Economic Commission for Asia (ESCAP)

Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP), United Nations
- Introduction to the UN Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP)
- Objectives and Programs of the Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP)
- 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
- Committee on Macroeconomic Policy, Poverty Reduction and Financing
for Development
- Economic and Social Survey of Asia and the Pacific
- Economic Growth in Asia-Pacific
- Regional Economic Cooperation and Integration in the Asia-Pacific Region. Development policies
- Needs to enhance regional economic cooperation and integration in the Asia-Pacific Region
- Financing for development
- Asian Capital Markets
- Socio-Economic Response to COVID-19: the ESCAP Framework
- COVID-19: Towards an inclusive, resilient and green recovery
- Committee on Trade and Investment of the Economic and Social Commission for Asia
- APTIP Asia-Pacific Trade Indicators Portal
- Trade Facilitation and Paperless Trade in the Asia-Pacific region
- Expansion of trade across the Asia-Pacific Region
- Asia-Pacific Trade and Investment Report
- Asia-Pacific Research and Training Network on Trade (ARTNeT)
- Regional Trade Agreements in Asia
- Asia-Pacific Trade and Investment Agreement Database (APTIAD)
- Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement
- Services and Global Value Chains: The Asia-Pacific Reality, Studies in Trade, Investment and Innovation
- Sustainable Business and Investment
- Outward Foreign Direct Investment and Home Country Sustainable Development
- Committee on Transport
- Introduction to transport and logistics in the Asia-Pacific Region
- Asian Highway
- Trans-Asian Railway
- Marine Transport
- Dry Ports and Intermodal Transport Linkages
- Transport Facilitation
- Inter-Island Shipping
- Intelligent Transport Systems
- Statistical Yearbook for Asia-Pacific of the Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP)
- Regionalism in Asia
The objectives of the subject “Economic and Social Commission of the UN for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP)” are the following:
- To understand the goals (regional integration, Asian development) of the Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP)
- To analyze the role of the Committees on International Trade and Investment, and Transport
- To know the importance of the regional trade agreements in Asia (Asian regionalism concept)
- To analyze the Asian economy and the main trade indicators
- To understand the Trade Facilitation programs in the Asia-Pacific region
- To analyze the impact of COVID-19 in the Asian Economy

The Subject “Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP)” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
Languages:  or
or  Comisión Económica y Social para Asia
Comisión Económica y Social para Asia  Commission économique et sociale pour l’Asie
Commission économique et sociale pour l’Asie  ESCAP.
ESCAP.
- Credits of the Subject “Economic and Social Commission of the UN for Asia and the Pacific”: 1

- Duration: one week

Sample - Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP)
The UN Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP) is the regional body of the UN for the Asia-Pacific region.
The mission of the Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific is to surpass the greatest defiance of Asia and the Pacific region.
The Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific works in:
- Poverty reduction in Asia and the Pacific region
- Managing effects of the Globalization (international trade, foreign direct investment) in the ESCAP economies
- Facing new social topics
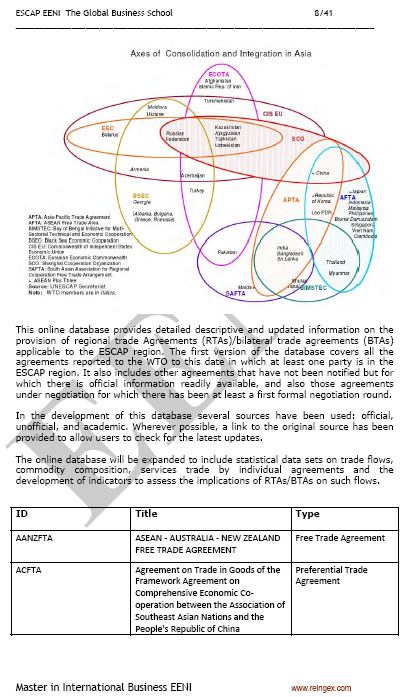
The Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP) region has experimented a fast increase in the number of Preferential Trade Agreements that has changed the scenery of the foreign trade relations in the Asia-Pacific region and augmented the regional markets access difficulty.
- UNESCAP is located in Bangkok (Thailand)
- The Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific consists of 53 member countries and 9 associate members
- UNESCAP is the largest United Nations institution serving the Asia-Pacific region with over 600 staff
Regional bodies (Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific):
- Asian Centre for Agricultural Engineering and Machinery
- Asian Centre for Transfer of Technology
- Centre for Poverty Reduction through the Secondary Crops' Development in Asia and the Pacific
- United Nations Statistical Institute for Asia and the Pacific
The Member economies of the Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP) are Afghanistan, Armenia, Australia, Azerbaijan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Brunei, Cambodia, Fiji, France, Georgia, India, Indonesia, Iran, Japan, Kazakhstan, Kiribati, Kyrgyz Republic, Laos, Malaysia, Maldives, Marshall Islands, Micronesia, Mongolia, Myanmar, Nauru, Nepal, Netherlands, New Zealand, North Korea, Pakistan, Palau, Papua New Guinea, Philippines, Russia, Samoa, Singapore, Solomon Islands, Sri Lanka, South Korea, Tajikistan, Thailand, East Timor, Tonga, Turkey, Turkmenistan, Tuvalu, UK, U.S., Uzbekistan, Vanuatu, and Vietnam.
The associate members are American Samoa, Cook Islands, French Polynesia, Hong Kong, Macau, New Caledonia, Niue, and the Northern Mariana Islands.
The Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP) is an inter-civilization agreement between the Sinic-Buddhist Civilization, the Hindu Civilization, and the Islamic Civilization.
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page



