Course: Taoism, Confucianism, Business, China
Online Course: Sinic Economic Area. Confucianism, Taoism and Business (5 ECTS)

Confucianism and Taoism, two fundamental philosophies of Chinese culture, have profoundly influenced business thought and practices, not only in Asia but also in the global business context.
Many Asian companies combine both approaches. For example, Confucianism guides relationship building and corporate ethics, while Taoism inspires innovation and adaptability. This duality allows Asian companies to compete in global markets while maintaining a strong cultural identity.
“With more rules and regulations, more people will impoverish” Tao LVII
“Benevolence is not to do to others what you would not want to be done to yourself” Analects XII-1 (Confucius).
Companies like Alibaba, Huawei, and Haier integrate both Confucian principles (hierarchy, loyalty, ethics) and Taoist principles (adaptability, simplicity), allowing them to balance structure with agility in a global context.
Global Application: Although Confucian and Taoist principles have Asian roots, non-Asian companies such as Patagonia, Unilever, Zappos, and Airbnb demonstrate how these values can be universalized, especially in areas such as sustainability, ethics, and adaptability.

Religions and Global Business -
Religious diversity
The Professional Course “Taoism, Confucianism and Business” offered by EENI Global Business School consists of four subjects:
- Taoism and Business
- Confucianism and Business
- Other religions in China: Islam, Christianity and Buddhism
- Sinic Economic Area
- Case Study: Restrictions on Religious Freedom in China
- Case Study: Companies that apply Confucian and Taoist principles

This Course is aimed at executives and enterprises wishing to do business in China (a BRICS Country, the largest market in the world), a market where the influence of Taoism and Confucianism (as well as Buddhism) is fundamental.
 Enrol / Request for Information
Enrol / Request for Information

- Credits :
5

- Duration: five weeks
- Tuition Fees: EUR 120
- Open Online Enrollment
- Requires an average dedication of 12 hours per week
- Download the syllabus: “Taoism and Confucianism” (PDF)
Languages:  or
or  Religiones
de China
Religiones
de China  Religions de la Chine
Religions de la Chine  Religiões da China (free multilingual training).
Religiões da China (free multilingual training).
This course belongs to the following Higher Education Programs offered by EENI:
Masters: International Business, Religions and Business.

Doctorate: Global Ethics, Religions, and International Business, World Trade.
The goals of the course are the following:
- To learn about pillars of Taoism and Confucianism
- To understand the ethical principles of these religions
- To study its influence on business and the Sinic Economic Area
- To analyze the profiles of Confucian and Taoist entrepreneurs and companies
- To define the characteristics of Sinic Economic Area
- To explore the economic and political relations of Sinic Civilization with other civilizations (Western, Hindu, Buddhist, Islamic and African)
- To understand the processes of economic integration and the main Organizations related to Sinic Economic Area
- To learn about economic profile of the countries of influence of Sinic Civilization

This course contains exercises that are evaluated, which the student must work out and pass to obtain the Diploma of the Professional Course: “Taoism, Confucianism and Business” granted by EENI Global Business School.

Subjects
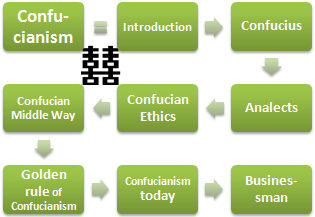
1- Confucianism, Ethics and Business:
- Introduction to Confucianism
- The figure of Confucius
- The Analects (Confucian books)
- Fundamentals of Confucianism
- Arts of peace
- Education - Ritual
- Humanity
- Power
- Principles of Confucian Ethics
- Confucian Middle Way
- The Man morally superior
- Right words
- Confucian Golden Rule
- The importance of Confucian hierarchy
- Influence of Confucianism on business
- Confucianism today
Chinese enterprises and Confucian Values:
- Zhang Ruimin: Confucian businessman (China) “essence of globalization is localization”
- Chinese enterprises: Menglan, COSCO, KONKA, Sanhuan Guanxi, Jindie, Tianfa, Hong Qing Ting, Jiangsu Changfa

