Business in Sudan, Khartoum

Foreign Trade and Business in Sudan, Mo Ibrahim, Osama Abdul Latif. Sudanese Economy
- Introduction to the Republic of Sudan (East Africa)
- Sudanese economy
- Economic Profile of the States of Sudan
- International Trade of Sudan
- Port Sudan
- Case Study: Sudanese Businesspeople and Companies;
- Mohamed Ibrahim
- Osama Abdul Latif
- Sudatel Telecommunications
- Investment in Sudan
- Business Opportunities in:
- Agriculture
- Infrastructure
- Services
- Access to the Sudanese market
- Business Plan for Sudan
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in Sudan” are the following:
- To analyze the Sudanese Economy and Global Trade
- To know the business opportunities in Sudan
- To explore the Sudanese trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the Sudanese Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of the Sudanese businesspeople and companies
- To develop a business plan for the Sudanese market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Sudan” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate: African Business, World Trade.

Masters: Business in Africa International Business, Foreign Trade.
Languages:  or
or  Soudan
Soudan  Sudão
Sudão  Sudán.
Sudán.
- Credits of the subject “Doing Business in Sudan”: 3

- Duration: three weeks

Masters adapted to  Sudanese Students.
Sudanese Students.
International Trade and Business in Sudan.
Sudan is the third largest African Country. Sudan is rich in natural resources.




Sudanese Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Sudan and the East African Economic Area
- Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA)
- COMESA-EAC-SADC Agreement
- African Continental Free-Trade Area
- Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD)
- Community of Sahel-Saharan States (CEN-SAD)
- Greater Arab Free-Trade Area (GAFTA)
- Islamic Trade Preferential System
- Islamic Centre for Development of Trade
- Arab Bank for Africa (BADEA)
- Nile Basin Initiative
- Conference on the Great Lakes
- Global System of Trade Preferences
- EU-Sudan
- Sudan is not eligible for the AGOA

- WCO
- BIC (Containers)
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization
- Sudan is not a member of the WTO (in process of accession)

- Afro-Arab Cooperation
- BADEA
- Economic Commission for Western Asia (ESCWA)
- Arab League
- OIC
- Committee for Economic Cooperation
- Islamic Chamber of Commerce
- Islamic Centre for Development of Trade
- Statistical Economic Centre for Islamic Countries
- Summit of South American-Arab Countries
- Asia-Middle East Dialogue

- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Union
- AU Convention on Preventing and Combating Corruption (not signed)
- AUDA-NEPAD
- African Development Bank
- Africa-Asia Partnership
- Africa-Korea Partnership
- Africa-Japan Cooperation
- Africa-India Cooperation

- WB
- WTO
- UN
- IMF
The Republic of the Sudan has a privileged situation in the Red Sea, making the “Sudan Arab” a significant International trade centre between East Africa, the Middle East, Asia, and Europe through the Suez Canal.
- Borders of Sudan: Egypt, Libya, Ethiopia, Eritrea, Chad, the Central African Republic, and South Sudan.
- Sudan shares Maritime borders with Saudi Arabia (Red Sea)
- Area of Sudan: 1,886,068 km²
- Sudan is the third largest African country (after Algeria and the DR Congo)
- Sudan has a population of 39 million people
- Arabic and English are the official languages of Sudan
- Sudan is divided into twenty-five states (wilayat) and 133 districts
- Khartoum is the capital of Sudan
- Omdurman is the second largest city in Sudan
- Largest cities: Khartoum, Port Sudan, El-Obeid and Kassala
- Sudan is a federal republic
- Sudan gained the independence from the UK and Egypt in 1956
- Independence of South Soudan from Sudan in 2011
More information about Sudan (EENI African Business Portal).
Religions in Sudan.
-
Islam is the largest religion in Sudan
- Islam is the official religion in Sudan
- About 97% of the Sudanese population is Sunni Muslim
- The Sudanese legal system is based on the English Common law and the Islamic Sharia
- Fiqh (Islamic Jurisprudence): Maliki
- African Traditional Religions

Sudan belongs to the East African Economic Area.

Economy of Sudan:
- Sudan is the only African-Arab nation where the agricultural balance is positive
- Sudan is rich in natural resources (agricultural and animal production)
- The Sudanese agricultural sector represents 45% of the total economic growth and 80% of the population is related to this sector
- 90% of the Sudanese exports are agricultural products: cotton, Arabic gum, cattle, meat, oilseeds, sorghum, vegetables, and fruits
- The Petroleum extraction is another fundamental pillar of the Sudanese economy
- Currency of Sudan: Sudanese Pound (SDG)


Foreign Trade of Sudan.
- Top Sudanese export products are petroleum, benzene, kerosene, natural gas, gold, sesame, cotton, Arabic gum, sugar, meat, peanuts, leather, molasses, livestock, and animal feed
- Top Sudanese export markets: the Asian markets (79% of the total exports). China is the largest importer of the Sudanese products (60% of the total exports) followed by Singapore, Japan, and South Korea
- Top Sudanese imports: machinery, foodstuffs, manufactured products, transport, chemicals, and textiles
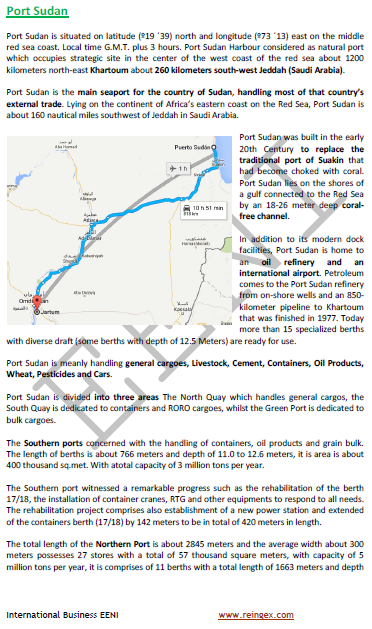
- Port Sudan is the largest foreign trade port
They are significant foreign direct investment opportunities in infrastructure and service sectors: Railway, Roads, internal waterways, Civil Aviation, Air transport, seaports, Shipping, and land transport.


