Russian Economy

Russian Economy (industry, energy, banking, transportation, customs) and foreign trade
- Introduction to the Russian economy
- Historical background
- Russia and the BRICS Countries
- Russian Privatization Process
- Russian Economy today
- Russian Natural Resources
- Agriculture Sector in Russia
- Russian Energy Sector
- International Trade of Russia
- Russian Customs
- Customs Union among Russia, Belarus, and Kazakhstan
- International Relations of Russia: APEC, Eurasian Economic Union, Commonwealth of Independent States, SCO, and Organization of the Black Sea Economic Cooperation
- Trade Agreements with Armenia and Serbia
- Case Study:
- Automotive Industry in Russia
- Gas Group
Russian Businessman:



The Subject “Russian Economy and Foreign Trade” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Course: Orthodoxy and Business.

Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
Ports of Russia, Leo Tolstoy...
- Credits of the Subject “Russian Economy”: 2

- Duration: two weeks

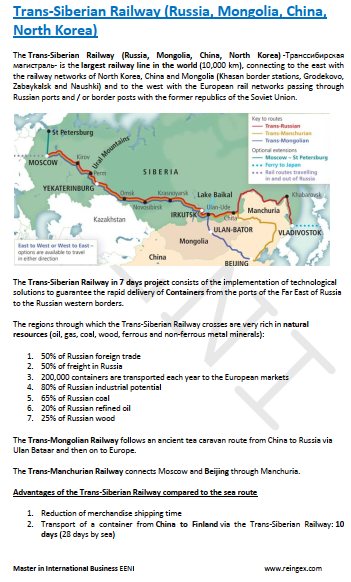
Russian Economy.
Russian Economy.
- Russia is one of the BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, South Africa) markets
- The Russian Federation (Europe) has one of the most dynamically developing and attractive economies in the World
- Russian GDP (nominal): 2.118 billion dollars (the eighth
largest economy in the World)
- Agriculture 2.2%
- Industry: 36.8%
- Services: 61%
- GDP (purchasing power parity): 3.558 billion dollars (the sixth worldwide)
- Russian GDP per capita: $ 24,370 (PPP)
- Inflation in Russia: 15%
- The Russian Federation is the biggest nation in the World
- The Russian Federation is a middle revenue nation with a population of 146 million people
- Russia is one of the richest countries in raw materials in the World, many of which are important inputs for an industrial economy
- Russia accounts for 20% of petroleum and natural gas production in the World (with large reserves)
- Petroleum production in Russia is expected to grow 10.7% yearly to 646 billion cubic meters
- Russia holds the second largest coal reserves in the World
Russia belongs to the Orthodox Economic Area.
Foreign companies or Businessman, wishing to do business in Russia, will study the Russian mentality. They should take into consideration the Russian idiosyncrasy, and learn to understand the Russian people.
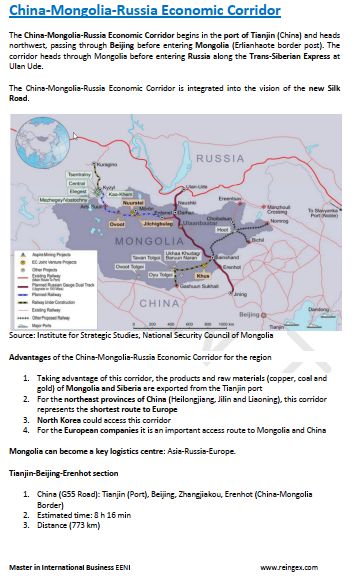

Foreign Trade of Russia.
- Russia can be a great platform to access the former Soviet Republics of Central Asia (Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan)
- Russia is a natural link between Europe and Asia even borders the American continent
- Russian Exports: 350 billion dollars
- Top Russian export markets: Netherlands, Italy, Germany, Turkey, Ukraine, China, and Poland
- Russian Imports: 230 billion dollars
- Russia's main suppliers: China, Germany, Japan, Ukraine, and the U.S.
- The Russian Federation is overly dependent on raw materials exports: petroleum, gas, and metals accounting for 80% of its exports, being too sensitive to international fluctuations in these commodities prices
- Among the largest importers of the Russian gas are Germany, Turkey, Italy, and France
- Russia is a member of the UN (permanent member of the Security Council), Commonwealth of Independent States, Eurasian Economic Community, Shanghai Cooperation Organization, and APEC
- The Customs Union between Russia, Kazakhstan, and Belarus came into force 2010 with the objective to foster the economic integration and remove all the customs borders between Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Russia (Union State Russia-Belarus)

(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page




 (
(
