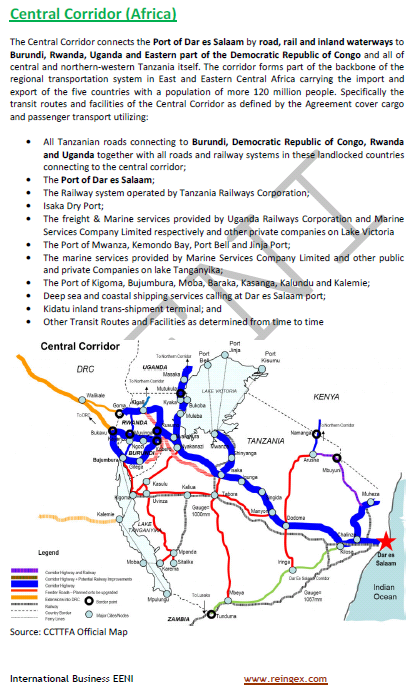
Business in Uganda, Kampala

Uganda (Foreign Trade): an African fastest-growing frontier market. Mbarara, Floriculture
- Introduction to the Republic of Uganda (East Africa)
- Ugandan Economy
- Ugandan Floriculture Sector
- Ugandan information and communications technology sector
- International Trade of Uganda
- Case Study:
- Ugandan flower exporters association
- Rosebud Ltd
- Madhvani Mehta
- AYA
- BIDCO Petroleum Refineries
- Business Opportunities in agribusiness sector: fish, fruits, and vegetables
- Invest in Uganda
- Access to the Ugandan Market
- Business Plan for Uganda
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in Uganda” are the following:
- To analyze the Ugandan Economy and Global Trade
- To know the business opportunities in Uganda
- To explore the Ugandan trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the Ugandan Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of Ugandan Companies
- To develop a business plan for the Ugandan Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Uganda” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate: African Business, World Trade.
Masters: Business in Africa, International Business, Foreign Trade.
Diploma: Business in East Africa.

EENI in Swahili: Shule ya biashara.
Languages:  or
or  Ouganda
Ouganda  Uganda
Uganda  Uganda.
Uganda.
- Credits of the subject “Doing Business in Uganda”: 2

- Duration: two weeks

Masters adapted to  Ugandan Students.
Ugandan Students.
International Trade and Business in Uganda.
Uganda is one of African fastest-growing frontier markets. Open to the foreign investment (FDI).



Ugandan Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Uganda and the East African Economic Area
- Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA)
- COMESA-EAC-SADC Agreement
- African Continental Free-Trade Area
- Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD)
- East African Community (EAC)
- Uganda-EU
- Uganda-US
- AGOA United States
- EAC-U.S. Agreement
- Trade Agreement with India
- Nile Basin Initiative
- Conference on the Great Lakes
- Global System of Trade Preferences among Developing Countries (GSTP) - accession process

- WTO
- Agreement on Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures
- GATS
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- BIC (Containers)
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization
- Istanbul Convention - not a member
- Hamburg Rules (Sea)
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member

- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Union
- AU Convention on Preventing and Combating Corruption
- AUDA-NEPAD
- Africa Agriculture Development Programme
- African Development Bank
- Africa-Asia Partnership
- Africa-India Cooperation
- Africa-BRICS
- Africa-Turkey Partnership
- Africa-Korea Partnership
- Africa-Japan Cooperation
- Africa-South America Summit
- Forum on China-Africa Cooperation

- Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OCI)
- Islamic Chamber of Commerce
- Islamic Centre for Development of Trade
- Committee for Economic Cooperation (OIC-COMCEC)
- Islamic Development Bank
- Afro-Arab Cooperation
- BADEA

- UN
- UNCTAD
- ITC
- UNCITRAL
- WIPO
- WB
- WTO
- IMF
- The Republic of Uganda enjoys a strategic location in East Africa, placed in the African geographical centre
- Uganda shares borders with South Sudan, Kenya, Tanzania, Rwanda, and the DR Congo
- Ugandan main languages are English and Swahili
- Ugandan Population: 42 million people
- Area of Uganda: 236,040 km²
- Capital of Uganda: Kampala (Nansana, Kira, Makindye-Ssabagabo, Mukono)
- The largest Ugandan cities of Uganda are Kampala, Mbarara and Gulu
- Government type: Presidential Republic
- Ugandan independence (UK): October 1962
More information about Uganda (EENI African Business Portal).
religion in Uganda:
- African Traditional Religions
- Christians (84%)
- Catholic (15 million - 42%)
- Protestants
- Anglican Church of Uganda (35.9%)
- Islam (12%, Sunni Muslim)

Uganda belongs to the East African Economic Area.
Ugandan Economy
- The Republic of Uganda is one of the fastest growing economies in Africa
- Uganda is a frontier market in Africa
- Uganda is the African second largest coffee producer
- Multinational companies and international Organizations are being established in Uganda to access to the Ugandan and regional markets
Information and communications technology in Uganda.
- The Ugandan Information and communication technologies (ICT) is a dynamic and vibrant sector; ICT has registered double-digit growth since 2000 and grew by 33%
- The Foreign direct investment flows have been very unyielding; the ICT sector attracted more than 73 million dollars
- Direct employment stands at 6,000 people, while more than 350,000 people are employed indirectly
- The dynamism of the sector is the result of a good legal and regulatory framework for the ICT in Uganda, a stable economic environment and economic reforms implemented since early 1990
- The telecommunications sub-sector, previously dominated by a single national operator, has been liberalized gradually over the past decade

International Trade of Uganda.
- The main export products of the Republic of Uganda are coffee (second leading producer in Africa, 15% of the total exports), tea, and tobacco
- The main exports of non-traditional products are apparel, hides, skins, vanilla, vegetables, fruits, cut flowers, and fish
They are important foreign direct investment opportunities in the agricultural sector, mainly in:
- Fish
- Coffee
- Flowers
- Fruits and Vegetables
- Forestry
The Uganda Export Promotion Board is a Public International Trade Promotion Organization, which works under the Ministry of Tourism, international trade, and Industry.