Course Indian Religions and Business
Course: Indian Religions and Business (Hinduism, Zoroastrianism, Jainism and Sikhism)

India is one of the most religiously diverse countries in the world, with 79.8% Hindus, 14.2% Muslims, 2.3% Christians, and other minorities such as Sikhs, Buddhists, Zoroastrian, and Jains.
Why study the course “Indian Religions and Business?.
This Professional Course is aimed at those executives and enterprises wishing to do business in India (a BRICS Country), a market where the influence of Hinduism (1,210 million Hindus, the third religion in the world) is fundamental, as well as in the countries of the Hindu Economic Area (Mauritius, Nepal, Bhutan...).
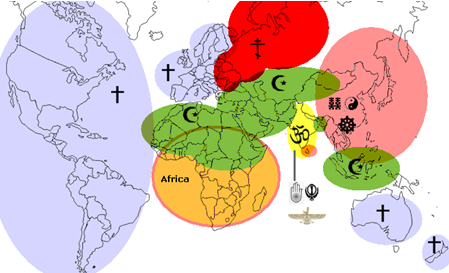
Religious diversity and geopolitical tensions
But it is also necessary to know the influence of Zoroastrianism (the Tata Group controls Western brands such as Jaguar, Land Rover or the Korean Daewo), Jainism (the family Sahu Sain controls the largest Indian communication group), Sikhism (multinationals such as Rotchild or Mastercard have hired Sikh managers because of their rectitude) and Islam (Yusuf Khwaja Hamied is the founder of CIPLA, one of the largest generic pharmaceutical enterprises in the world) in India.

Religions and Global Business -
Religious diversity
The “Professional Course: Indian Religions and Business (Hinduism, Zoroastrianism, Jainism and Sikhism)” (6 ECTS, Online) offered by EENI Global Business School consists of six modules:
- Hinduism and Business
- Jainism and Business
- Sikhism and Business
- Zoroastrianism and Business
- Other religions in India: Islam, Christianity and Buddhism
- Hindu Economic Area
 Enrol / Request for Information
Enrol / Request for Information

- Credits: 6

- Duration: 6 weeks It is recommended to dedicate about twelve hours of study per week following a flexible schedule. It is possible to reduce the duration dedicating more hours a week
- Tuition Fees: EUR 144
- Open Online Enrollment
- Download the syllabus: “Indian Religions and Business” (PDF)
- Hindu Economic Area (PDF)
Languages: 
- Also available in For improving international communication skills, student has free access to the learning materials in these languages (free multilingual training).
 Religiones de India
Religiones de India  Religions de l’Inde
Religions de l’Inde  Religiões da Índia
Religiões da Índia



The goals of the course are the following:
- To learn about pillars of Hinduism, Jainism, Sikhism and Zoroastrianism
- To understand the ethical principles of these religions
- To analyze its influence on business and in the Hindu Economic Area
- To study the profiles of Hindu, Jain, Sikhs and Zoroastrian entrepreneurs
- To define the characteristics of the Hindu Economic Area
- To analyze the economic and political relations of Hindu Civilization with other civilizations (Western, Sinic, Buddhist, Islamic and African)
- To understand the economic integration process and main organizations related to the Hindu Economic Area
- To learn about economic profile of the countries of influence of Hindu Civilization

This course contains exercises that are evaluated, which the student must work out and pass to obtain the Diploma of the “Professional Course Indian Religions and Business (Hinduism, Zoroastrianism, Jainism and Sikhism)” granted by EENI Global Business School.
This course belongs to the following Higher Education Programs offered by EENI:
Bhagavad Gita Courses, Realization of the Gita
Masters: International Business, Religions and Business.

