Area
- Logistics in the Maghreb
- Interactions of the Maghrebian Economic Area with the other African Economic Areas
- Interactions of the Maghrebian Economic Area with the other economic areas
- Economic institutions related to Maghrebian Economic Area
Maghrebian countries.
- Algeria: 50% of the African gas. An African frontier market
- Morocco: an African frontier market. The emergence of the Moroccan entrepreneurs in Africa
- Tunisia: the world's leading dates exporter
- Mauritania: the importance of mining and fishing sector
- Libya: the largest proven petroleum reserves in Africa
Objectives of the Program “Maghrebian Economic Area”:
- To define the economic characteristics of the Maghrebian Economic Area
- To understand the influence of Islam on the Maghrebian Economic Area
- To know the economic profile of the Maghrebian countries
- To understand the Economic Integration process in the Maghrebian Economic Area
- To analyze the main Businessmen of the Maghreb
- To know economic relations with the other Economic Areas of different civilizations
- To analyze the main economic institutions related to Maghrebian Economic Area
The subjects of the first semester of the Bachelor of Science in Inter-African Business and International Trade.
Note:
- ECTS = European Transfer and Accumulation System
- CECT = Credit of Capitalisable and Transferable Evaluation (CAMES)
Samples: African Economic Areas (Online Bachelor of Science in Inter-African Business and International Trade).




Language of the subject “African Economic Areas” of the Bachelor of Science in Inter-African Business and International Trade:  or
or  EENI
EENI  EENI
EENI  EENI.
EENI.
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page

