Business in North Korea. State-owned companies

North Korean Economy, Pyongyang, Kaesong Industrial Complex
- Introduction to the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK)
- North Korean Economy
- Business in Pyongyang
- Foreign Trade of North Korea
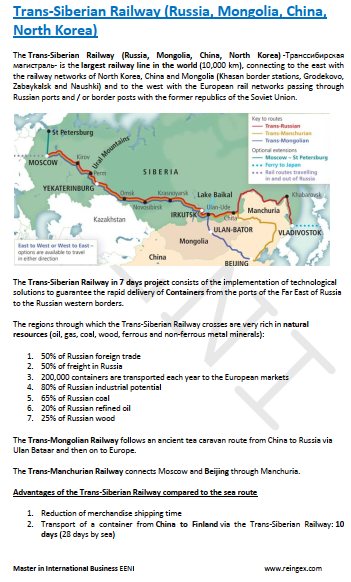
- Trans-Siberian Railway (Russia, North Korea)
- International Korean Business Centre
- Case Study: Doing Business with the DPRK Government
- Access to the North Korean Market
The aims of the subject “Foreign Trade and Business in the Democratic People's Republic of Korea” are the following:
- To analyze the North Korean Economy and Global Trade
- To know the trade opportunities in the Democratic People's Republic of Korea
- To explore the North Korean trade relations with the country of the student

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in North Korea” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
Languages:  or
or  Corea del Norte
Corea del Norte  Corée du Nord.
Corée du Nord.
Credits of the subject “Doing Business in North Korea”: 1 
 Masters in International Business for
North Korean Students.
Masters in International Business for
North Korean Students.
International Trade and Business in North Korea.
All business in North Korea is done directly with the Government (state-owned companies).
- Organization for Cooperation between Railways (OSJD)
- Is not a member of the
- WTO
- WCO
- Kyoto Convention
The Democratic People's Republic of Korea is a member of:
- Asian Development Bank
- Economic Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific
- Food and agriculture Organization
- UN
- International Telecommunications Union
- United Nations Development Programme
- Global System of Trade Preferences
- World Health Organization
- WIPO
- IMF (Not-Member)
- World Meteorological Organization
- Nonaligned Movement
On July 2000, the Democratic People's Republic of Korea began participating in the ASEAN Regional Forum.
Democratic People's Republic of Korea
- The Democratic People's Republic of Korea (Asia) has a centralized Government under the absolute control of the communist Korean Workers' Party
- Kim Il-Sung ruled North Korea from 1948 until his death on July 1994
- North Korean population: 24 million people
- North Korean Capital: Pyongyang
- North Korea has the highest percentage of military per capita in the World
- Borders of North Korea: China and South Korea. Japan (by sea)
- Language: Korean (석사 무 역 및 국제 마케팅)
- Type of State: North Korea is a socialist state
- Independence from Japan: 1945
- Area of North Korea: 120,540 km²
- Currency: North Korean Won
North Korean Economy.
- North Korean industry is operating at only a small fraction of his capacity owing to the lack of fuel, spare parts, and other inputs
- North Korean agriculture and fisheries: 21.6% of the GDP
- Index of Economic Freedom (Heritage) of North Korea score is 1, making the least free economy in the Index.
- North Korea ranks last out of forty-one countries in the Asia-Pacific region
- The Communist Party controls every aspect of the North Korean economic activity
- North Korea has the highest percentage of military personnel per capita in the World
- North Korean GDP (nominal): 40,000 million dollars
Global Trade and Business in North Korea:


International Trade of North Korea.
- North Korean Government controls all imports and exports, and formal trade is minimal
- North Korea usually does not welcome foreign direct investment
- Total North Korean Exports: 2.06 billion dollars
- The main North Korean exports products are minerals, non-ferrous metals, garments, chemicals/plastics, machinery/electric and electronic products, animal products, wood products, vegetable products, and precious metals
- Most of the exported products from the Kaesong Industrial Complex are distributed in South Korea; a small quantity, 18% of the Kaesong Industrial Complex products is exported to international markets
- International Trade between the North and South Korea, legalized in 1988, had risen to near 1.68 billion dollars, much of it related to out-processing or assembly work undertaken by firms of South Korea in the Kaesong Industrial Complex
- Imports of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea: 3.58 billion dollars
- Top North Korean import products are minerals, petroleum, machinery/electronics, vegetable products, textiles, chemicals, non-ferrous metals, plastics, vehicles, and animal products
- The largest North Korean trade partners are China, South Korea, Singapore, India, and Russia
- China is the largest foreign direct investment source (FDI)
The Democratic People's Republic of Korea also expanded its bilateral diplomatic ties, establishing diplomatic relations with Italy, the Philippines, Australia, Canada, the UK, Germany, and many other European Countries.
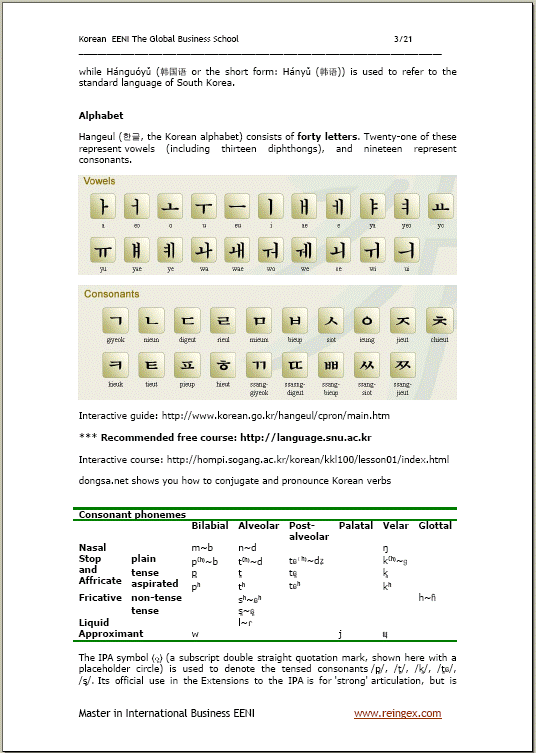
Korean language:
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page



