Business in Malaysia

Foreign Trade and Business in Malaysia - Kuala Lumpur
- Introduction to Malaysia (Southeast Asia)
- Malaysian Political System
- Ethnic Groups
- Bahasa Malayu
- Government policies
- Malaysian Economy
- Infrastructure in Malaysia
- Key sectors in Malaysia:
- Metal
- Electrical and electronics
- Engineering
- Food industry
- Machinery and equipment
- Medical devices
- Petrochemical and polymer
- Pharmaceuticals
- Rubber
- Malaysian Textiles
- Wood
- Business in Kuala Lumpur
- Malaysian International Trade
- Business Environment
- Case Study:
- Tan Sri Mokhtar
- Telekom Malaysia Berhad
- PADINI
- Access to the Malaysian Market
- Business Plan for Malaysia
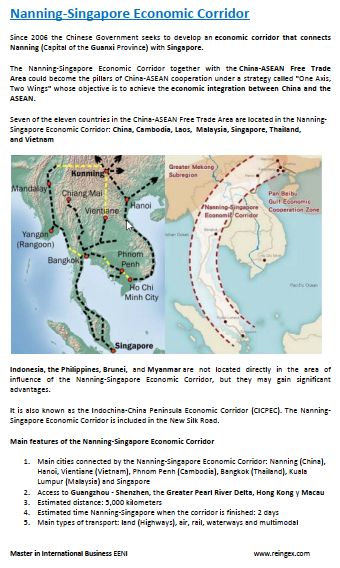
Economic Corridors related to Malaysia
- Nanning-Singapore Corridor
- Access to the East-West Economic Corridor (Myanmar-Thailand-Laos-Vietnam)
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in Malaysia” are the following:
- To analyze the Malaysian Economy and Global Trade
- To know the business opportunities in Malaysia
- To explore the Malaysian trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the Malaysian Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of Malaysian Companies
- To develop a business plan for the Malaysian Market
Global Trade and Business in Malaysia:

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Malaysia” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate: Islamic Business, World Trade.
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
Languages:  or
or  Malasia
Malasia  Malaisie.
Malaisie.
- Credits of the subject “Doing Business in Malaysia”: 2

- Duration: two weeks

Masters adapted to  Malaysian Students.
Malaysian Students.
International Trade and Business in Malaysia.

Malaysian Market Access and Trade Agreements.
- ASEAN
- ASEAN Free-Trade Area
- ASEAN Economic Community
- East ASEAN Growth Area
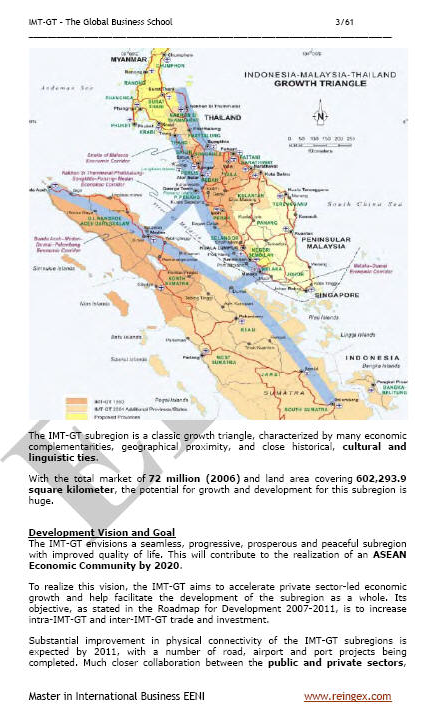
- Indonesia-Malaysia-Thailand Growth Triangle
- Cambodia has trade agreements (as a member of the ASEAN) with China, India, the EU, Japan, Korea, Russia, the U.S., Australia-New Zealand Agreement
- APEC
- Indian-Ocean Rim Association
- Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership
- Islamic Trade Preferential System
- Islamic Centre for Development of Trade
- Regional Comprehensive Economic Association
- Global System of Trade Preferences
- EU-Malaysia Partnership and Cooperation Agreement (negotiation)
- India-Malaysia Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement
- Japan-Malaysia Agreement
- New Zealand-Malaysia Agreement
- Malaysia-Australia Agreement
- Pakistan-Malaysia Agreement
- Malaysia has Trade Agreements with Chile and Jordan


