African Corridors and Ports (Online Bachelor of Science)
African Transport Corridors and Ports (Bachelor of Science in Inter-African Business, e-learning, second semester)
| Bachelor of Science in Inter-African Business |
Subject - “African Transport Corridors and Ports” (10 ECTS) - Online Bachelor of Science in Inter-African Business (second semester).

The objectives of the subject “Transport and Logistics in Africa”:
- State of the transport in Africa (forecasts, costs, programs...)
- African Transport Infrastructure Network
- Air transport in Africa, main routes and airports
- Causes for the decline of the railway in Africa
- The main African logistic corridors
- The largest African ports
- How to access to the fifteen landlocked African Countries through the African Ports and corridors
- Importance of the Programme for Infrastructure Development in Africa (PIDA)
- Relationships between the African integration and logistics and the regional impact on the Intra-African Trade
- How the intensive use of information and communication technologies can reduce the African logistics costs
- African Road Safety Action Plan
- African value chains and how companies can take advantages
Syllabus of the Program - Introduction to Transport in Africa.
- Introduction to transport in Africa
- African Transport Outlook 2040
- African Regional Transport Infrastructure Network
- Forecast Demand for Transport in Africa
- Economic transport costs inefficiencies in Africa
- Air transport in Africa
- Case Study: Ethiopian Airlines, the best African Airline
- Decline of the African Rail transport traffic
- Road transport in Africa
- African Multimodal Transport
- Case Study: Bollore Logistics in Africa
- Introduction to the Maritime Transport in Africa
- Introduction to the African Corridors
Syllabus of the Program - Infrastructures in Africa.
- African Infrastructure Knowledge Programme
- Infrastructure Consortium for Africa
- Trends in African Infrastructure Investment
- Analysis of infrastructure in Africa
- Infrastructure and African economic growth
- Infrastructure and poverty reduction
- Institutional framework for infrastructure
- Urbanization and delivery of infrastructure services
- Regional Integration and infrastructures
- Growth of the Information and communication technologies
- Energy
Syllabus of the Program - Programme for Infrastructure Development in Africa (PIDA).
- Introduction to the Programme for Infrastructure Development in Africa
- Key sectors of the Programme for Infrastructure Development in Africa
- PIDA - energy
- PIDA - transport
- PIDA - information and communication technologies
- PIDA - Transboundary Water Resources
- PIDA's outcomes: development through the regional integration
- Costs and investments of the Programme for Infrastructure Development in Africa
Syllabus of the Program - Maritime Transport in Africa.
- Introduction to the Maritime Transport in Africa
- The main African maritime ports
- Revised African Maritime Transport Charter
- Durban Resolution on Maritime Safety, Maritime Security and Protection of the Marine Environment in Africa
Syllabus of the Program - Ports of Southern Africa
- The main ports of Southern Africa
- South Africa: Port of Durban
- Other ports of South Africa: Richards Bay East London, Ngqura, Port Elizabeth, Mossel Bay, The Cape, Saldanha
- Namibia: Port of Walvis Bay
Objectives of the Program “Ports of Southern Africa”:
- To know the main ports of Southern Africa
- To analyze the main characteristics of the ports of Southern Africa
Port of Durban (South Africa).
- Introduction to the ports of South Africa
- Port Authority of South Africa (Transnet)
- Port of Durban
- Access to the landlocked Southern African Countries: Botswana, Lesotho, Eswatini, Zambia, and Zimbabwe
- Other South African ports: East London, The Cape, Mossel Bay, Ngqura, Port Elizabeth, Saldanha, and Richards Bay
Port of Walvis Bay (Namibia).
- Introduction to the Namibian ports
- Port of Walvis Bay
- Gateway to Angola, Botswana, the DR Congo, South Africa, Zambia. And Zimbabwe
- Port of Lüderitz
- Namibian corridors: Walvis Bay, Trans-Orange, Trans-Kalahari, Trans-Caprivi, and Trans-Cunene
Syllabus of the Program - Ports of East Africa
- The main ports of East Africa
- Port of Djibouti
- Egypt: Port-Said and Port of Alexandria.
- Suez Canal
- Kenya: Port of Mombasa - the largest Port of the region
- Madagascar: ports of Madagascar (Toamasina)
- Mozambique: ports of Beira, Nacala and Maputo
- Sudan: Port Soudan
- Tanzania: Port of Dar es-Salaam
Objectives of the Program “Ports of East Africa”:
- To know the main ports of East Africa
- To analyze the main characteristics of the ports of East Africa
Ports of Djibouti
- Introduction to the Port of Djibouti
- Main characteristics of the Port of Djibouti
- Access to the Ethiopian Market
- Other ports of Djibouti: Port of Goubet and Port of Tadjourah
Egyptian ports:
- Maritime transport in Egypt
- Port Said
- Port of Alexandria
- Port of Dekheila
Suez Canal (Egypt)
- Introduction to the Suez Canal
- Authority of the Suez Canal
- Strategic importance of the canal
- New Suez Canal
Port of Mombasa (Kenya)
- Introduction to the Port of Mombasa (Kenya): the largest East African port
- Gateway to Burundi, the DR Congo, Ethiopia, Rwanda, Sudan, South Sudan, Somalia, and Tanzania
- Other ports of Kenya: Kiunga, Lamu, Malindi..
