Business in Turkey. Istanbul Ankara

Turkey: sixteenth world largest economy. Customs Union with the EU (Foreign Trade)
- Introduction to the Republic of Turkey
- Turkish economy
- Main sectors of the Turkish economy
- Business in Istanbul and Ankara
- International Trade of Turkey
- EU-Turkey Customs Union
- Investment in Turkey
- Establishing a Business in Turkey
- Special Investment Zones
- Case Study: Koç Holding
- Africa-Turkey Partnership
- Turkic Council / Türk Dili Konuşan Ülkeler İşbirliği Konseyi (Türk Konseyi - TDİK)
- Access to the Turkish market
- Business Plan for Turkey
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in Turkey” are the following:
- To analyze the Turkish Economy and Foreign Trade
- To know the business opportunities in Turkey
- To explore the Turkish trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the Turkish Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of the Turkish companies
- To analyze the customs union between Turkey and the EU and the Turkey-Africa Partnership
- To develop a business plan for the Turkish market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Turkey” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
Doctorate: Islamic Business, European Business.
Languages:  (or
(or  Turquía
Turquía  Turquie).
Turquie).
- Credits of the subject “Doing Business in Turkey”: 3

- Duration: three weeks
DIŞ TİCARET VE ULUSLAR ARASI ÇALIŞMA YÖNETİMİ (UYGULAMALI EĞİTİM).

 Uluslararası İşletme Yüksek Lisans.
Uluslararası İşletme Yüksek Lisans.
International Trade and Business in Turkey.
Turkey is the sixteenth World's largest Economy.

- Europe-Caucasus-Asia Corridor
- Trans-Caspian Corridor
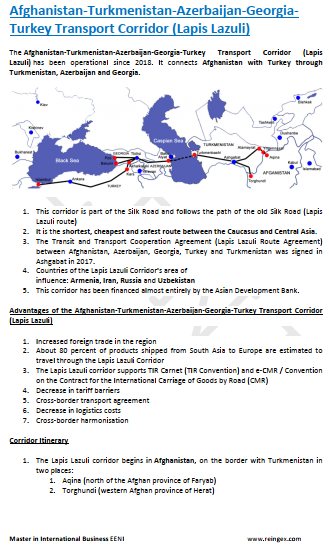
- Afghanistan-Turkey Corridor
- China-Central-West Asia Corridor
- Islamabad-Istanbul Corridor
- Pan-European Corridor IX (Finland-Greece)
- Access to the International North-South Transport Corridor (India-Russia)
- Access to the Eurasian Land Transport Initiative (Silk Road)
- Transit and Transport Cooperation Agreement (Lapis Lazuli Route Agreement)
- Iran-Pakistan-Turkey Transit Transport Framework Agreement (TTFA)


Turkish Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Turkey and the Central Eurasian Economic Area
- Economic Cooperation Organization (ECO)
- Black Sea Cooperation
- EU-Turkey Customs Union
- Turkey-Morocco Agreement
- Turkey-Tunisia Agreement
- Turkey-Egypt Agreement
- Turkey-Serbia Agreement
- Turkey-Montenegro Agreement
- Turkey-Israel Agreement
- Turkey-Macedonia Agreement
- Turkey-Syria Agreement
- Turkey-Albania Agreement
- Turkey-Georgia Agreement
- Turkey-Palestine Agreement
- United Kingdom-Turkey Agreement
- Turkey-Moldova Agreement
- Turkey-Mauritius Agreement
- Turkey-Bosnia and Herzegovina Agreement
- Turkey-Singapore Agreement
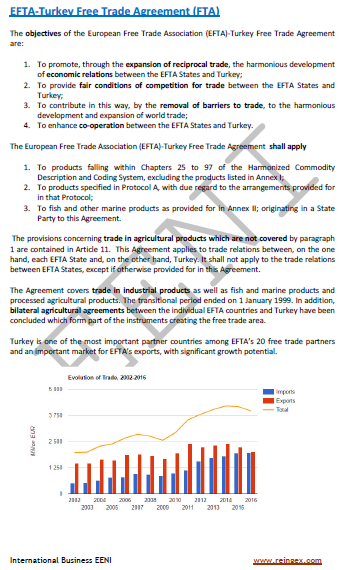
- EFTA-Turkey Agreement
- Trade Agreements with
Jordan, Lebanon, Chile, South Korea.
- FTA not yet ratified: Lebanon, Malaysia, Kosovo, and Ghana
- Islamic Trade Preferential System
- Trade Negotiations Among Developing Countries
- Regional Cooperation Council
- GUAM (Observer)
- ACS (Observer)
- SICA (observer)
- IORA (dialogue partner)
- SCO (Dialogue Partner)

