Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement (APTA China)
Tariffs Concessions, Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement (APTA) India, South Korea
The objective of the Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement (APTA) is to set-up a preferential tariff arrangement to promote intra-regional trade through exchange of reciprocally agreed concessions among the member countries of the Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement: Bangladesh, China, Bharat (India), Korea, Laos, Mongolia, and Sri Lanka.

The Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement is the only working agreement involving China and India, two of the fastest growing emerging markets with 2.4 billion people.
- Introduction to the Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement (APTA)
- Economic and Trade profile of APTA members: Bangladesh, China, India, South Korea, Laos, Mongolia, and Sri Lanka
- Free Trade Agreement and Economic Integration of the Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement (APTA)
- Tariffs Concessions under APTA Agreement
- Rules of Origin of the Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement
- Performance Indicators for the members of the Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement

The Subject “Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement (APTA)” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.


Languages:  Also available in
Also available in  Acuerdo comercial Asia-Pacífico
Acuerdo comercial Asia-Pacífico  Accord commercial Asie-Pacifique APTA
Accord commercial Asie-Pacifique APTA  Acordo Comercial Ásia-Pacífico (APTA).
Acordo Comercial Ásia-Pacífico (APTA).


Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement (APTA).
Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement (APTA):
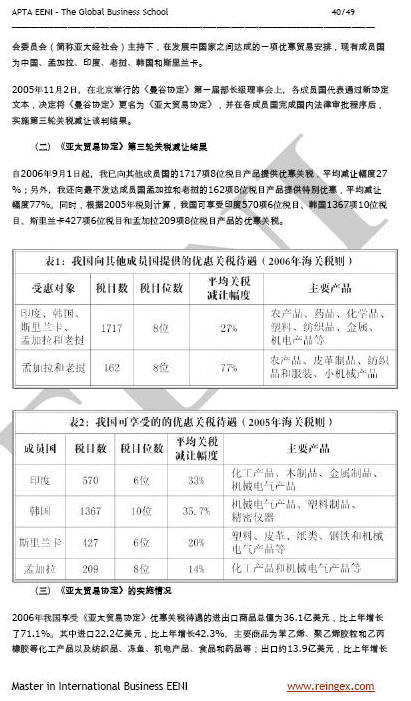
- The member economies of the Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement represent 11% of global trade
- Near 30% of imports from Bangladesh are from the other members of the Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement
- 23% of exports from the Republic of Korea are exported to other APTA members
- Foreign Trade between China and India reached an amazing average annual growth rate of 34% over the past decade
The members of the Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement (APTA) furthermore committed to expanding their cooperation in Foreign Direct Investment and Trade Facilitation. A framework agreement on Trade in Services was also finalized and will be signed.
The Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement (APTA) (formerly known as Bangkok Agreement) was signed on 1975 as an initiative of the UN Economic and Social Commission for Asia (ESCAP).

Religions and Global Business -
Religious diversity
The Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement (APTA) consists of one Muslim country (Bangladesh), one Hindu (India) and two Buddhists Countries (Laos and Sri Lanka). China and Korea can be considered multi-religious countries (Buddhism, Confucianism, and Taoism).
亚太贸易协定.
The Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement belongs to:
- Hindu Economic Area
- Central Eurasian Economic Area of Islamic Civilization
- Buddhist Civilization

Economic Corridors related to APTA Region:
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page










 WhatsApp
WhatsApp