Ports of Madagascar
- Introduction to the ports of Madagascar
- Port of Toamasina
- Port of Ehoala
- Port of Tamatave
Ports of Mozambique
- Introduction to the ports of Mozambique
- Port of Maputo
- Port of Beira
- Port of Nacala
- Project of the Nacala road corridor
Port Sudan
- Introduction to Port Sudan
- Main characteristics of Port Sudan
- Ports of Bashayr 1 and Bashayr 2
- Other ports of Sudan: Port of Prince Osman Digna, Port of Oseif, Wadi Halfa (Riverport)
Port of Dar es-Salaam (Tanzania).
- Introduction to the Port of Dar es-Salaam (Tanzania)
- Main characteristics of the Port of Dar es-Salaam
- Gateway to Burundi, the DR Congo, Kenya, Malawi, Rwanda, Uganda, and Zambia
Syllabus of the Program - Ports of Central Africa
- The main ports of Central Africa
- Angola: Port of Luanda and Port of Lobito
- Cameroon: Port of Douala
- The Republic of the Congo: Port of Pointe Noire
- Gabon: Port of Libreville and Port Gentil
- Equatorial Guinea: ports of Malabo, Bata and Luba Freeport
- Maritime Organization of West and Central Africa (MOWCA)
Objectives of the Program “Ports of Central Africa”:
- To know the main ports of Central Africa
- To analyze the main characteristics of the ports of Central Africa
Port of Lobito (Angola).
- Introduction to the Port of Lobito
- Main characteristics of the Port of Lobito
- Access to Zimbabwe, Zambia and the DR Congo
- Benguela railway
Port of Luanda (Angola).
- Introduction to the Port of Luanda
- Main characteristics of the Port of Luanda
- Access to Zambia and the DR Congo
Autonomous Port of Douala (Cameroon).
- Autonomous Port of Douala
- Main characteristics of the Port of Douala
- Access to Chad and the Central African Republic
Autonomous Port of Pointe Noire (the Republic of the Congo).
- Introduction to the Port of Pointe Noire
- Gateway for the Congo Basin: the Central African Republic, Chad, Cameroon, Gabon, Angola and the DR Congo
- railway Congo-Ocean
- Congo terminal
Ports of the Gabonese Republic
- Introduction to the ports of the Gabonese Republic
- Port Gentil
- Port of Libreville
- Port of Mayumba
Ports of Equatorial Guinea
- Introduction to the ports of Equatorial Guinea
- Port of Malabo
- Port of Bata
- Luba Freeport
Syllabus of the Program - Ports of West Africa
- The main ports of West Africa
- Ivory Coast: Port of Abidjan
- Senegal: Port of Dakar
- Togo: Port of Lomé
- Benin: Port of Cotonou
- Nigeria: Port of Lagos
- Ghana: Port of Unit and Port of Takoradi
Objectives of the Program “Ports of West Africa”:
- To know the main ports of West Africa
- To analyze the main characteristics of the ports of West Africa
Autonomous Port of Cotonou (Benin)
- Autonomous Port of Cotonou
- Main characteristics of the Port of Cotonou
- Access to Burkina Faso, Mali and Niger
Port of Abidjan (Ivory Coast)
- Port of Abidjan
- Main characteristics of the Port of Abidjan
- Access to Mali, Burkina Faso and Niger
Port of Unit and Port of Takoradi (Ghana)
- Port Authority of Ghana
- Port of Topic
- Port of Takoradi
- Main characteristics of the ports
- Gateway to the West African Markets
Ports of Nigeria
- Port of Lagos
- Port of Apapa
- Port of the Port Harcourt
- Port Complex of Calabar
- Port Complex of Onne Port
- Port Complex of Rivers Port
- Port Complex of Can Island
- Port Complex of Delta Port
Autonomous Port of Dakar
- Autonomous Port of Dakar
- Main characteristics of the Port of Dakar
- Areas of the Port of Dakar
- Access to the Malian market
- Infrastructures in Senegal
Autonomous Port of Lomé
- Autonomous Port of Lomé
- Main characteristics of the Port of Lomé
- Access to Burkina Faso, Mali and Niger
- Togolese free zone
Syllabus of the Program - Ports of the Maghreb
- Main ports of the Maghreb
- Morocco:
- Port of Casablanca
- Ports of Mohammedia, Agadir, Tangier, Al-Hoceima..
