African Business and Economy (Online Bachelor)
African Business and Economy (Bachelor of Science in Inter-African Business, e-learning, second semester)
| Bachelor of Science in Inter-African Business |
Subject - “African Business and Economy” (5 ECTS) - Online Bachelor of Science in Inter-African Business (second semester).

The objectives of the subject “African Business and Economy” are to know...
- State of the African Economy: trends by African regions, the most dynamic African markets, influence of commodity prices, African fiscal policy, risks facing the African economy, investment flows (FDI), official development assistance (ODA), tax revenues in Africa..
- The Fundamental role of the African women (519 million), one of the pillars of the African Economy
- Profile of twenty-five African women who are Leading the African Economic Transformation, such as the former president of the African Union (AU), PhD Nkosazana Dlamini-Zuma, or the Angolan businesswoman Isabel do Santos (the richest African Women)
- Profile of forty African businessmen, such as the Nigerian Alhaji Aliko Dangote (the richest African), the Sudanese Mohammed Ibrahim or the South African Patrice Motsepe
- State of governance in Africa: the indices on how to do business in the African Markets, business climate, corruption, civil conflicts or the Ibrahim Index of African Governance
- The concept of “African frontier (pioneer or pre-emerging) markets”

Syllabus of the Program - African Economy
- Introduction to the African Economy
- African Macroeconomic prospects
- Case Study: saving, investment and the economic growth in Africa
- Economic trends by African regions;
- West and Eastern African Countries: the fastest growing regions
- Central Africa
- Southern Africa
- North Africa
- Influence of commodity prices, inflation, fiscal and monetary policies
- Case studies: African fiscal policy and business cycles
- Risks affecting the African Economy
- Invest in Africa
- The main recipients (countries and sectors)
- FDI sources in Africa
- Intra-African investments
- Remittances to Africa
- Official Development Assistance
- Tax revenues in Africa
- Case Study:
- Socio-economic implications of the Ebola virus in Guinea, Liberia, and Sierra Leone
- Historical evolution of the African Economy
Syllabus of the Program: Role of the African Women. African Businesswomen
Women are one of the pillars of Africa's economic development. They provide approximately 70% of the agricultural labour force and produce about 90% of all food (OECD).
African Centre of Gender.
- Introduction to the African Centre of gender (ACG) of the Economic Commission for Africa (CEPA)
- Woman in Africa
- African Women's Report
- African Women's Rights Observatory
- Case Study: H.E. Nkosazana Dlamini-Zuma, former Chairperson of the African Union Commission
Women Rights in Africa
- Introduction to the women rights in Africa
- Protocol to the African Charter on Human Rights
- Programs of the SADC on gender and development
- AUDA-NEPAD
- Solemn declaration by the heads of state of Africa on Gender Equality
African women awarded the Nobel Prize, heads of state or presidents.
- Wangari Maathai (Kenya)
- Ellen Johnson Sirleaf (Liberia President, Nobel Peace Prize Laureate)
- Leymah Gbowee (Liberia)
- Her Excellency PhD Joyce Banda (former President of Malawi)
- Catherine Samba-Panza (Acting President of the Central African Republic)
Syllabus of the Program: African Businesswomen.
- Isabel dos Santos (Angola): the richest African Women
- Folorunsho Alakija (the richest Nigerian Businesswoman)
- Cheryl Carolus (South Africa)
- Hajia Bola Shagaya (one of the wealthiest African Businesswomen)
- Divine Ndhlukula (Zimbabwe)
- Mimi Alemayehou (Ethiopia/United States)
- Tara Fela-Durotoye (Nigeria)
- Minoush Abdel-Meguid (Egypt)
- Adenike Ogunlesi (Nigeria)
- Bridgette Radebe (South Africa)
- Sibongile Sambo (South Africa)
- Wendy Appelbaum (South Africa)
- Iman (Somalia)
- Amina Odidi (Nigeria - Canada, Businesswoman)
- Rapelang Rabana (South Africa)
- Monique Katebe Musonda (Zambia)
- Amini Kajunju (Democratic Republic of the Congo)
- Folake Folarin-Coker (Nigerian Fashion designer)
- Irène Charnley (South Africa)
- Other African Businesswomen
Syllabus of the Program - African Businessmen.
1- The richest African
2 Nigeria:
- Alhaji Aliko Dangote (The richest African Businessman and philanthropist. Founder of the Dangote Group)
- Théophile Yakubu Danjuma (Politician, Businessman and philanthropist)
- Tony Elumelu (Director of the “United Bank for Africa”, Afro-capitalism)
- Tunde Folawiyo (Businessman and philanthropist)
- Mike Adenuga (The second richest man in Nigeria, founder of Globacom, philanthropist)
- Olufemi Otedola (Founder of Forte Oil)
- Adewale Tinubu (Founder of “Oando Energy Resources”)
- Orji Uzor Kalu (Director of the SLOK Holding)
- PhD Alhaji Muhammadu Indimi (Founder of “Eastern Energy Resources”)
- Jim Ovia (banker, the third richest man in Nigeria)
- Abdulsamad Rabiu (Nigerian Banker)
- Hakeem Belo-Osagie
- Oba Otudeko
4- South Africa:
- Patrice Motsepe (South African entrepreneur and philanthropist)
- Cyril Ramaphosa (South African entrepreneur and politician)
5- Sudan:
- Mohammed Mo Ibrahim (Sudanese Businessman): one of the one hundred most influential people of the World
- Oussama Abdul Latif (Sudanese Businessman)
6- Egypt:
- Onsi Sawiris (Egyptian Orthodox Businessman)
- Hassan Abdalla (Egyptian Banker and Businessman)
- Mohammed Mansour (Egyptian Businessman)
- Tarek Talaat Moustafa (Egyptian Businessman)
- Ahmed Mekky (Egyptian Businessman)
7-Ethiopia:
- Sheikh Mohammed Hussein Ali Al-Amoudi (Businessman and philanthropist, Saudi - Ethiopian)
8- Kenya:
- Naushad N. Merali (Kenyan Entrepreneur)
- Bhimji Depar Shah (Kenyan Businessman)
9- Morocco:
- Othman Benjelloun: the richest Moroccan man
- Mohammed Hassan Bensalah (Moroccan Entrepreneur)
- Miloud Chaabi (Moroccan Businessman)
- Anas Sefrioui (Moroccan Businessman)
- Aziz Akhannouch (Moroccan Businessman and politician)
- Ali Wakrim
10- Algeria:
- Ali Haddad (Algerian Entrepreneur)
- Issad Rebrab (Algerian Businessman)
11- Tunisia:
- Mohammed Ali Harrath (Tunisian Businessman)
12- Zimbabwe:
- Sifiso Dabengwa (Zimbabwean Businessman)
- Strive Masiyiwa (Zimbabwean Businessman)
13- Tanzania.
- Mohammed Dewji (Tanzanian Businessman)
- Said Salim Awadh Bakhresa (Tanzanian Businessman)
- Reginald Mengi (Tanzanian Businessman)
14- Angola:
- André Diakité Jackson
Syllabus of the Program: Doing Business in Africa. Economic Governance in Africa.
- Introduction to the Political and Economic Governance in Africa
- Role of the African Union, the African Development Bank and the Economic Commission for Africa (UNECA)
- AUDA-NEPAD (African Peer Review Mechanism)
- Indexes “Doing business in Africa”
- Democratic governance in Africa
- Civil tensions in Africa
- Armed conflicts in Africa
- Economic governance in Africa
- Business environment in Africa
- Corruption in Africa
- Illegal financial flows in Africa
- Intergovernmental Action Group on Money Laundering in West Africa
- Eastern and Southern African group against money laundering
- Forum on African Tax Administration
- Ibrahim Index of African Governance
Syllabus of the Program: African Frontier Markets (pioneers)
Nigeria: the first pioneer (frontier) market of the World.
- Introduction to the African frontier markets
- African context
- Emerging African middle classes
- Reducing the conflicts in Africa
- Human Development
- Regional integration of Africa
- Improving the African business environment
- Africa is not a region hostile to investment
- Major investors in Africa
- Emerging countries
- Investment flows to Africa
- Top sectors receiving FDI: natural resources and telecommunications
- Africa will be the world's largest labour market
Africa: the next emerging continent. Why do business in Africa?
- African population
- New role of the African Women
- Profound African socio-economic transformation
- Emergence of the African Entrepreneurs
- Intra-African trade and African regional integration
- Need for infrastructure in Africa
- Better governance in Africa
- Africa and the global market

