Business in Bhutan, Thimphu
Bhutanese Economy. Gross National Happiness. Foreign Trade of Bhutan
Bhutan has one of the highest per capita incomes in South Asia (1,321 dollars).
- Bhutanese Mineral resources: coal, slate, dolomite, gypsum, and graphite
- Huge hydroelectricity potential
- The Gross National Happiness was founded by His Majesty (the third Druk Gyalpo Jigme Dorji Wangchuck)
- Introduction to the Kingdom of Bhutan
- Bhutanese economy
- Bhutanese industry
- Case Study: Gross National Happiness Index
- Doing Business in Thimphu
- Foreign Trade of Bhutan
- Case Study: Tashi Group
- Transport and Logistics
- Access to the Bhutanese market
- Business Plan for Bhutan


The purposes of the subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Bhutan” are:
- To analyze the Bhutanese Economy, Logistics and Global Trade
- To conduct research on business opportunities in Bhutan
- To explore the Bhutanese trade relations with the student's country
- To learn about Bhutanese Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of Bhutanese companies
- To develop a business plan for the Bhutanese market

The Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Bhutan” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Course: Hinduism and Business.

Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.


Masters adapted to  Bhutanese Students.
Bhutanese Students.
- Subject Credits “Doing Business in Bhutan”: 1

International Trade, Logistics and Business in Bhutan

Bhutanese Trade Agreements and Preferential Access.
- Bhutan and the Buddhist Economic Area / Hindu Economic Area
- India-Bhutan Agreement
- Agreement on Trade, Commerce and Transit with India
- Bangladesh-Bhutan Agreement
- Asian Clearing Union (ACU)
- South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation
- South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA)
- Bay of Bengal Initiative
- Generalized System of Preferences (EU)
- South Asia Economic Cooperation (SASEC)

- Asia-Middle East Dialogue
- Asian Development Bank
- Economic Commission for Asia (ESCAP)
- Colombo Plan
- Asia Cooperation Dialogue
- Africa-Asia Partnership

- United Nations
- World Bank
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- International Monetary Fund
- Bhutan is eligible for the European Investment Bank
- World Customs Organization (WCO)

- WTO (in process of accession)
- World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Kyoto Convention (Containers)
The Kingdom of Bhutan.
- Population of Bhutan: 768,198 people
- Bhutan is one of the smallest countries (38,394 km²)
- Bhutan is a landlocked country
- Bhutanese Frontiers: China (Tibet) and Bharat (India) (Sikkim, West Bengal, Assam, and Arunachal Pradesh)
- Official language of Bhutan: Dzongkha
- Main Bhutanese ethnic group: Dzongs
- Type of Government: Unitary Parliamentary constitutional monarchy
- King of Bhutan: Jigme Khesar Namgyel Wangchuck
- The capital of Bhutan is Thimphu (45% of the GNP of the country)
- Bhutanese Internet TLD: bt
Buddhism (Vajrayana) is the main religion in Bhutan
- Hinduism is the second religion (30% of the Bhutanese population)


Religions and Global Business -
Religious diversity
Bhutan belongs to Buddhist and Hindu Economic Area.
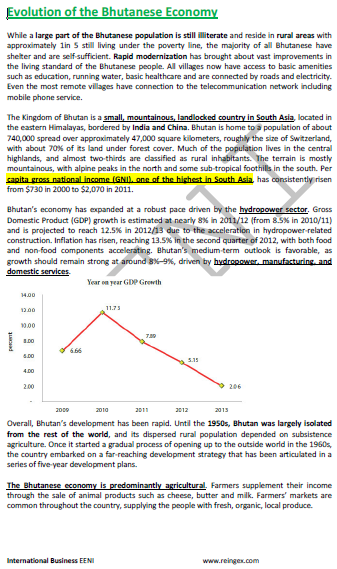
Bhutanese Economy.
- Main sectors of the economy of Bhutan are agriculture, cottage industries, and tourism
- Main Bhutanese crops are rice, wheat, maize, apples, and oranges
- Industrial sector of Bhutan (mainly located in Pasakha): cement, steel, breweries (Coca-Cola), and wood based industries
- Currency of Bhutan: Bhutanese ngultrum (BTN) and Indian Rupee (INR)

Foreign Trade and Business in Bhutan

International Trade of Bhutan.
- The largest Bhutanese export markets are India, Bangladesh, the United States, the Netherlands, Germany, Singapore, and Nepal
- Main imports are oils, parts, motors, wood charcoal, rice, and coke
- Main providers of Bhutan are India, China, Thailand, Singapore, Sweden, Saudi Arabia, and Malaysia

(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp
 (
(