- WTO
- Agreement on Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures
- GATS
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- Kyoto Convention
- COTIF Convention (Rail)
- BIC
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization
- Istanbul Convention
- Customs Convention on Containers
- COTIF Convention
- CIM & CIT Rules (Rail)
- CMR Convention (UN)
- ICS
- IRU
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport

- Asian Development Bank
- Islamic Development Bank
- Asia-Middle East Dialogue
Euro-Asian Organizations:
- Economic Commission for Europe
- European Investment Bank
- Asia Cooperation Dialogue
- OSCE

- UN
- WB
- IMF
- African Development Bank
- OECD
- CPLP (observer country)

- The Republic of Turkey has a total population of 78 million people (24 million people are active)
- Area of Turkey: 783,562.38 km²
- Turkish Capital: Ankara (5.1 million)
- Turkish largest city: Istanbul (14.3 million)
- Official language of Turkey: Turkish
- Borders of Turkey: Bulgaria, Greece, Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Iran, Iraq, and Syria
- Abolition of Slavery in Turkey: 1876
Religion in Turkey: Islam.
- Fiqh (Islamic Jurisprudence): Fiqh-el-hanafi (Hanafi)

Turkey belongs to the Central Eurasian Economic Area (Turkic area, Islamic Civilization).

Turkish Economy.
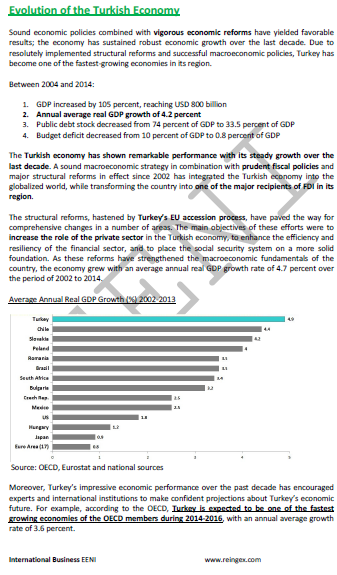
- The economy of Turkey has had a steady economic growth rate for the last twenty quarters
- The Turkish gross national product and GNP per capita shows the strength of the Turkish economy as well as its integration into the global economy
- The Republic of Turkey has made significant steps in restructuring Turkish financial sector, improving the public sector governance, and business environment
- Turkish GDP: 800 billion USD
- Average annual real GDP growth: 4.2%
- The main sectors of the Turkish economy are agriculture and food, automotive, Business Services, chemicals, electronics, energy and renewable, Financial Services, Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals, ICT, Infrastructure, Machinery, manufacturing, mining, property (real estate), tourism, transportation, and Logistics
Business in Turkey:
- Turkish manufacturing sector: 24% of the GDP
- Turkey is the Sixteenth World's largest pharmaceutical product producer
- The Turkish agriculture sector will be one of the top five world producers (2023)
- Property (real estate) sector in Turkey: 4.6% of the Turkish GDP
- A Global leader in dried figs, dried apricots, and hazelnuts production
- Turkey is the Seventeenth largest car maker in the World
- Turkey is the Seventh largest plastic producer in the World
- 30 million tourists every year
- Inflation in Turkey: 8%
- Deep structural reforms
- Universal Health Insurance
- Health “free zones”
- Currency of Turkey: Turkish Lira (TRY)
- Turkey is a EU candidate member


Turkish Foreign Trade.
- Turkey is a natural bridge between the Asian and the European Markets (Eurasian)
- Total Turkish exports: 158 billion USD
- Total Turkish imports: 242 billion USD
- The main Turkish exports markets are the EU (56%) (4%), the U.S. (4%), Romania (3%), the UAE (3%), and Iraq (3%)
- Textiles and transport equipment are the main imports of the EU from Turkey
- The main import providers are Russia, China, Germany, the U.S., Italy, Iran, India, and Spain
- The main imports origin of Turkey are the EU (41%), Russia (14%), China (8%), the U.S. (5%), Iran (4%) and Switzerland (3%)
- The main European Union exports to Turkey are machinery, Transport material, and chemical products
- Turkey has a Customs Union with the EU
- Access to the CIS and the Middle East markets
- Access to the Eurasian Land Transport Initiative
Foreign direct investment in Turkey.
- Total FDI: 12.5 billion USD
- Turkey is the thirteenth most attractive nation in the World for foreign direct investment
- 41,397 foreign companies are established in Turkey working in wholesale and retail trade, manufacturing, and property (real estate)
- Textile production leads the manufacturing sector in foreign direct investment followed by chemicals and food and beverage products
- Government body: Ministry of Investment Support and Promotion Agency (ISPAT)