Doctorate: Global Ethics, Religions, and International Business.
Modules
“Truth is one; the wise call it by different names.” (Rig Veda).
1- Hinduism (Vedanta), Ethics and Business:
- Introduction to Hinduism “Sanatana Dharma” Vedanta: the third religion in the world
- Sacred books of Hinduism. Analysis of the Bhagavad Gita according to Gandhi
- The four paths to God. The Paths of Yoga
- Main traditions of Hinduism (Sampradaya): Shivaism, Shaktism, Vaisnavism and Smartism
- The pillars of Hinduism: interreligious tolerance, body and Atman, Samsara, Bhagavan (God, Parabrahman...) Pervades all Things
- Ethical principles of Hinduism:
- Ahimsa (Non-violence)
- Detachment from the results of actions
- Truth (Satya)
- Do not steal
- Sexual moderation
- Renewal of Hinduism: Sri Ramakrishna (Harmony of Religions), Swami Vivekananda and Mahatma Gandhi
- Hinduism in Nepal, Bhutan, Mauritius, Bangladesh (15 million), Indonesia (Bali 3.3 million), Guyana and Fiji
- The expansion of Hinduism in Africa
- Influence of Hinduism on business
Hindu Businesspeople (Hinduism)
- Kumar Birla: president of the Aditya Birla Group
- Senapathy Gopalakrishnan: co-president of Infosys
- Shri Mukesh Ambani: director of Reliance Industries (3% of Indian GDP)
- Srichand P Hinduja: president of the Hinduja Group (one of the largest diversified groups in the world)
- Kiran Mazumdar: founder of BIOCOM, the largest biotechnology company in India (Bharat)

“When the kindness declines
When the wickedness increases
When the purpose of the life is forgotten.
I will manifest, I will return.
To pronounce the sacred; to destroy the sin of the sinner, to re-establish the way of the principles”
IV- Yoga of Knowledge and Renunciation of Action 7-8
Ahimsa (Non-violence): “Any living organism deserves our respect.”
- Introduction to Jain Dharma (Jainism)
- SHANTINATHA CHARITHRA (Jain scriptures)
- The importance of Mahavira in Jainism
- Jain schools: Digambaras and Svetambaras
- Fundamentals of Jainism doctrine and philosophy (Tattvas)
- Principles of Jainism ethics
- The twelve Jain vows
- The five pillars of Jainism
- Non-violence (Ahimsa)
- Respect for all life
- Relationships between Jainism and Hinduism
- Jainism and business
Jain Businessmen
- Sahu Jain: The Times Group, belonging to the Jain family Sahu Jain, is the largest communication company in India (Bharat)
- Ajit Gulabchand: President of one of the largest Indian construction companies
- Gautam Adani: President of the Adani Group
- Bhavarlal Jain: Founder of Jain Irrigation Systems

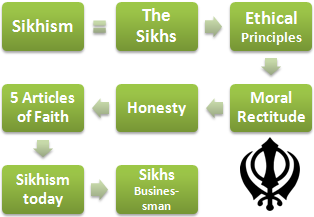
Presence of Sikh managers in multinationals due to their moral rectitude and honesty
- Introduction to Sikh Dharam (Sikhism): 26 million Sikhs around the world
- The importance of Guru Nanak
- Relationship of Sikhism with Hinduism and Islam
- Ethical principles of Sikhs
- Moral rectitude and honesty
- The five articles of faith (five K) of Sikhism
- Case study:
- Manmohan Singh (former Indian Prime Minister)
- Narinder Singh (inventor of the optical fiber)
Sikh Businessmen
- Malvinder and Shivinder Singh: Founders of one of the largest healthcare providers in Asia-Pacific
- Ajaypal Singh Banga: CEO of MasterCard
- Hardeep Singh: founder of Tulip Telecom
- Jogishwar Singh: managing director of the Rothschild Group

