Business in Georgia, Tbilisi. Georgian Economy

Foreign trade and Business in Georgia. Georgian market
- Introduction to the Georgia (Europe)
- Georgian Economy
- Business in Tbilisi
- International Trade of Georgia
- EU-Georgia trade relations
- Investment in Georgia
- Business Opportunities in Georgia
- Access to the Georgian Market
- Business Plan for Georgia
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in Georgia” are the following:
- To analyze the Georgian Economy and Global Trade
- To know the trade opportunities in Georgia
- To explore the trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the Georgian Trade Agreements
- To develop a business plan for the Georgian Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Georgia” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate: European Business, World Trade.
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
- Credits of the subject “Doing Business in Georgia”: 1

- Duration: one week

 მაგისტრი საერთაშორისო ბიზნესის (Georgia).
მაგისტრი საერთაშორისო ბიზნესის (Georgia).
Foreign Trade and Doing Business in Georgia.

- Europe-Caucasus-Asia Corridor
- Trans-Caspian Corridor
- Afghanistan-Turkey Corridor
- Access to the Islamabad-Tehran-Istanbul Corridor (ITI-ECO)
- Access to the China-Central-West Asia Corridor
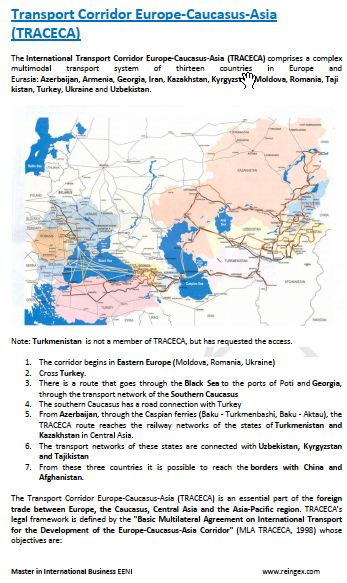

Georgian Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Georgia and the Orthodox Economic Area
- Regional Organization for Democracy and Economic Development
- Black Sea Economic Cooperation
- Central Asia Cooperation (CAREC)
- The EU
- EU-Georgia Free Trade and Agreement
- European Neighborhood Policy
- EU-South Caucasus
- The EU's Generalized System of Preferences (GSP) +
- Black Sea Synergy
- EU Eastern Partnership
- EFTA-Georgia Agreement
- Turkey-Georgia Agreement
- China-Georgia Agreement
- Georgia-Hong Kong China Agreement
- Georgia-Ukraine-Azerbaijan-Moldova Agreement
- UK-Georgia Free Trade and Economic Integration Agreement
- Georgia-Armenia Agreement
- Georgia-Azerbaijan Agreement
- Georgia-Kazakhstan Agreement
- Georgia-Russia Agreement
- Georgia-Turkmenistan Agreement
- Georgia-Ukraine Agreement
- Georgia-Uzbekistan Agreement
- SICA (observer)
Sample:

- WTO
- GATS
- Agreement on the Application of Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- Organization for Cooperation between Railways (OSJD)
- COTIF Convention
- CIM, CIT Rail Rules
- BIC
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- IMO
- Convention for Safe Containers
- Istanbul Convention
- Customs Convention on Containers
- Hamburg Rules
- IRU
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport
- Transit and Transport Cooperation Agreement (Lapis Lazuli Route Agreement)

European Organizations:
- OSCE
- European Council
- Economic Cooperation and Development
Global Organizations:
- UN
- WB
- WTO
- IMF
- CPLP (observer country)

- Georgia shares borders with Russia, Turkey, Armenia, and Azerbaijan
- The official languages of Georgia are Georgian and Abkhaz
- Capital of Georgia: Tbilisi
- Georgian Currency: Lari
- Georgian Population: 3.7 million people
- Area of Georgia: 69,420 km²
- Independence of Georgia from the Soviet Union: 1991
Religion in Georgia: Most of the Georgian population practices the Eastern Orthodox Christianity (84%).

Georgia belongs to the Orthodox Economic Area.
The Georgian Economy.
- Georgia is a link between Europe and Asia, Georgia offers direct access to the EU, the Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf, and the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) markets (1 billion consumers)
- Georgia is a key location for centralized regional market operations in the Black Sea Region
- Georgia ranks thirteenth out of 183 economies (Doing Business Report, World Bank)
- Previous to the global economic crisis, Georgia experienced a sole Economic growth
- Notwithstanding recent slowdowns in the GDP growth and foreign direct investment caused by the Global financial crisis, a real GDP of Georgia growth rate was 6.4%. This growth has been fuelled by substantial local and foreign direct investment

International Trade of Georgia.
- Total Foreign Trade turnover of Georgia was 6.7 billion dollars
- Georgia is a partner in the TRACECA corridor
Foreign trade regimes of Georgia:
- Free Trade Regime - with the Commonwealth of Independent States countries and Turkey (since 2008)
- Most-favoured-nation Regime (MFN) - with the WTO member countries
- Preferential Regime (Generalized System of Preferences) - with the U.S., Canada, Japan, Switzerland, and Norway
- Preferential Regime (GSP+) - with the EU (7,200 products duty-free)
- Possibility of Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with the EU in the nearest future (European Neighborhood Policy - Black Sea Synergy)
The Georgian National Investment Agency is a sole public agency responsible for promoting and facilitating the foreign direct investment in Georgia.
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page