- ECTS = European Transfer and Accumulation System
- CECT = Credit of Capitalisable and Transferable Evaluation (CAMES)
Samples: African Business and Economy (Bachelor of Science in Inter-African Business, e-learning, second semester).
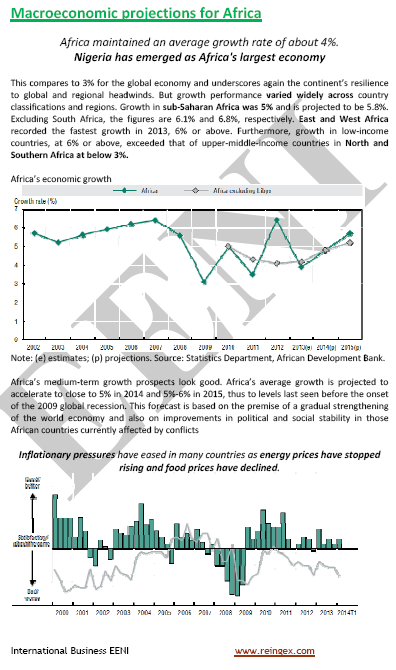




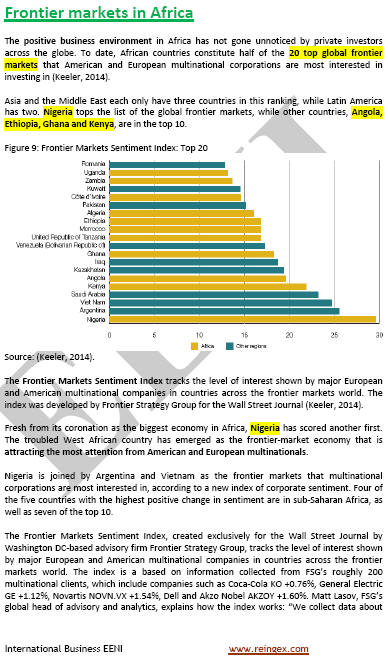
Language of the subject “African Business and Economy” of the Bachelor of Science in Inter-African Business taught by EENI Global Business School (second semester):  or
or  EENI
EENI  EENI
EENI  EENI.
EENI.
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page