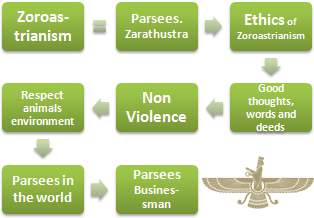
“Good Thoughts, Words, and Deeds.”
- Introduction to Zoroastrianism
- The Prophet of Zoroastrianism: Zarathustra
- Principles of the Zoroastrian ethics
- Non-violence
- Respect towards animals and the environment
- The three H (Good thoughts, words, and deeds) and business strategy
- Zoroastrianism and business
Zoroastrian Businessmen
- TATA Group: one of the largest enterprises in the world (3.2% of Indian GDP)
- Cyrus S. Poonawalla: founder of one of the largest pharmaceutical enterprises in the world
- Adi Godrej: president of the Godrej Group (one of the main Indian conglomerates)
- Musli Wadia: President of the Wadia Group, one of the oldest conglomerates in India (Bharat)
5- Other religions in India: Islam, Christianity and Buddhism
1- Islam in India (the second religion in India).
- Influence of Islam on Hindu Civilization
- Indian Muslim businessmen:
- Azim Premji: director of Wipro (a global information technology company), he is one of twenty-five people who “have drastically changed the way we live, work or think”
- Yusuf Hamied: founder of CIPLA, one of the largest generic pharmaceutical enterprises in the world
Tensions between Hindus and Muslims in India pose market risks. In 2022, Walmart faced boycotts in Uttar Pradesh for sourcing from Muslim suppliers, affecting 8% of its regional sales (Bloomberg).
Kashmir, a disputed region between India, Pakistan, and China, is a flashpoint where religious diversity intersects with geopolitical tensions. Jammu and Kashmir's population is predominantly Muslim (68.3%), but it is governed by India, a Hindu-majority state, leading to historical conflicts.
2- Christianity and Buddhism in India.