- Free zone of Tangier
- Tunisia: ports of the Goulette, Rades, Bizerte, Sousse, Sfax
- Algeria:
- Ports of Algiers and Oran
- Transport sector in Algeria
Objectives of the Program “Maghrebian ports”:
- To know the main ports of the Maghreb
- To analyze the main characteristics of Maghrebian ports
Ports of Algiers and Oran (Algeria).
- Algerian Ports
- Port of Algiers
- Port of Oran
- Transport sector in Algeria
Ports of Morocco
- National Agency of the Moroccan Ports
- Port of Casablanca
- Other Moroccan ports: Mohammedia, Agadir, Tangier, Al Hoceima..
- Free zone of Tangier
Ports of Tunisia
- Introduction to the Tunisian ports
- Ports of la Goulette, Rades, Bizerte, Sousse, Sfax, Gabes, Zarzis
Syllabus of the Program - African Transport Corridors.
- Introduction to the African Transport Corridors
- Almaty Action Program of the UN
- Trans-African Roads network
- Corridors in the region of the SADC
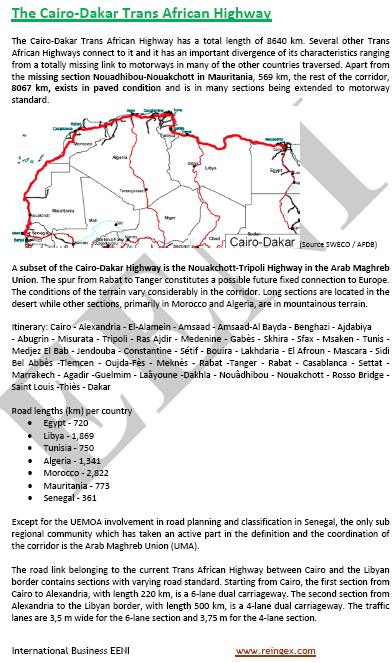
Cairo-Dakar Corridor (Trans-African highway)
- Introduction to the Cairo-Dakar Corridor (Trans-African highway)
- Main characteristics of the Cairo-Dakar Corridor
- Access to seven markets of West and North Africa: Egypt, Libya, Tunisia, Algeria, Morocco, Mauritania, the Western Sahara, and Senegal
Alger-Lagos Corridor (Trans-Saharan highway)
- Introduction to the Alger-Lagos Corridor (Trans-Saharan highway)
- Main characteristics of the Alger-Lagos Corridor
- Access to five markets of West of North Africa: Algeria, Niger, Nigeria, Mali, and Tunisia
Tripoli-Windhoek Corridor (Trans-African highway)
- Introduction to the Tripoli-Windhoek Trans-African highway
- Main characteristics of the Tripoli-Windhoek Corridor
- Access to eight markets of Central, Southern and North Africa: Angola, Chad, Cameroon, the Central African Republic, the Republic of the Congo, the DR Congo, Namibia, and Libya
Gaborone-Cairo Trans-African Corridor.
- Introduction to the Cairo-Gaborone Corridor
- Main characteristics of the Cairo-Gaborone Trans-African highway
- Access to five markets of Southern, Eastern and Northern Africa: Botswana, Egypt, Ethiopia, Kenya, South Africa, Sudan, Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe
Dakar-N'Djamena Trans-Sahelian Highway
- Introduction to the Dakar-N'Djamena Trans-Sahelian Highway
- Main characteristics of the Dakar-N'Djamena corridor
- Access to seven markets of Central and Western Africa: Senegal, Mali, Burkina Faso, Niger, Nigeria, Cameroon, and Chad
N'Djamena-Djibouti Trans-African Highway
- Introduction to the N'Djamena-Djibouti Trans-African Highway
- Main characteristics of the Djibouti-N'Djamena corridor
- Access to five markets of Eastern, Central and Western Africa: Sudan, Ethiopia, Nigeria, Djibouti, and Chad
Dakar-Lagos multimodal transport corridor
- Introduction to the Dakar-Lagos corridor (Trans Coastal West African Highway)
- Main characteristics of the Dakar-Lagos corridor
- Access to twelve markets of West Africa and the Maghreb: Mauritania, Senegal, the Gambia, Guinea-Bissau, Guinea, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Ivory Coast, Ghana, Togo, Benin, and Nigeria
Lagos-Mombasa African transport corridor
- Introduction to the Lagos-Mombasa Trans-African Corridor (Trans-African highway 8)
- Main characteristics of the Mombasa-Lagos corridor
- Access to six Markets of Eastern, Central and Western Africa: Nigeria, Cameroon, the Central African Republic, the DR Congo, Uganda, and Kenya
Beira-Lobito transport corridor (Angola).
