Business in Iran

Foreign Trade and Business in Iran, Tehran
- Introduction to the Islamic Republic of Iran (Central Asia)
- Influence of Shi'a Islam (Shiite) on Iran
- Business in Tehran
- Iranian Economy
- Privatization Process in Iran
- Iranian banking system and financial sector
- Islamic Revolutionary Guard - Bahman Group
- “Bonyads”: Mostazafen Foundation of Islamic Revolution
- International Trade of Iran
- Potential Iranian export sectors
- Development Export Bank of Iran
- Iranian Customs Administration
- Investment in Iran
- Access to the Iranian Market
- Business Plan for Iran
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in the Islamic Republic of Iran” are the following:
- To analyze the Iranian Economy and Global Trade
- To know the business opportunities in the Islamic Republic of Iran
- To explore the Iranian trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the Iranian Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of the Iranian Companies
- To develop a business plan for the Iranian Market
Global Trade and Business in Iran


The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Iran” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
Doctorate: Islamic Business, World Trade.
- Credits of the subject “Doing Business in Iran”: 2

- Duration: two weeks

Masters adapted to  Iranian Students.
Iranian Students.
International Trade and Business in Iran.

- India-Afghanistan Corridor
- Kyrgyzstan-Iran Corridor
- North-South Corridor (India-Russia)
- China-Central-West Asia Corridor
- Islamabad-Istanbul Corridor
- Corridor of the Ashgabat Agreement
- Europe-Caucasus-Asia Corridor
- Access to the:
- Afghanistan-Turkey Corridor
- Trans-Caspian Corridor
- Silk Road
- Asia-Africa Growth Corridor


Iranian Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Iran and the Central Eurasian Economic Area
- Economic Cooperation Organization (ECO)
- Asian Clearing Union
- Indian-Ocean Rim Association
- Trade Agreements with Algeria, Syria, and Venezuela
- Armenia-Iran Agreement
- Transit and Trade Agreement between India, Iran and Afghanistan
- Iran-Pakistan-Turkey Transit Transport Framework Agreement (TTFA)
- Islamic Trade Preferential System
- Global System of Trade Preferences
- South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (Observer)
- Shanghai Cooperation Organization (Observer)

- WTO (in process of accession)
- WCO
- Convention Harmonization of Frontier Controls of Goods
- Organization for Cooperation between Railways (OSJD)
- CIM & CIT Rules (Rail)
- CMR Convention (UN)
- COTIF Convention
- BIC (Containers)
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- IMO
- Convention for Safe Containers
- Istanbul Convention
- Customs Convention on Containers
- IRU
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport

- Islamic Development Bank
- OIC
- Committee for Economic Cooperation
- Islamic Chamber of Commerce
- Asia-Middle East Dialogue
- OPEC Fund for International Development

- Asian Development Bank
- Colombo Plan
- Africa-Asia Strategic Partnership
- Boao Forum for Asia
- Asia Cooperation Dialogue
- ESCAP

- UN
- WB
- WTO
- IMF
- ...
Bonyads - Mostazafen Foundation of Islamic Revolution

The Islamic Republic of Iran.
- Politics of Iran takes place in the framework of a Republic with an Islamic ideology
- the Iranian Constitution (December 1979) and its rectification (1989) define the political, economic, and social order of the Islamic Republic of Iran
- The Iranian Constitution declares that Shi'a Islam (Shiite) of the Twelve school of thought is the official religion of Iran
- Persian (Farsi) is the most broadly spoken language
- Persian has had a significant influence on neighboring languages, particularly Turkic languages in Central Asia
- The borders of Iran are Afghanistan, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Iraq, Pakistan, Turkey, and Turkmenistan
- Iranian Population: 78 million people
- Area of Iran: 1,648,195 km²
- Iranian Currency: Rial
- Abolition of Slavery in Iran: 1928
Religion in Iran.
- Islam. Almost 90% of the Iranians are Shiite Muslims, thus being the spiritual leader of Shiite community in the World
- An estimated 9% are Sunni
- Iran is a Shiite Muslim country Imani - Twelver Shi'ism - (89% of the population), this branch is the majority in Shi'ism
- “Jaafari” is the most common by the Iranian Shi'a school of law (fiqh)
- Iran became an Islamic Republic after the Islamic Revolution (1979)
- Before the Arab invasion, Persia (Iran) was the homeland of Zarathustra, founder of Zoroastrianism (Parsis), today virtually non-existent in Iran
- In Iran was born Bahaullah, the founder of Baha’i Faith

Iran belongs to the Central Eurasian Economic Area (Islamic Civilization).
Iranian Economy.
The economy of the Islamic Republic of Iran was crippled by the Islamic revolution, the Iran-Iraq war, and attendant economic mismanagement.
- The Islamic Republic of Iran ranks fourth on agricultural products export diversity in the World
- Iran is the second petrol and gas manufacturer in the World
- Iran holds fourth to ninth rank in zinc, lead, cobalt, aluminum, manganese, and copper production in the World
- 233 Techno-Engineering projects have been executed in thirty-three countries by the Iranian companies over the last decade
- Industrial commodities make up 70% of non-petroleum export
- Iranian import structure consists of capital, intermediated goods, and consumer products
- Iran holds the seventh standing in tourist attractions
- Access to the Eurasian Land Transport Initiative, China-Pakistan Economic Corridor and to the Asia-Africa Growth Corridor
Iranian petroleum industry is a largely developed industry with highly rated and valuable resources and capabilities with immense crude oil reserves from which 130.798 billion barrels can be exploited in the form of primary and secondary recoveries.
Iranian Muslim Businesspeople and Companies.
- Islamic Revolutionary Guard
- Bahman Group“Bonyads”: Mostazafen Foundation of Islamic Revolution Iranian National Shipping Lines
- Wagon Pars
- Iran Carpet
- Cooler Iran
- Misr-Iran Textile
- Aburaihan Pharmaceutical
Esfahan's Mobarakeh Steel is the largest industrial complex in the Islamic Republic of Iran and has been established and commissioned after the victory of the Islamic Revolution and entered into the functional stage in early 1993.
Omid R. Kordestani is an Iranian-American Businessman was a senior adviser to the founders of Google and non-Executive Director of Vodafone.


Foreign direct investment (FDI) is allowed in agreement with the prevailing laws and regulations of the Islamic Republic of Iran. All foreign investors are allowed to invest, for the goal of development and producing activities, in all the sectors of industry, mining, agriculture, and services.
However, from the standpoint of the Iranian Government, only those investments should be eligible to benefit from the privileges and protections under the Foreign Direct Investment Promotion and Protection Act that have obtained the required License under the act.
The Iranian Foreign Investment Company was incorporated on March 1998 as a Private Joint Stock company with a mission to manage and expand the Iranian holdings abroad.
The Central Bank of the Islamic Republic of Iran is the responsible for the conception and implementation of the Monetary and Credit Policies with due regard to the general economic policy of the Islamic Republic of Iran.
The Iran Customs Administration consists of a central Headquarters and ten branches of supervision. The President of the Iranian Customs serves as Deputy Minister of Finance and Economic Affairs, which is the highest position of the Customs Administration.
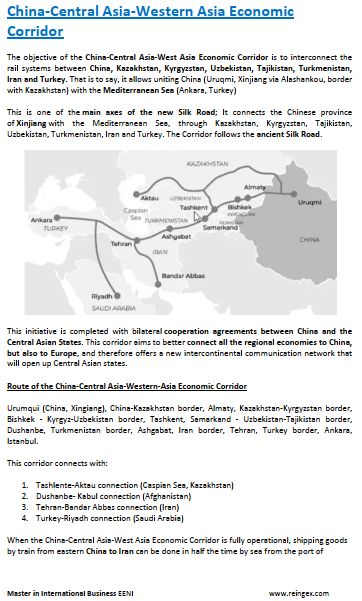

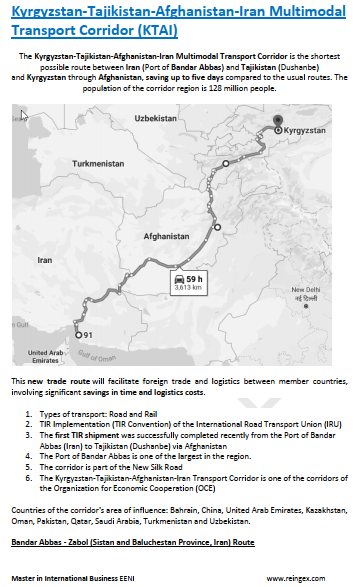




 (
(
