Business in Japan

Foreign Trade and Business in Japan. Tokyo, Osaka
- Introduction to Japan
- Japanese economy
- Economic Profile of the Japanese regions
- International Trade of Japan
- A gateway to the Asian market
- Business in Tokyo and Osaka
- Tips for penetrating the Japanese market
- Investing in Japan
- Case Study:
- Japan's retail market
- GOTO INC
- Kazuo Inamori. Founder and Director of Japan Airlines and Buddhist monk
- Shinichi Inoue (Buddhist Economics)
- Tokyo International Conference on African Development
- Access to the Japanese market
- Business Plan for Japan
- Port of Tokyo
- Asia-Africa Corridor
- Access to the Trans-Siberian Railway (Russia, Mongolia, China, North Korea)
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in Japan” are the following:
- To analyze the Japanese Economy and Global Trade
- To know the business opportunities in Japan
- To explore the Japanese trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the Japanese Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of Japanese businesspeople and companies
- To develop a business plan for the Japanese market
Global Trade and Business in Japan:


The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Japan” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
Course: Taoism, Confucianism & Business.
- Credits of the subject “Doing Business in Japan”: 2

- Duration: two weeks
Masters adapted to  Japanese Students.
Japanese Students.
International Trade and Business in Japan.
Japan is one of the largest markets for the luxury products in the World.

Japanese Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Japan and the Buddhist Economic Area
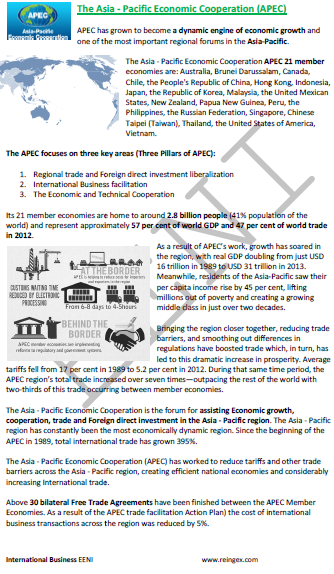
- APEC
- Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership
- Regional Comprehensive Economic Association
- Brunei-Japan Agreement
- Singapore-Japan Agreement
- Japan-Indonesia Agreement
- Japan-Thailand Agreement
- Japan-Malaysia Agreement
- UK-Japan Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA)
- Japan-Australia Agreement
- Japan-Vietnam Agreement
- Japan-Switzerland Agreement
- Mexico-Japan Agreement
- Chile-Japan Strategic Economic Agreement
- EU-Japan Agreement
- ASEAN-Japan Agreement
- ASEAN Plus Three
- Japanese Bilateral Economic partnership agreements: the Philippines, Mongolia, and India
- IORA (dialogue partner)
- Japan is an observer country:
- ALADI
- SAARC
- SICA

- WTO
- GATS
- Agreement on the Application of Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- Kyoto Convention
- COTIF Convention (Rail)
- BIC (Containers)
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- IMO
- ICS
- International Road Transport Union (IRU)
- TIR Convention - not a member
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member

Asian Trade Organizations. Japan is a member of:
- ESCAP
- Colombo Plan
- Asian Development Bank
- Boao Forum for Asia
- Asia Cooperation Dialogue
- Asia-Middle East Dialogue
- FEALAC
Global Organizations:
- OECD
- OECD anti-corruption measures
- ECLAC
- Inter-American Development Bank
- African Development Bank
- UN
- WB
- WTO
- IMF
- PEEC
- CPLP (observer country)

The State of Japan (Asia).
- Borders of Japan: China, North Korea, South Korea, and Russia
- Capital of Japan: Tokyo
- Language: Japanese
- Type of Government: Constitutional monarchy
- Japanese Area: 377,835 km²
- Japanese Population: 127 million people. Most Japanese reside in densely populated urban areas
- Japanese Currency: Yen (JPY)
Religions in Japan:
- Zen Buddhism (70% of the Japanese population)
- Shinto
- Taoism
- Confucianism
- Christianity (1 million)