- The religions of India and their relationship with Hindu Civilization
- Hindu Economic Area
- India (Bharat) as a central state of Hindu Civilization
- Countries of the area of influence of Hindu Civilization
- The expansion of Hindu Civilization in East Africa
- Kenyan entrepreneurs of Hindu origin: Naushad N. Merali and Bhimji Depar Shah
- The Diaspora of Hindu Civilization
- Hindu businessmen
- Economic integration of the Hindu Economic Area (economic
organizations, free trade agreements...)
- South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation: India, Afghanistan, Bangladesh, the Maldives, Pakistan and Sri Lanka
- Bay of Bengal Initiative: India, Myanmar, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka and Thailand
- Asian Clearing Union: India, Bangladesh, Iran, Myanmar, the Maldives, Pakistan and Sri Lanka
- SASEC: India, Bangladesh, the Maldives and Sri Lanka
- Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement: India, Bangladesh, China, Korea, Laos, Sri Lanka and Mongolia
- Africa-India Cooperation
- Africa-BRICS Cooperation
- India is one of the BRICS Countries
- Bilateral agreements of India: Sri Lanka, Thailand, Singapore, Chile, MERCOSUR, Andean Community, South Korea, the EU, New Zealand, Indonesia, GCC, Canada, Australia, EFTA, SACU, ASEAN
- Political-economic interactions with other civilizations
“Thus I have exposed the most secret of all knowledge, meditate on it fully, and then do as you want” Bhagavad Gita, XVIII- Yoga of Liberation through Renunciation-63.
Religions of India: Hinduism, Zoroastrianism, Jainism and Sikhism. Interreligious tolerance
India is one of the most tolerant countries to other religions. Hinduism is probably the most tolerant religion with others, as seen in the history of India in the last 2,500 years.
Hinduism has lived in peace with Parsees, Sikhs, Muslims, Christians, Buddhists, and Jain.
The Chapter IV of the Bhagavad Gita begins with one of the most beautiful and transcendental verses of Hinduism, which appreciate the tolerance of Hinduism to the other religions.
The most universal of these verses is the implicit acceptance of other prophets of the other religions. Many Hindus believe on the holiness of Jesus, Rama, Sri Krishna, Buddha, Guru Nanak, or Zarathustra.
This principle of universal tolerance (Harmony of Religions) is one of the greatest contributions of Hinduism to global ethics, furthermore to the principles of truthfulness, detachment, and non-violence (Ahimsa).
Hinduism is a major religion in India. 80.5% of Indian Population practices Hinduism, 960 millions of followers (Total population: 1,210 million people).
Percentage of the population by Indian Religions.
- Hinduism 80.46%
- Muslims 13.43%
- Christians 2.34% (25 million)
- Sikhs 1.87%
- Buddhists 0.77%
- Others 0.72%
- Jains 0.41%
In India, there are some 2 million Baha'i Faith, 7.5 million Methodists and 2.4 million Baptists.
The Catholic Church Siro-Malabar (Eastern Catholic Churches) has 4.6 million.
After India, Hinduism is important in Nepal (23 million), Bangladesh (15 million), Indonesia -island of Bali (3.3 million), Mauritius, Guyana, Fiji, or Bhutan.
A perfect example of Hindu tolerance is that the former President of India, Manmohan Singh is Sikh.
Sikh population represents less than 2% of Indian Population!
- Yoga of the Threefold Faith of the Bhagavad Gita
Below; we show the ministers of his Government. As we can even observe the majority belongs to Hinduism but there are also Sikhs, Muslims, Christians, Buddhists, Atheists.
- Shri A. K. Antony. Minister of Defense. He was born into a Syrian Catholic family, now declared atheist. It is also stated devotee of Mata Amritanandamayi
- Shri Sharad Pawar. Minister of Agriculture. Hinduism.
- Shri P. Chidambaram. Minister of Finance. Hinduism.
- Shri Ghulam Nabi Azad. Minister of Health and Family Welfare. Muslim.
- Shri Sushil Kumar Shinde. Minister of Interior. Secularism (Nehru)
- Shri M. Veerappa Moily. Minister of Petroleum and Natural Gas.
- PhD Farooq Abdullah. Minister of New and Renewable Energy. Muslim.
- Shri S. Jaipal Reddy. Minister of Science and Technology. Minister of Earth Sciences. Hinduism.
- Shri Sis Ram Ola. Minister of Labour and Employment
- Shri Kamal Nath. Minister of Urban Development. Minister of Parliamentary Affairs. Hinduism.
- Shri Ajit Singh. Civil Aviation Minister. Sikh
- Shri Vayalar Ravi. Minister of Indian Affairs abroad. Hinduism.
- Shri Mallikarjun Kharge. Minister of Railways. Buddhist.
- Shri Oscar Fernandes. Minister of Road transport and Highways.
Catholic Christian.
- Shri Kapil Sibal. Minister of Communications and information Technology. Hinduism.
- Shri Anand Sharma. Minister of Trade and Industry. Hinduism.
- Kumari Selja. Minister of Social Justice and Empowerment. Hinduism.
- PhD Girija Vyas. Minister for Housing and Urban Poverty Alleviation.
Hinduism.
- Shri K. G. Vasan. Minister of
Shipping
- Shri Praful Patel. Minister of Heavy Industries and Public Enterprises. Hinduism.
- Shriprakash Shri Jaiswal. Coal Minister
- Shri Salman Khursheed. Minister of foreign Affairs. Muslim.
- Shri V. Kishore Chandra Deo. Minister of Tribal Affairs. Minister of Panchayati Raj. Hinduism.
- Shri Beni Prasad Verma. Steel Minister. Hinduism.
- Shri Jairam Ramesh. Minister of Rural Development. Hinduism.
- Shri K. Rahman Khan. Minister of Minority Affairs. Muslim.
- Shri Dinsha J. Patel. Minister of Mines. Hinduism.
- Shri M. M. Pallam Raju. Minister of Human Resource Development.
Hinduism.
- Shri Harish Rawat. Minister of Water Resources. Hinduism.
- Smt. Chandresh Kumari Katoch. Minister of Culture. Hinduism.
- PhD Kavuru Sambasiva Rao. Minister of textiles.
(Note: If is not specified a religion, is that the Minister has not publicly stated their religion).
Why study Religions and Business?.
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page










 WhatsApp
WhatsApp


