Business in Sri Lanka, Colombo, Foreign Trade
Sri Lankan Economy, Logistics and International Trade. Agreement with India. Buddhism
The Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka (formerly Ceylon before 1972) is located in South Asia, about thirty-one kilometers from the Southern coast of India.
Sri Lanka has a relatively modern industrial economy and one of the highest levels of per capita income in the South Asian region
Sri Lanka has positioned as a regional logistics centre and International Trade hub
Sri Lanka is known worldwide for tea, coffee, coconuts, and rubber exports
- Introduction to the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka (Asia)
- Doing Business in Colombo
- Sri Lankan Economy
- International Trade of Sri Lanka
- Trade Relations Sri Lanka-India
- Transport and Logistics
- Investment in Sri Lanka
- Case Study: Sri Lankan enterprises
- Brandix Lanka
- Sri Lanka Telecom
- Access to the Sri Lankan Market
- Business Plan for Sri Lanka


The educational aims of the Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka” are:
- To analyze the Sri Lankan Economy, Logistics and Global Trade
- To conduct research on business opportunities in the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka
- To explore the Sri Lankan trade relations with the student's country
- To learn about Sri Lankan Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of Sri Lankan companies
- To develop a business plan for the Sri Lankan Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Sri Lanka” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.


Masters adapted to the  Sri Lankan Students.
Sri Lankan Students.
Languages:  (
( Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka  Sri Lanka).
Sri Lanka).
- Subject Credits “Doing Business in Sri Lanka”: 2

International Trade, Logistics and Business in Sri Lanka.

Sri Lankan Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Sri Lanka and the Buddhist Economic Area
- South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation
- Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement
- Bay of Bengal Initiative
- South Asia Economic Cooperation (SASEC)
- Indian-Ocean Rim Association
- Asian Clearing Union
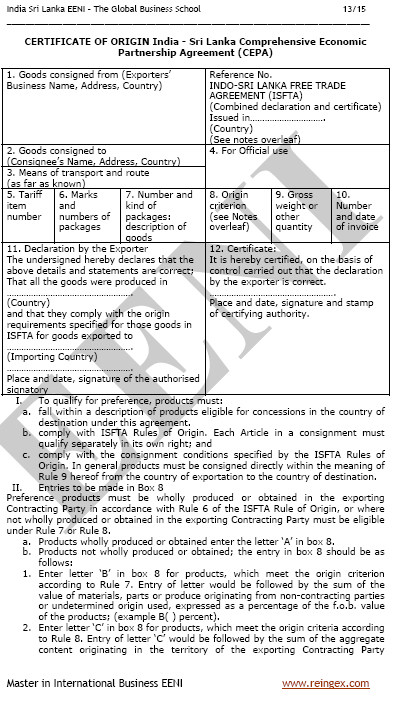
- India-Sri Lanka Agreement
- Pakistan-Sri Lanka Agreement
- Global System of Trade Preferences
- SCO (Dialogue Partner)

- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- Agreement on Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures
- Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS)
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Kyoto Convention
- BIC
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization
- Istanbul Convention - not a member
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member

- Asian Development Bank
- Boao Forum for Asia
- Asia Cooperation Dialogue
- Economic Commission for Asia (ESCAP)
- Colombo Plan
- Africa-Asia Partnership
- Asia-Middle East Dialogue

- Commonwealth
- United Nations
- World Bank
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- International Monetary Fund
- Population of Sri Lanka: 21 million people
- Sri Lanka is in 102 position out of 182 countries in the Human Development Indicators, ahead of Argentina (105), Vietnam (116th), Indonesia (111), India (134), Pakistan (141), and Bangladesh (146)
- Sinhalese constitute 74% of the population
- The two official languages of Sri Lanka are Sinhala and Tamil
- Capital of Sri Lanka: Sri Jayawardenapura Kotte
- Sri Lankan main city: Colombo
- Sri Lankan Area: 65,610 km²
- Sri Lanka is a Parliamentary Republic
- Independence of Sri Lanka from the United Kingdom: 1948
- Sri Lankan currency: Sri Lanka Rupee
- Maritime borders of Sri Lanka: Bharat (India) and the Maldives
Religions in Sri Lanka:
- Sri Lanka is a multi-ethnic and multi-religious nation
- 70% of the Sri Lankans belongs to Theravada Buddhism
- Sri Lanka has been a Buddhist religion and culture centre from ancient times
- Hinduism: 15% of the population
- Catholic Christians (1.2 million)
Sri Lanka belongs to Buddhist Economic Area
Sri Lankan Economy
- The Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka has a strategic location in Southern Asia, in the centre of one of the principal marine routes between Europe and the Far East: The Indian Ocean
- The services sector of Sri Lanka generates 60% of GDP
- Main sectors of the Sri Lankan economy are telecommunications, trade, logistics and transport, and financial services
- Sri Lanka Multimodal Transport Project
- Brandix is the leading import apparel producer in Sri Lanka
- Sri Lanka Telecom is one of most valuable blue chip enterprises in Sri Lanka


International Trade of Sri Lanka.
- The vision of the former President Rajapaksa (Mahinda Chintana) wishes to open the economy to Globalization process, attracting Foreign Direct Investment and establishing Free Trade Agreements with the strategic partners
- Top Sri Lankan exports products are garments, tea, rubber products, coffee, jewelry and gems, refined petroleum, and coconuts
- Top Sri Lankan export markets are the United States, the UK, and India
- The largest suppliers of Sri Lanka are India, Singapore, Hong Kong, Iran, Malaysia, Japan, the UK, the Emirates, Belgium, Indonesia, South Korea, and the United States
Free trade zones in Sri Lanka are one of the pillars of economic development and Foreign Direct Investment source (FDI).
- Malaysia is the largest investor
- Other notable investors in Sri Lanka are the UK, Singapore, and Hong Kong
- 50% of all the Indian investments in the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation countries are invested in Sri Lanka
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp