Business in Lesotho, Maseru. Switzerland of Africa

Foreign Trade of Lesotho (African monarchy). Business in Maseru. Textile, garment
- Introduction to the Kingdom of Lesotho (Southern Africa)
- Business in Maseru
- Economy of the Kingdom of Lesotho (Switzerland of Africa)
- Foreign Trade of Lesotho
- Access to the Port of Durban (South Africa)
- Lesotho Customs and Excise Administration
- Business and Investment Opportunities in Lesotho
- Textile and garment sector
- Plastic products
- Leather and footwear
- Consumer electrical and electronic appliances
- Food processing and beverages
- Mining
- Environmental projects
- Energy
- Health sector
- Infrastructure development
- Case Study:
- Lesotho Highlands Water Project
- Exporters’ guide to the preferential trade arrangements applicable to Lesotho
- Lesotho Textile Industry
- Lesotho National Development Corporation
- Access to the Market
- Business Plan for Lesotho
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in the Kingdom of Lesotho” are the following:
- To analyze the economy and foreign trade of Lesotho
- To know the trade opportunities in the Kingdom of Lesotho
- To explore the Lesotho's trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the Trade Agreements of Lesotho
- To develop a business plan for the Lesotho's market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Lesotho” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate in African Business, World Trade.
Master in Business in Africa, International Business, Foreign Trade.

Course: Business in Southern Africa.

Languages:  or
or  Lesotho
Lesotho  Lesoto
Lesoto  Lesoto.
Lesoto.
Credits of the subject “Doing Business in Lesotho”: 1


Masters adapted to  Basotho Students.
Basotho Students.
International Trade and Business in Lesotho.
Lesotho: “Switzerland of Africa.” An African monarchy and landlocked country.


Trade Agreements and preferential access of Lesotho
- Lesotho and the Southern African Economic Area
- Southern African Development Community (SADC)
- EU-SADC Agreement
- COMESA-EAC-SADC Agreement
- Southern African Customs Union (SACU)
- India-SACU Agreement
- EFTA-SACU Agreement
- UK-SACU and Mozambique Economic Partnership Agreement
- MERCOSUR-SACU Preferential Trade Agreement
- African Continental Free-Trade Area
- Preferential market access arrangements with Australia, Canada, the EFTA, Japan, New Zealand, Turkey, and the U.S.
- EU-Lesotho:
- Africa-EU Partnership
- EU-GSP
- The U.S.-Lesotho: AGOA


- WTO
- GATS
- Agreement on Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- Kyoto Convention
- Convention Harmonization of Frontier Controls of Goods
- Hamburg Rules (Sea)
- IMO - not a member
- Istanbul Convention - not a member
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member

- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Union
- AU Convention on Combating Corruption
- AUDA-NEPAD
- African Development Bank
- Africa-India Cooperation
- Africa-BRICS
- Africa-Turkey Partnership
- Afro-Arab Cooperation
- Arab Bank for Africa (BADEA)
- Africa-Asia Partnership
- Africa-Korea Partnership
- Africa-Japan Cooperation
- Africa-South America Summit
- Forum on China-Africa Cooperation

- UN
- WB
- WTO
- IMF
- Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA)
- The Kingdom of Lesotho (Africa) is a monarchy
- Mosotho Capital: Maseru (393,000)
- Borders of Lesotho: South Africa
- Mosotho Area: 30,355 km²
- Population of Lesotho: 2.2 million people
- The main languages are Sesotho, Zulu, and English
- Currency of Lesotho: Loti (plural Maloti)
- Independence from the UK in 1966
- The currency of Lesotho: Loti and South African Rand
- The Rand Monetary Area is formed by Lesotho, Eswatini, Namibia and South Africa (the South African rand as a common currency)
More information about Lesotho (EENI African Business Portal).
Main religion in Lesotho: Christianity.
- African Traditional Religions
-
Christians (90% of the population)
- Protestants (45%)
- Catholics (45%)
Lesotho belongs to the Southern African Economic Area.

Economic Profile of Lesotho.
- Lesotho has a Free market economic system
- Manufacturing: 10.3% of the GDP
- Service industries: 53%
- Agriculture: 10.3%
- Inflation of Lesotho: 5.9%
- Unemployment in Lesotho: 25%
- The main resource: water
- The main economic activities of Lesotho are farming and animal husbandry, clothing, footwear, textiles, food processing, and construction
- Most dynamic sectors of Lesotho are real estate and services
Lesotho Textile Industry.
- The U.S. Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA) is one of the reasons for the textile industry growth; today Lesotho is one of the top African garments exporter to the U.S. market (340 million dollars)
- Textile exported products to the SACU members are exported without taxes
- More than 40,000 people work in this sector, mainly woman
- Global brands like Wal-Mart or Pepe Jeans has facilities in Lesotho
- Lesotho Textile Exporters Association is the main employer association
Lesotho Highlands Water Project is one of the largest projects in Africa. In this bi-national project (Lesotho and South Africa) working near 2,500 people.
Lesotho National Development Corporation is the institution of the Government of Lesotho that design and implements the industrial development policy.
Global Trade and Business in Lesotho:


International Trade of Lesotho:
- Imports: 89% of Lesotho's imports comes from South Africa, other import partners are the SADC countries
- Exports. The main export markets of Lesotho (86%) are South Africa and the U.S.
- The European markets represent 21% of exports
Nearest port: Port of Durban (South Africa).
- Distance from Durban to Maseru: 552 kilometers
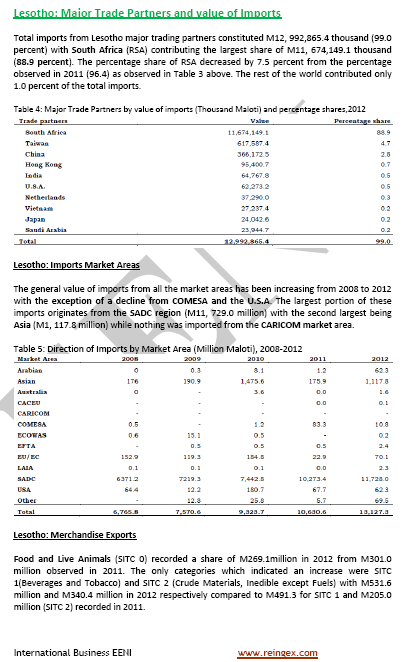
Sample - Foreign trade of Lesotho:
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page