- Introduction to the Beira-Lobito Corridor (Trans-African highway 9)
- Main characteristics of the Beira-Lobito highway
- Access to five markets of Central, Eastern and Southern Africa: Angola, the DR Congo, Mozambique, Zambia, and Zimbabwe
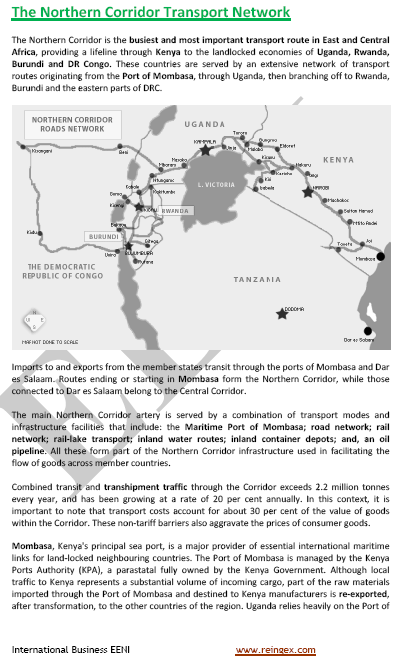
Northern Corridor.
- Introduction to the Northern Corridor (East Africa): Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Kenya
- Transport network of the Northern Corridor
- Institutional framework
Lobito Corridor.
- Introduction to the project of the Lobito Corridor
- Port of Lobito
- Railway of Benguela
- Lobito Oil refinery
Central Corridor
- Introduction to the Central Corridor (Burundi, the Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, Tanzania, and Uganda)
- Main characteristics of the Central Corridor
- Access to five Eastern and Central African Markets: Burundi, the DR Congo, Rwanda, Tanzania, and Uganda
North-South Corridor
- Introduction to the North-South Corridor
- Main characteristics of the North-South Corridor
- A project of the Tripartite Free Trade Agreement (COMESA-SADC-EAC)
- Access to eight Eastern and Southern African Markets: Botswana, the DR Congo, Malawi, Mozambique, South Africa, Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe
Syllabus of the Program - Road Infrastructure Costs in Africa.
- Introduction to the costs of highways infrastructures in Africa
- Building a Database for the Analysis of the Road Costs in Africa
- Analytical Approach for the African Road Infrastructure Costs
- Unit Cost Curve by Project Size
Syllabus of the Program - African Transport and Regional Integration.
- Assessing African Regional Integration (ARIA) report
- Macroeconomic policy convergence
- Free movement of people and right of establishment
- Developments in the major areas across the Regional Economic Communities
- African Physical integration
- Trans-African Corridors
- Railways
- Air transport
- Energy
- Mainstreaming African Regional Integration
- Harmonicing the rules of origin across Africa
- Market access and services
- Trade Facilitation Measures and Programs
- Best Practices in African regional integration
Syllabus of the Program - ICT, Trade and African regional integration.
- Next growth frontier of Africa: e-Commerce
- ITC Initiatives in the Regional Economic Communities
- ICT and trade facilitation
- Automated System for Customs Data and Management (ASYCUDA)
- Automated Terminal Operating System
- ICT and transport corridors
- ICT and payment systems
- Cross-border mobile payments
- Case Study:
- Online Nigerian retail sites (DealDey, Konga, Jumia)
- National single window (NSW) in Ghana, Namibia, Malawi and Mozambique
- Eastern Africa payment system
- Kenya Ports Authority and Kilindini Waterfront
Syllabus of the Program - African Road Safety Action Plan.
- Introduction to the African Road Safety Action Plan
- The five pillars of the African Road Safety Action Plan
- Road Safety Management
- Safer Road Users
- Safer vehicles
- Safer roads and mobility
- Post-crash response
Syllabus of the Program - African Value Chains.
- Introduction to the African value chains
- African Growth Poles
- How can the African companies take advantage of the value chains?
- Opportunities for the African Companies
- Rules of origin and transport costs
- Export costs in Africa
- Trade facilitation
- One-stop border post
- FDI cooperation
- Global value chains: Africa, the global factory?
- Case Study:
- Cacao value chain in West Africa
- Shoprite (the largest African food distributor)

- ECTS = European Transfer and Accumulation System
- CECT = Credit of Capitalisable and Transferable Evaluation (CAMES)
Samples: the transport corridors and the African ports (Bachelor of Science in Inter-African Business, e-learning, second semester).




Language of the subject “International Transport and Logistics” of the Bachelor of Science in Inter-African Business taught by EENI Global Business School (second semester):  or
or  EENI
EENI  EENI
EENI  EENI.
EENI.
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page