Japan belongs to the Buddhist Civilization / Sinic Civilization

The Japanese economy is the third largest market economy in the World. The Japanese brands like Fujifilm, Honda, Yamaha, Toyota, Sony, or Panasonic are world-famous.
Japanese Economy.
- The manufacturing sector is one of the Japanese economy strengths
- Japan has few natural resources
- One of the most promising fields is robotics, in which the Japanese technology leads the world
- One common pattern for the Japanese companies is to import raw materials and then process them to make finished products, which are distributed in the Japanese market or exported abroad
- Furthermore, to possessing a high purchasing power, the Japanese consumers are early adopters and move quickly to stay on the cutting edge of the latest technologies
- Many global products have originated in Japan or have gained a competitive advantage by being developed in Japan
- Japan is often seen as a splendid test market for new global products and services introduction
- Japanese nominal GDP: 4.5 billion USD
- Agriculture: 1.6% of the Japanese GDP
- Industry: 25.3%
- Services: 73.1%
- Japanese main products are vehicles, electronic products, transport equipment, chemicals, steel, machine tools, food products, and pharmaceuticals
- Japan is a member of the Economic Cooperation Forum Asia-Pacific (APEC)
Japanese Retail Market.
- Japan boasts the second largest retail market in the World (USD 1,124 billion)
- Furthermore, to its size, the enormous influence of Japanese retail industry attracts global attention as being the origin of many Asian trends
Tokyo is the centre of one of the largest metropolitan regions in the World and a hub of dynamic economic and consumer activity.
- 50% of the publicly listed companies in Japan are located in Tokyo, along with a high number of venture capital firms and Small and Medium Enterprises
- 360,000 foreign people are living in Tokyo
- The Port of Tokyo handles fifteen container berths, including the piers at Oi and Aomi, which can handle 50,000-ton, large container vessels
Osaka, being situated practically in the centre of Japan, is the largest city in western part of Japan and one of the largest urban conurbations as well.
- The Osaka Port is one of the Japanese leading ports
- The Kinki region, with Osaka at its centre, boasts an economy larger than those of Australia and the Netherlands and haves immense potential for such reasons as its strength in international trade with Asia and other areas
Economic profile of the Japanese regions:
- Hokkaido. Fishing and forestry are important parts of Hokkaido's agriculture and underlie much of the island's industrial activity, including the food processing, woodworking, pulp, and paper industries. The capital is Sapporo
- Tohoku. The Tohoku area is primarily agricultural
- Kanto. This region, which includes key cities as Tokyo, Yokohama, Kawasaki, Saitama, and Chiba, is the most populous region of Japan. The hub of the region, the Tokyo-Yokohama district, is the core of the Japanese international trade and industry
- Chubu. It has three industrial areas: The Chukyo Industrial Zone, which is home to the main facility of Toyota Motors; the Tokai Industrial Region, where Yamaha is based; and the Hokuriku Industrial Region
- Kinki Kansai. Situated in west-central Honshu, the Kinki region is the second largest area regarding the industry in Japan. The ancient capital of Kyoto is in Kinki
- Chugoku (Hiroshima and Nagasaki)
- Shikoku is the smallest of Japan's four main islands
- Kyushu (Okinawa). The Kita Kyushu Industrial Zone contains a concentration of heavy and chemical industry


- The main exported products by Japan are cars, electronics, and computers
- The largest Japanese trading partner is the U.S., representing more than 25% of all the Japanese exports
- The largest Japanese export markets include Taiwan, Hong Kong, South Korea, China, and Singapore
- The largest Japanese imports are raw materials such as petroleum, food, and wood products
- The main Japanese suppliers are the U.S., China, Indonesia, South Korea, and Australia
Foreign direct investment in Japan.
- Japanese attractiveness as a destination for the foreign direct investment is increasing significantly; the Japanese Government has made significant changes to get a more transparent investment environment
- JETRO (the Japan External Trade Organization) conducted a series of surveys of foreign companies based in Japan and the results show that investment problems in Japan (high costs in the form of doing business, exclusivity, and tradition in the form to conduct international business transactions, complexity of administrative procedures) were reduced significantly compared to ten years ago




 or
or 