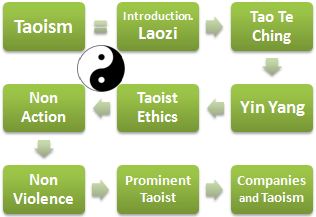
2- Taoism, Ethics and Business:
- Introduction to Taoism
- Laozi (founder of Taoism)
- Tao Te King Tao (Sense) and Te (Virtue)
- Yin and Yang
- Principles of Taoist Ethics
- Wu Wei: principle of non-action
- Non-violence and Taoism
- Control of senses
- Wisdom
- Detachment
- Taoism today
- Famous Taoists
- Government and Taoism
- Enterprises with Taoist influence. Chang Yung-fa (I-Kuan Tao). Director of Evergreen (Taiwan)


3- Other religions in China: Islam, Christianity and Buddhism
- Buddhism in China: the most important religion in China (even though China is a secular country)
- Christianity in China (67 million)
- Islam in China
- Shamanism
Note: the analysis of Buddhism is not done in this course, but in the course on Buddhism.
4- Sinic Economic Area
- Religions of China (Taoism, Confucianism and Buddhism) and their relationship with Sinic Civilization
- Sinic Economic Area
- China as the central state of Sinic Civilization
- Countries of the area of influence of Sinic Civilization: China, South
Korea, Hong Kong, Japan, Macau, Singapore, Taiwan and Vietnam
- Although Buddhism is the majority religion in Japan, the influence of Taoism and Confucianism is very significant in the Japanese culture as well as in Shintoism
- North Korea has historically been a country of influence of Sinic Civilization. However, the communist dictatorship impedes freedom of religion
- The expansion of Sinic Civilization in Africa (sinicization of Africa)
- The Diaspora of Sinic Civilization
- Chinese businessmen and companies
- Economic integration of Sinic Economic Area
- Interactions with other civilizations
- Economic Organizations related to Sinic Economic Area
Why study the course “Taoism, Confucianism and Business”?.
Taoism and Confucianism, Yin and Yang, responsibility and freedom, represent the two poles of Chinese society; like the Yin and Yang, Confucianism would not exist without Taoism, and vice versa. These two traditions of wisdom, along with Buddhism and Shamanism are part of Sinic Civilization and its entire area of influence: the Sinic Economic Area: China, South Korea, Hong Kong, Japan, Macao, Singapore, Taiwan and Vietnam
Relevance in the global context
- Cross-Cultural Management
- In a globalized world, Western companies operating in Asia must understand Confucian values (such as guanxi) and Taoist values (such as adaptability) to negotiate and collaborate effectively.
- For example, companies like Apple have been successful in China by adapting to local expectations for personal relationships and operational flexibility.
- Sustainability and ethics
- Confucian values of social responsibility and Taoist values of balance with nature fit with global trends toward sustainability and business ethics, making these philosophies relevant beyond Asia
- Innovation and agility
- Taoism, with its emphasis on adaptability, is particularly useful in industries like technology, where change is constant. Global companies can adopt this approach to stay competitive
Confucianism and Taoism offer complementary perspectives that enrich business management in a global context. Confucianism provides structure, ethics, and strong relationships, while Taoism encourages adaptability, simplicity, and balance. In a globalized business environment, these philosophies are not only relevant to Asian companies but also offer valuable lessons for any organization seeking to combine stability with agility, ethics with innovation. Companies that successfully integrate these principles will be better positioned to navigate the complexity of the global marketplace.
China presents a paradigmatic case of regulatory obstacles to religious freedom due to its policy of state control over religious practices. The Chinese government promotes the “sinicization” of religions, requiring religious communities to adapt their beliefs and practices to the values of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and national culture. This case focuses on the restrictions imposed on Uyghur Muslims in Xinjiang and Christians nationwide, based on recent information and analysis of regulatory policies.