- WTO
- GATS
- Agreement on Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- BIC
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- IMO
- Convention for Safe Containers
- Istanbul Convention
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member


- Islamic Development Bank
- OIC
- Asia-Middle East Dialogue

- ESCAP
- Asian Development Bank
- Boao Forum for Asia
- East Asia-Latin America Cooperation
- Asia Cooperation Dialogue
- Colombo Plan
- Africa-Asia Strategic Partnership

- UN
- WB
- WTO
- IMF
- PEEC
- 50% of the population of Malaysia are Malays. 22% are Chinese
- The Malays originated from the Malayo-Polynesian Ethnic Group
- The official language in Malaysia is Bahasa Malayu.
- English is recognized
- Malaysian Population: 30.8 million people
- Malaysian Area: 329,847 km²
- Malaysian Capital: Kuala Lumpur
- Administrative capital of Malaysia: Putrajaya
- Borders of Malaysia: Thailand, Indonesia, Singapore, and Brunei
- Type of Government: Federal Parliamentary constitutional monarchy
- Yang di-Pertuan of Malaysia: Agong Abdul Halim
- Malaysian independence: 1957 (UK)
Main religion in Malaysia: Sunni Islam (18 million, 63% of the population).
- Islam is the official religion of Malaysia
- Unifying factors among Malays is Islam
- In Malaysia, nearly all Malays are Muslims
- Fiqh (Islamic Jurisprudence): Shafi
- Other religions: Buddhism (20%), Christianity (9%), Hinduism (6%), Confucianism, and Taoism

Malaysia belongs to the Islamic Civilization.
Kuala Lumpur, and its surrounding urban areas, form the most industrialized region in Malaysia.
- The Greater Kuala Lumpur, also known as the Klang Valley, is an urban agglomeration of 7.2 million people
- Kuala Lumpur is poised to become the Global Islamic Financing hub with an increasing the number of financial institutions providing Islamic Financing


Malaysian Economy.
From a nation dependent on agriculture and primary commodities in the 60´s, Malaysia has become an export-driven economy speed up by high-technology, knowledge-based and capital-intensive industries.
- The Malaysian Government policies that sustain a business environment with opportunities for growth and profits have made Malaysia an attractive manufacturing and international trade base in the region
- The private sector in Malaysia has become partners with the public sector in achieving development objectives
- The Malaysian Industrial Development Authority is the first point of contact for the foreign investors who intend to set up projects in manufacturing and services sectors in Malaysia
- Malaysia offers the world it's Multimedia Super-corridor which brings together a legislative framework and a next-generation of telecommunications infrastructure in eco-friendly surroundings to create the best environment for multimedia industries development
- Malaysian currency: The Ringgit (RM) (MYR)
Telekom Malaysia Berhad is the leading integrated information and communications group in Malaysia, offers an exhaustive range of communication services and solutions (broadband, data, and fixed-line). As a market leader in broadband and fixed-line companies, Telekom Malaysia Berhad is driven to deliver value to its stakeholders in a highly competitive environment.
Padini began as a back-end operation in the apparel industry, manufacturing, international trade, and supplying garments in Malaysia for retailers and distributors. It has entered the new millennium as a major force in Malaysia's multibillion textile and garment industry, a brand leader implicated in distribution and retail of its fashion brands through 190 freestanding stores, franchise, and consignment counters.
Port Klang is on the west coast of Peninsular Malaysia, 40 kilometers from the capital Kuala Lumpur. Its proximity to the greater Klang Valley - The commercial and industrial hub of Malaysia as well as Malaysia's most populous region guarantees that the port plays a key position in the economic development of Malaysia.