No to Corruption (e-Bachelor, Trade)
No to Corruption in International Trade (Bachelor of Science e-learning, third semester)
| Bachelor of Science in International Trade |

Subject - “No to Corruption in International Trade” (4 ECTS) - Online Bachelor of Science in International Trade (third semester).
Objectives of the Program “No to Corruption in International Business”:
- To analyze the causes of corruption in International Business
- To raise awareness about the terrible effects of the corruption
- To learn about the tools that a company can implement to fight against corruption
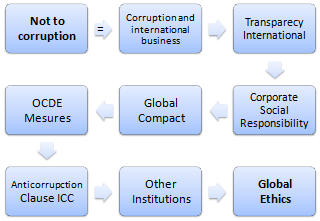
- Corruption and International Business
- Role of Transparency International
- Corporate Social Responsibility and corruption
- Global Compact of the UN
- United Nations Convention against Corruption
- Anti-corruption measures of the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development
- Anti-corruption clause of the International Chamber of Commerce
- Other institutions related to the fight against international corruption
- African Union Convention on Preventing and Combating Corruption
- Introduction to the Global Ethics and corruption
Why fight against corruption?
- 5% of the World's GDP
- Adds up to 10% to the total cost of doing business globally
- International Business would grow up to 3% faster
- Near 25% of the final cost of public procurement
- Infant mortality would drop by 75%

Syllabus of the Program: Transparency International.
- Introduction to Transparency International
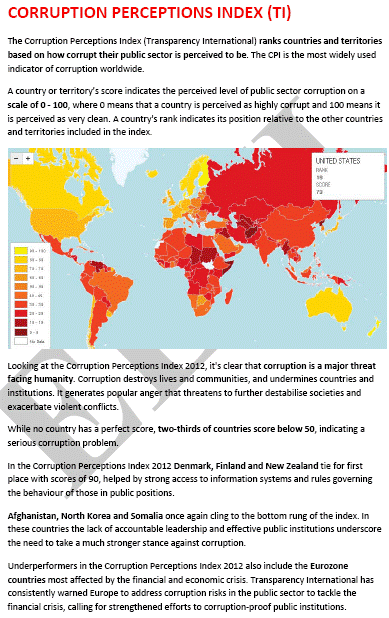
- Corruption Perceptions Index
- Global Corruption Barometer
- Bribe Payers Index
- Business Principles for Countering Bribery
- Principles of transparency and corruption prevention for businesses
- Case Study: The European Corruption Risk
Syllabus of the Program: Corporate Social Responsibility
- Introduction to the Corporate Social Responsibility
- Dow Jones Sustainability Index
- Corporate Social Responsibility and the EU
- Global Report and InFocus (International Labour Organization)
Syllabus of the Program: Global Compact of the UN:
- Introduction to Global Compact of the UN
- Ten principles of the Global Compact
- How to join the Global Compact
- Universal Declaration of Human Rights
- United Nations Convention against Corruption
- Rio Declaration on Environment and Development
Syllabus of the Program: Anti-corruption Measures of the OECD.
- Introduction to the OECD
- OECD Guidelines for Multinational Enterprises
- Fighting corruption in the public sector
- Guidelines for managing conflict of interest in the public service
- Bribery in the Public Procurement
- Business integrity in Africa
- Convention on Combating Bribery of Foreign Public Officials in the international business transactions (OECD)
- Good Practice Guidance on Internal Controls, Ethics, and Compliance
- Role of intermediaries in the international business transactions
- Electronic sales suppression
Syllabus of the Program: Anti-corruption Clause of the ICC
- Introduction to the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC)
- Anti-corruption clause of the ICC
- Outline of the anti-corruption clause
- How to implement the anti-corruption clause
Syllabus of the Program: Institutions and Initiatives related to the fight against international corruption.
- International Anti-Corruption Academy
- Global Financial Integrity
- Global Witness
- Financial Action Task Force
- Stolen Asset Recovery Initiative
- World Economic Forum Partnering Against Corruption Initiative
- International Association of Anti-Corruption Authorities
Syllabus of the Program: African Union Convention on Preventing and Combating Corruption.
- Introduction to the African Union Convention on Preventing and Combating Corruption
- Regional Anti-Corruption Programme for Africa
Syllabus of the Program: Global Ethics and International Business:
- Introduction to the Global Ethics
- Sources of the Global Ethics
- Religions as “Wisdom traditions” of humanity
- Searching for a Model of Global Ethics
- The two key principles of the global ethics;
- Harmony between the religions
- Ahimsa (Nonviolence)
- Compatibility of the Model of Global Ethics with the Religions of the World
- Implications for the international marketing
- Businesspeople who apply models based on the global ethics
- Why do we need the global ethics?


Objectives of the Program “Global Ethics”:
- To define the fundamentals of a Model of Global Ethics
- To understand the religions of humanity as the sources of a Model of Global Ethics
- To analyze the two key principles of the global ethics: Ahimsa (Nonviolence) and the Harmony between the religions
- To reflect on the impact of the Model of Global Ethics on global business
- To analyze the profile of Businessmen who apply Models of Global Ethics
Subjects of the third semester of the Bachelor of Science in International Trade.
ECTS: European Transfer and Accumulation System
Samples: No to Corruption in International Trade (Bachelor of Science in International Trade, e-learning, third semester).


Language of the subject “No to Corruption in International Trade” of the Bachelor of Science in International Trade (third semester):  or or
or or  EENI
EENI  EENI
EENI  EENI.
EENI.
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page