Economic integration of Sinic Economic Area (economic organizations, free trade agreements...).
- Singapore and Vietnam are members of ASEAN
- ASEAN Economic Community
- ASEAN Free Trade Area
- Vietnam is part of the Mekong Economic Cooperation
- China, Japan, South Korea and ASEAN countries are members of ASEAN plus Three
- China-ASEAN Agreement
- ASEAN-Japan Economic Partnership Agreement
- ASEAN-South Korea Free Trade Area
- Other ASEAN trade agreements with Australia-New Zealand, Pakistan, Canada, India, the EU, Russia, U.S.
- China-Singapore Agreement
- Economic Association Agreements of China with Hong Kong and Macao
- China also has trade agreements with Japan and South Korea
- China has a framework agreement for economic cooperation with Taiwan
- Korea-Singapore Trade Agreement
- China, South Korea, Hong Kong, Japan, Singapore, Taiwan and Vietnam are members of APEC and the PEEC
- China, Vietnam and Korea are members of the Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement and the Organization for Cooperation between Railways (OSJD)
- China and Vietnam are part of the Greater Mekong Subregion
- Japan has economic partnership agreements with Singapore, China, Vietnam and South Korea
- Singapore, Vietnam and Japan are members of the Trans-Pacific Economic Partnership Agreement (CPTPP)
- Singapore has trade agreements with Japan, Korea and China
Political-economic interactions of China with other civilizations:
- Western Civilization
- Latin America: China has Trade Agreements with Chile, Peru, Costa Rica, Andean Community
- Europe:
- Trade agreements with Iceland, Norway, Switzerland
- European Union-China Agreement
- Oceania: free trade agreement with New Zealand and Australia
- Islamic Civilization:
- China has Trade Agreements with Pakistan and the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC)
- China is a member of the Central Asia Regional Economic Cooperation (CAREC) Programme formed by Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Pakistan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan and Mongolia (Buddhist country)
- Hindu Civilization: China-India Regional Trading Agreement
- Orthodox Civilization: China-Moldova agreement, China-Eurasian Economic Union agreement
- African Civilization:
- China-Africa Cooperation: a key trade-policy tool for the African development
- China has preferential trade agreements with practically all African Countries
- Africa-BRICS Countries (China is one of the BRICS Countries)
- Multi-civilizations Agreements: China is a member of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization formed by Muslim countries (Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan) and Russia (orthodox country)
Political-economic interactions of South Korea with other civilizations:
- African Civilization:
- Africa-Korea Partnership
- Trade agreement with SACU
- Hindu Civilization: India-Korea Agreement
- Western Civilization:
- Latin America: trade agreements with Peru, Chile, MERCOSUR, Mexico, Central America and Colombia
- North America: agreement with the U.S. and Canada
- Oceania: trade agreements with Australia and New Zealand
- Europe:
- Islamic Civilization: trade agreements with GCC, Indonesia, Malaysia and Turkey
- Orthodox Civilization: trade agreement with Russia
Political-economic interactions of Japan with other civilizations:
- African Civilization: Tokyo International Conference on African Development
- Hindu Civilization: Economic Association Agreement with India
- Western Civilization:
- Latin America: free trade agreements with Mexico, Chile and Peru
- Oceania: trade agreement with Australia
- Europe: partnership agreement with Switzerland and the European Union
- Islamic Civilization: Economic Association Agreements with Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia
- Orthodox Civilization: trade agreement with Russia
- Buddhist Civilization: trade agreement with Thailand
Political-economic interactions of Singapore with other civilizations:
- Hindu Civilization: India-Singapore Agreement
- Western Civilization:
- Latin America: agreements with Panama, Peru, Costa Rica and Mexico
- North America: agreements with the United States and Canada
- Oceania: agreements with Australia and New Zealand
- Europe: agreement with the European Free Trade Association (EFTA)
- Islamic Civilization: Agreements with Jordan, Pakistan and GCC
- Orthodox Civilization: agreement with Ukraine
- Singapore is a member of the Indian-Ocean Rim Association
Political-economic interactions of Taiwan with other civilizations:
- Western Civilization (Latin America): agreements with Panama, Guatemala, Honduras-El Salvador, and Nicaragua
Political-economic interactions of Vietnam with other civilizations:
- Islamic Civilization: free trade zone with the Eurasian Economic Union
- Orthodox Civilization: Customs Union with Russia
- Buddhist Civilization: Laos-Vietnam trade agreement
- Vietnam is part of the Mekong River Commission

Other Economic Organizations related to Sinic Civilization
- Boao Forum for Asia
- Asia Cooperation Dialogue
- Asia-Europe Meeting
- Forum for East Asia-Latin America Cooperation (FEALAC)
- Asia-Middle East Dialogue
- Colombo Plan
- Economic Commission for Asia (ESCAP)
- Asian Development Bank
- Africa-Asia Strategic NAASP
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page










 WhatsApp
WhatsApp
